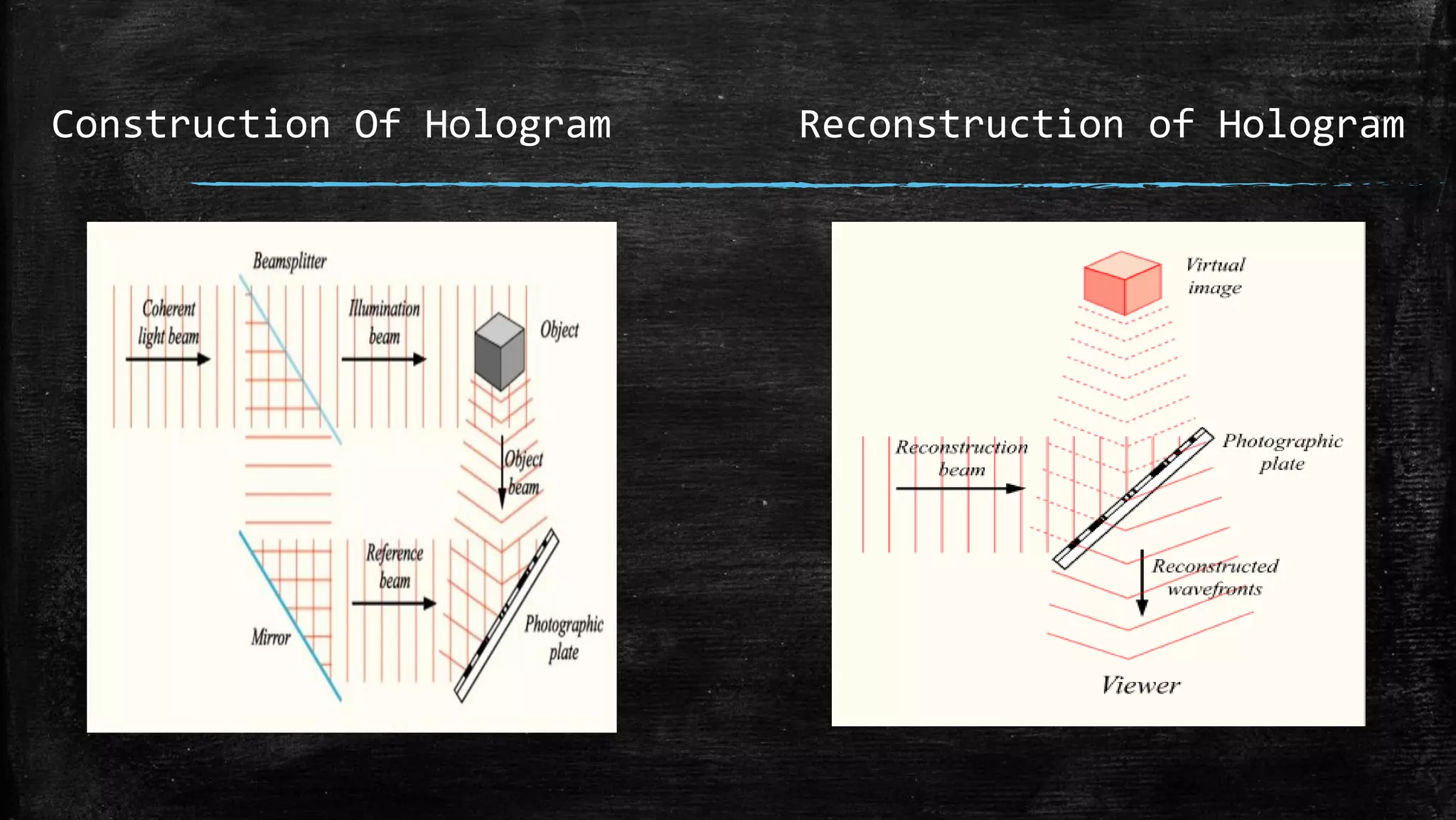
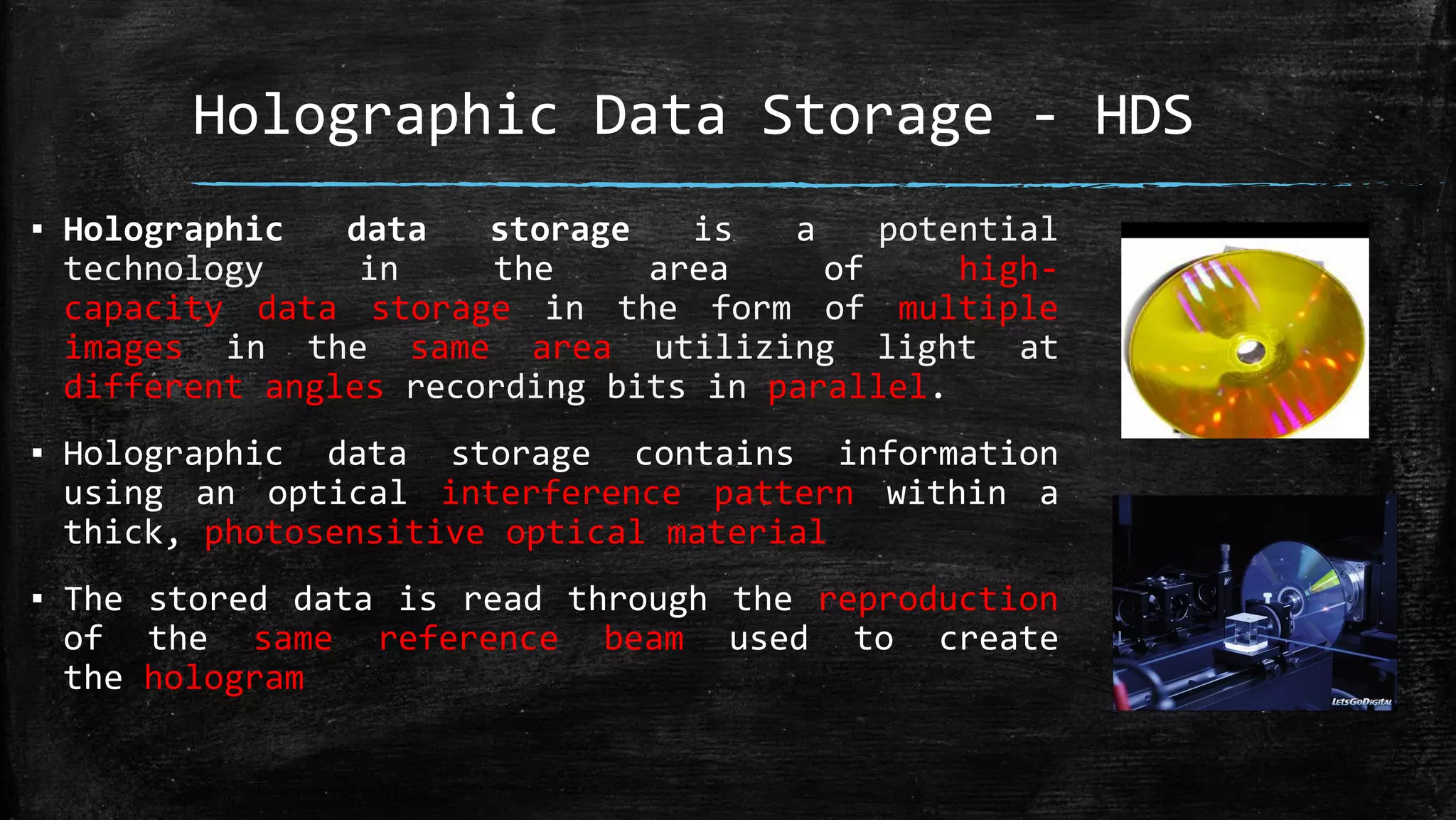
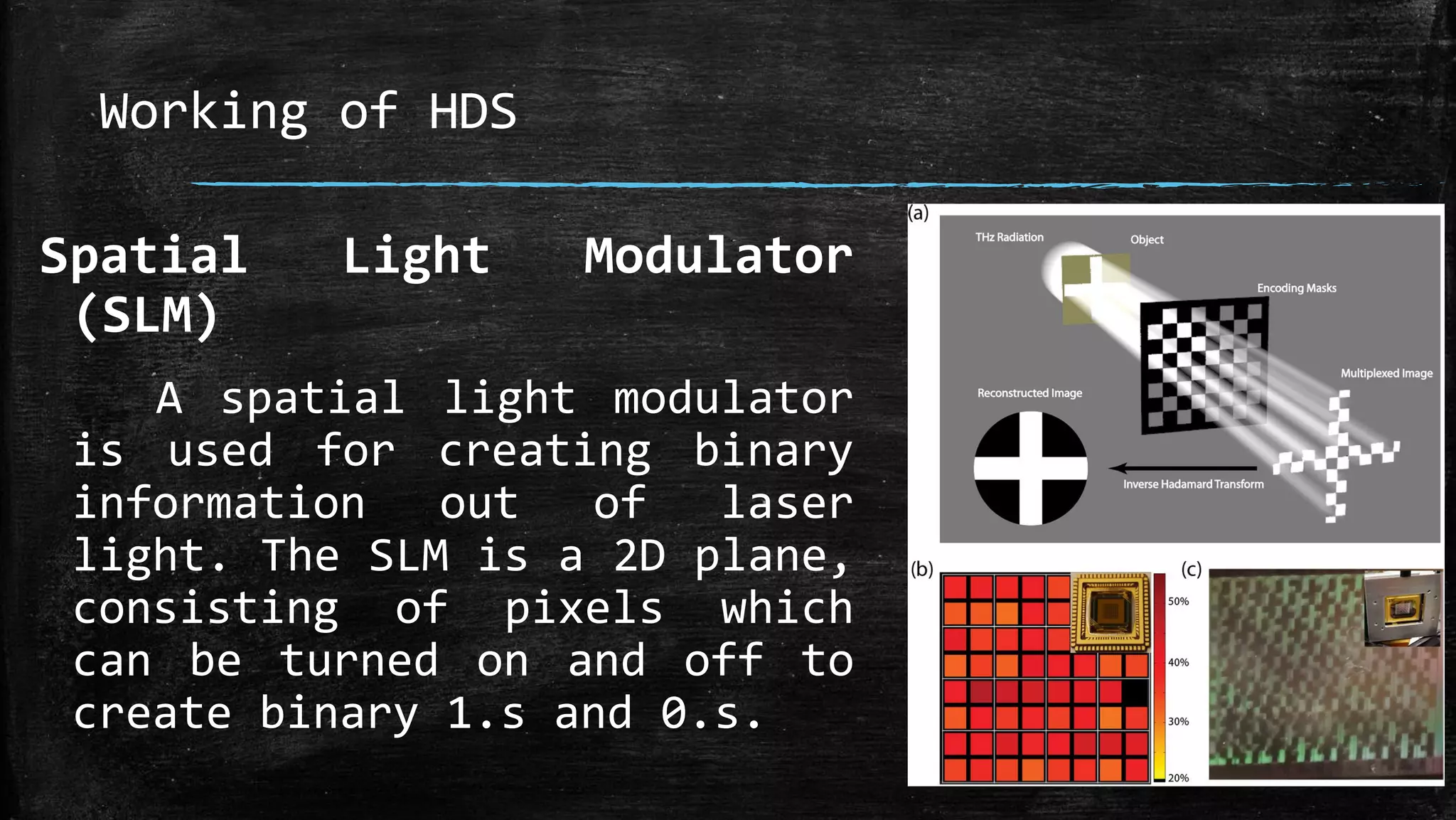
