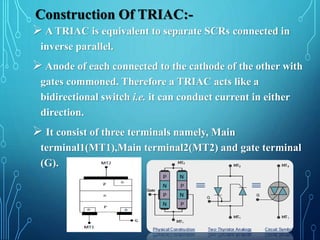
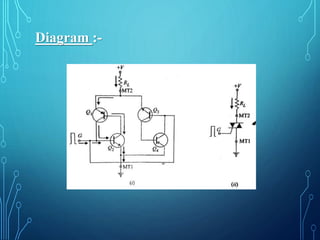
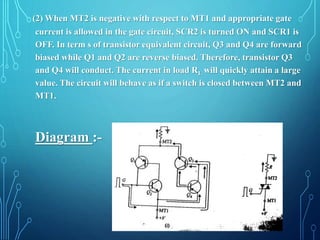
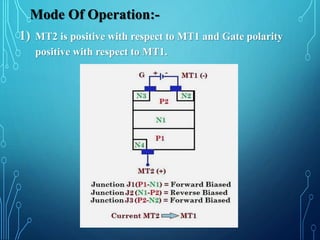
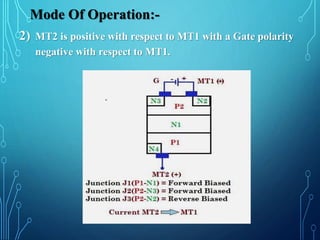
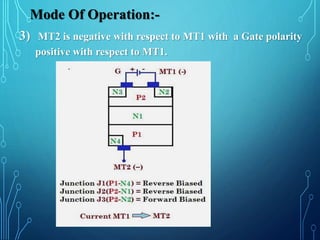
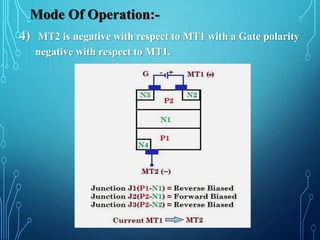
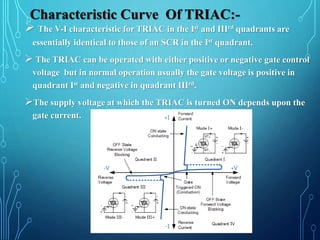
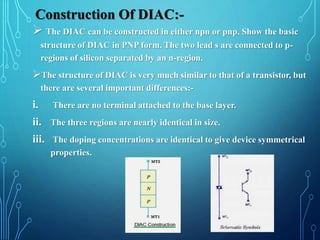
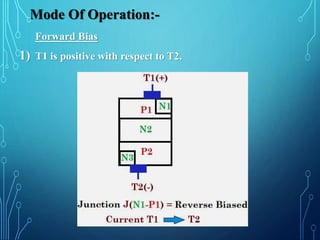
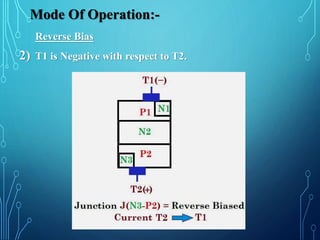
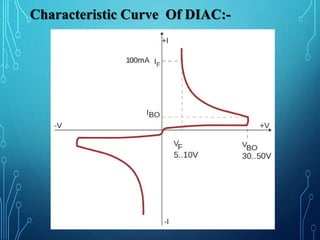
This document discusses TRIACs and DIACs. TRIACs are bidirectional semiconductor switches that can control AC in a load. They consist of two SCRs connected in inverse parallel with a common gate. DIACs are also bidirectional semiconductor devices that can be switched from off to on with either polarity of applied voltage. They have no control terminal. Both devices exhibit avalanche breakdown and negative resistance characteristics. TRIACs are used for phase control and lamp switching. DIACs are primarily used to trigger TRIACs in applications like light dimmers and heat controls.