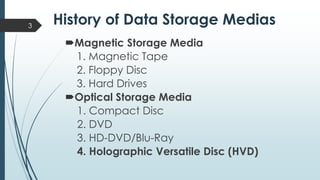
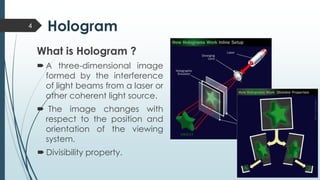
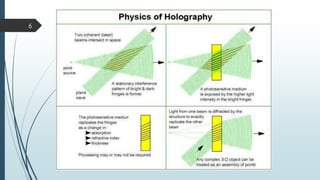
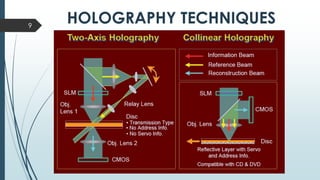
This document discusses holographic data storage technology (HDST). It provides a brief history of data storage medias, describes how holograms work, and explains the recording and reading processes in HDST. Key advantages of HDST include significantly higher storage density compared to optical discs, high durability, and fast read/write speeds of 1 Gbps. Challenges include the complexity of aligning system components and the need for high-quality recording materials. Potential applications include exascale computing and data mining.














![REFERENCES
[1] Benjamin Alfonsi, “Holographic Storage Ready for Market," IEEE Distributed
Systems Online, vol. 6, no. 10,2005.
[2] Lambertus Hesselink, Sergei S. Orlov, and Matthew C. Bashaw, “Holographic
Data Storage Systems”, Proceedings Of The IEEE, vol. 92, no. 8, August 2004.
[3] Demetri Psaltis, California Institute of Technology, Geoffrey W. Burr IBM
Almaden Research Center, “Holographic Data Storage”, 1998 IEEE.
[4] Aware Sachin B., Choudhary Anup S., Nannaware Madhuri M., Manjare
Ganesh B. “Three Dimensional Data Storage”, International Journal of Scientific
& Engineering Research, Vol. 3, Issue 12, December-2012.
[5] InPhase Technologies, Longmont, Colorado, http://www.inphase-
technologies.com/
[6] Wikipedia web site, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Holo graphic_data_storage
[7] Youtube video on Holographic data storage,
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R-NllWcgrFg
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/holographicdatastoragetechnolohy-150901212723-lva1-app6891/85/Holographic-data-storage-technolohy-24-320.jpg)