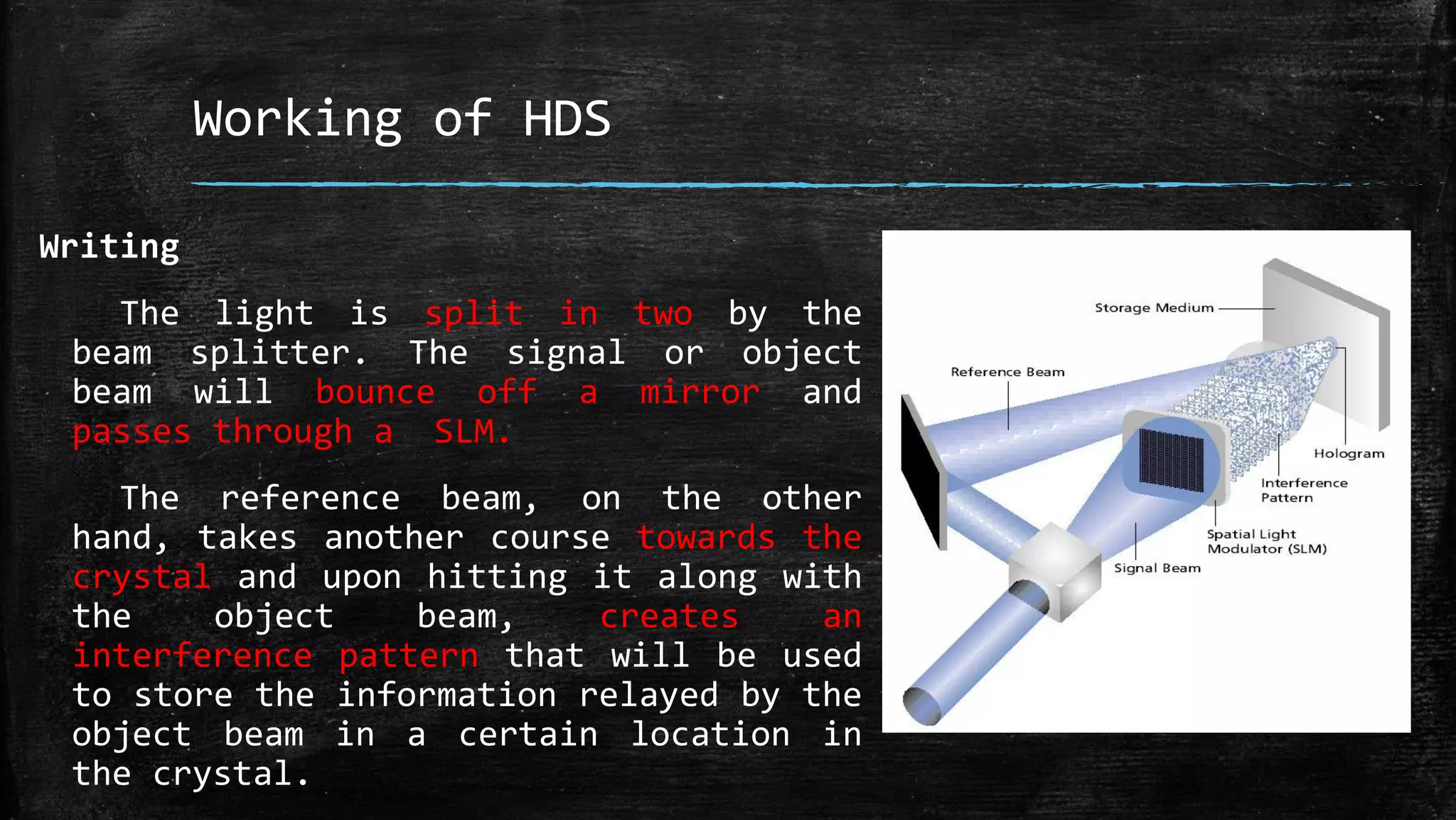
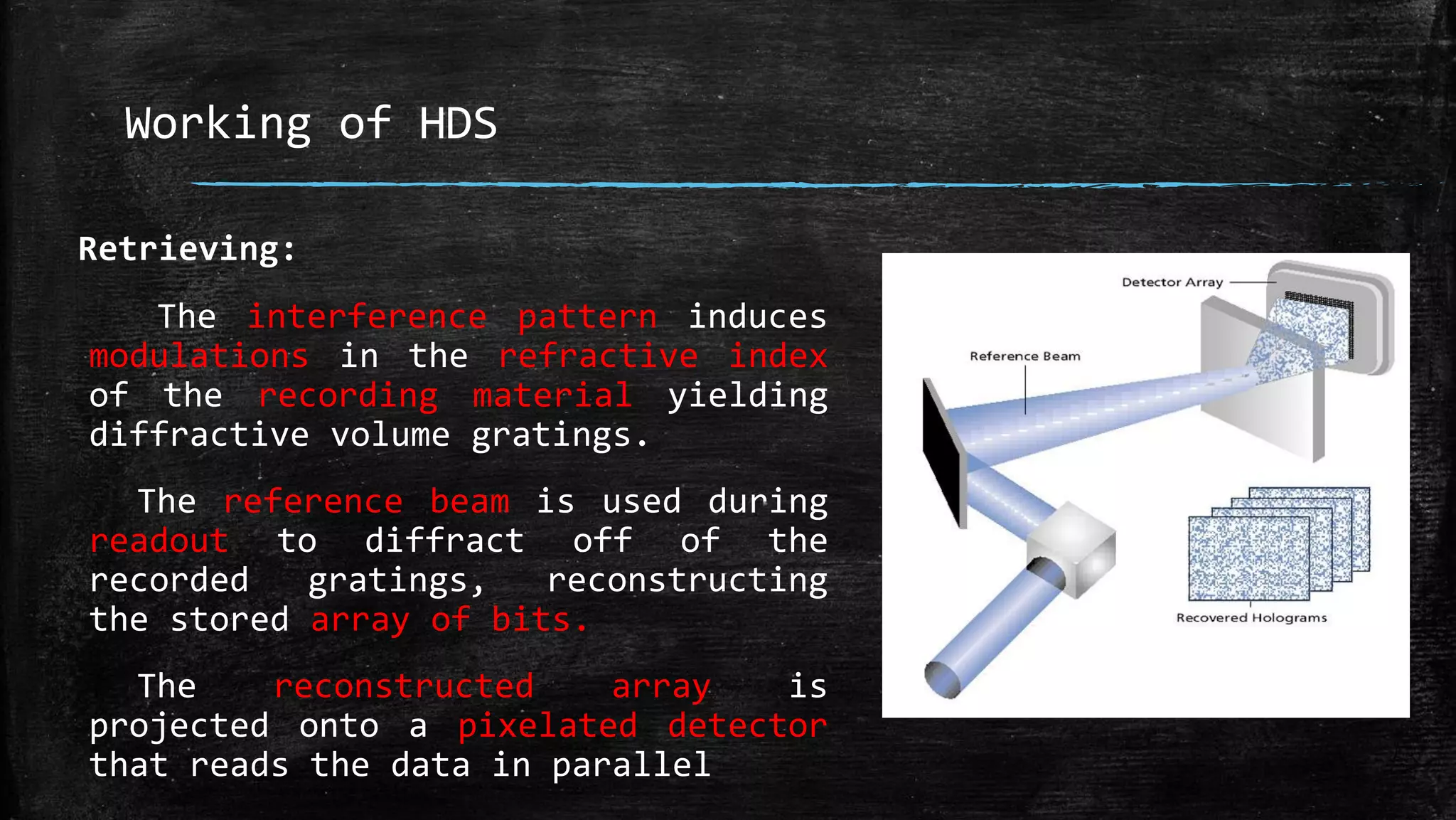
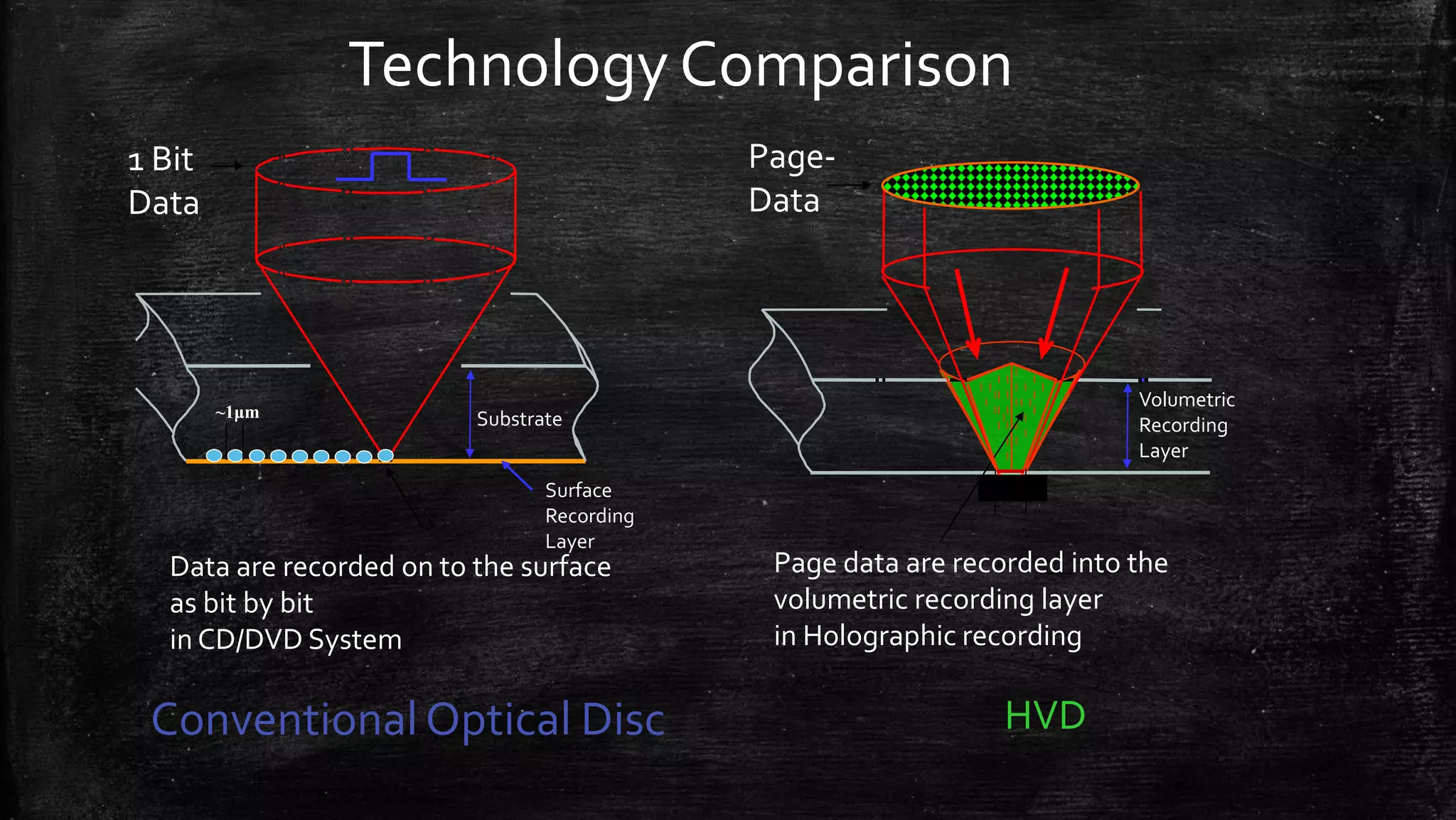
