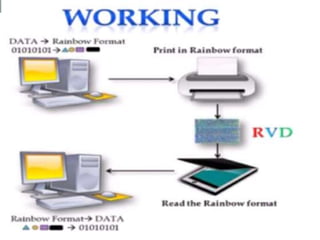
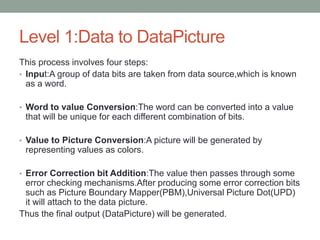
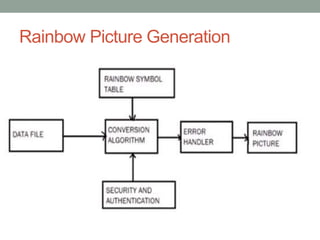
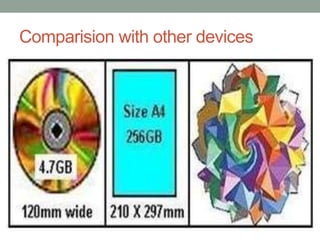
Rainbow technology is a paper-based storage technique that can store up to 450GB of data. It works by encoding files into colored geometric shapes printed onto paper at high density. Data is represented by colors rather than binary 1s and 0s. The process involves converting data bits into values, then pictures, with error correction added. Data retrieval reverses this process. Advantages include extremely low cost and biodegradability, while disadvantages are potential for data loss from fading or damage. Future applications could include high capacity paper cards and replacements for CD/DVD drives.