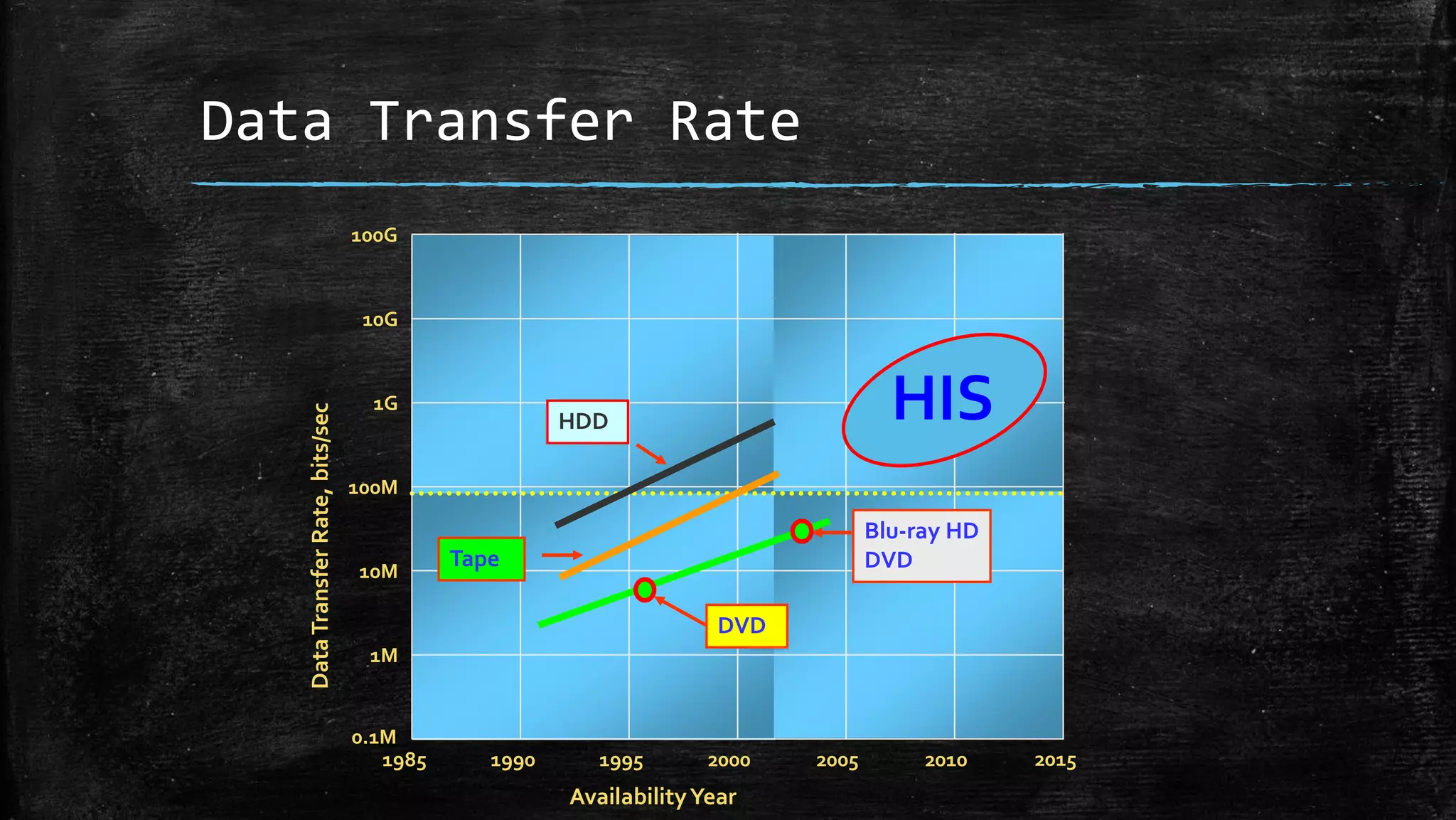
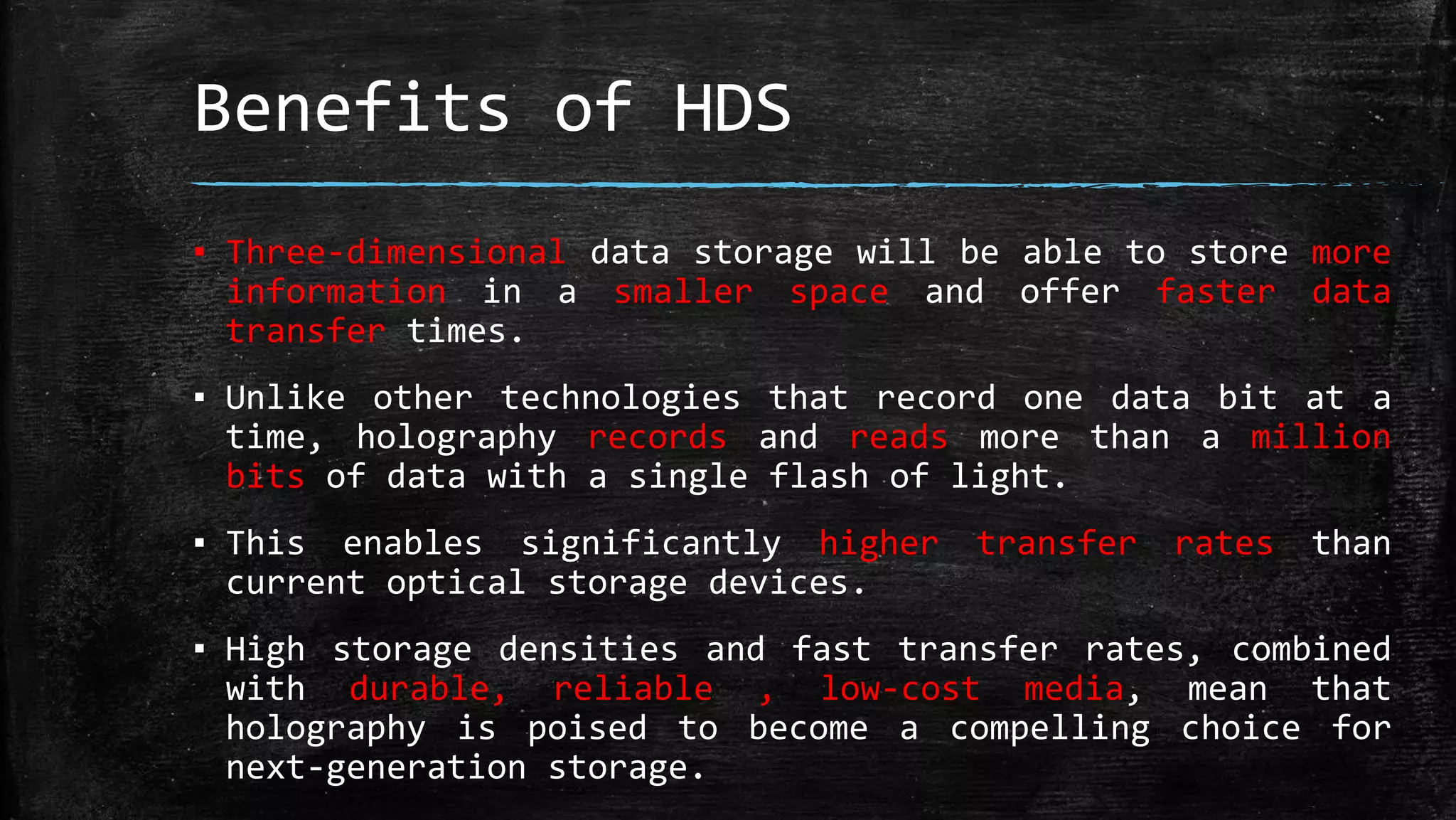
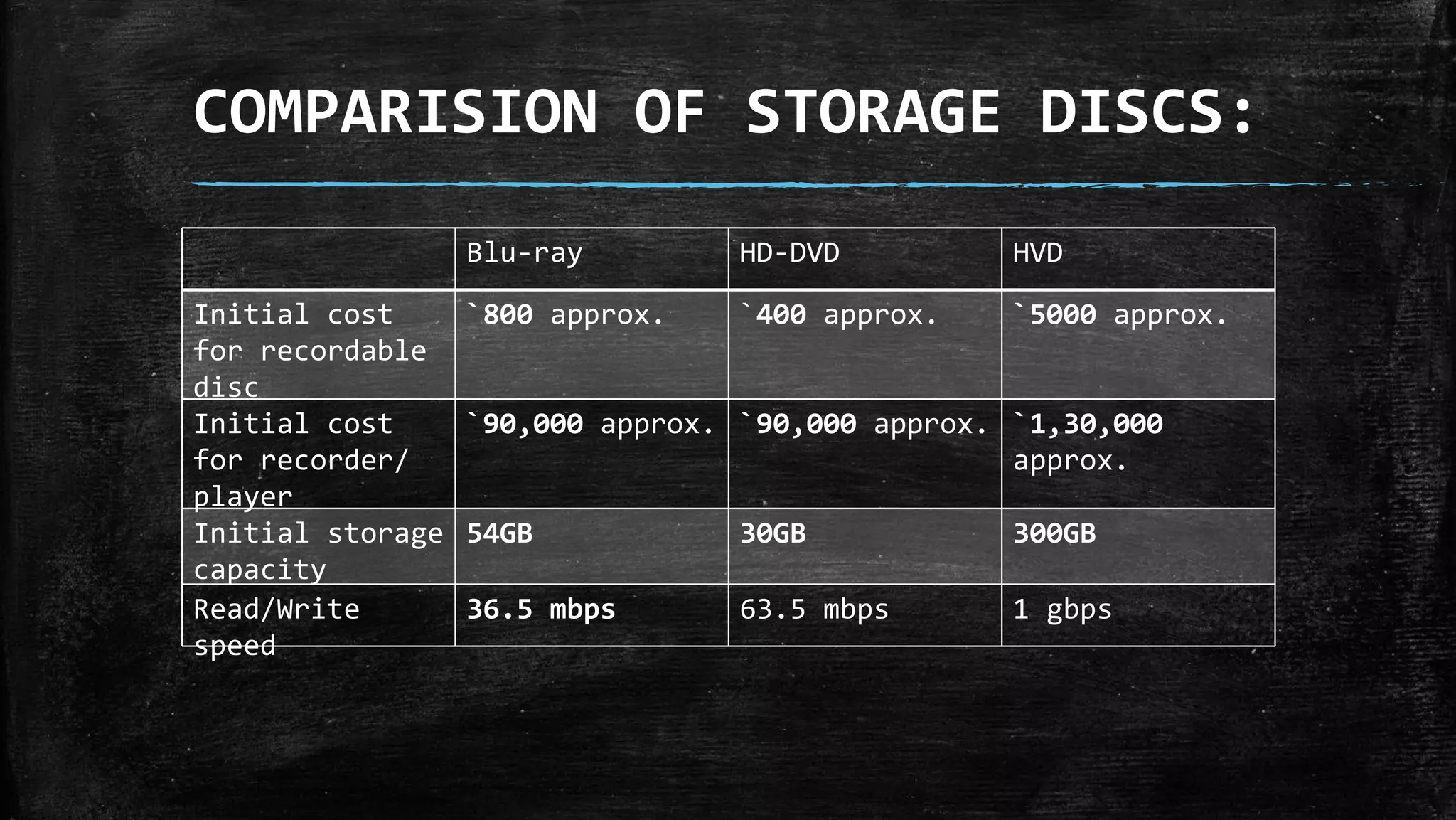
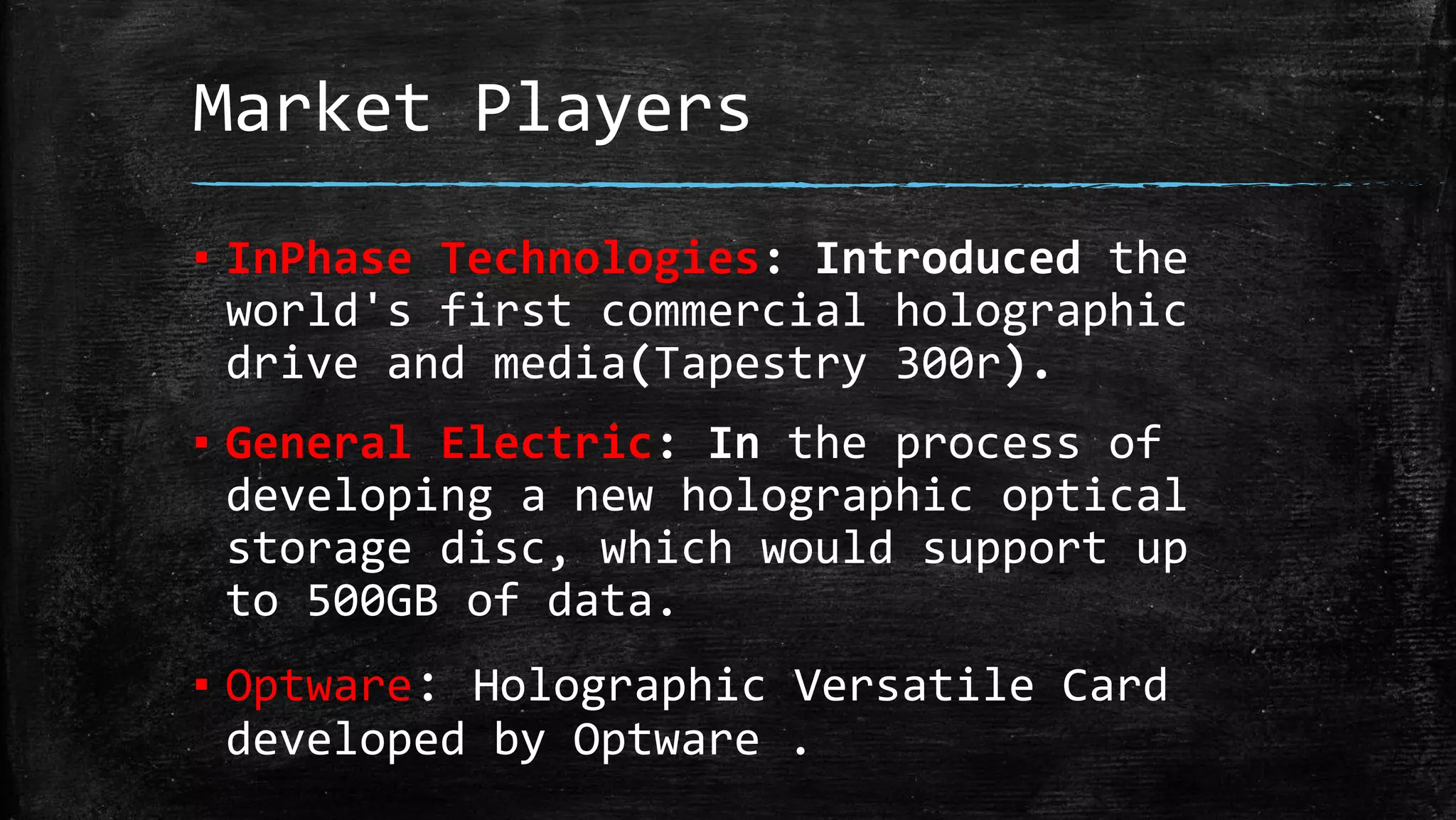
Holographic data storage uses lasers and photosensitive materials to store data in three dimensions, allowing for much higher storage capacities than existing magnetic tapes or optical discs. It works by using interference patterns created by splitting a laser into reference and object beams, with the pattern recording data pages in volumes of photosensitive crystals. While it offers terabyte storage capacities and fast data transfer rates, holographic data storage remains expensive compared to existing technologies and may not become widely adopted if another format emerges as the standard.