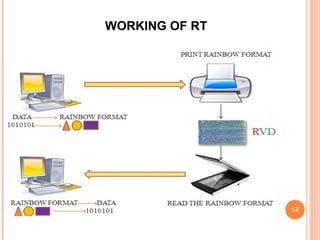
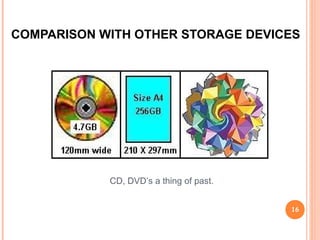
Rainbow technology allows for massive data storage on ordinary paper or plastic sheets. It uses colored geometric shapes and symbols to represent data rather than binary, allowing 450GB to be stored on an A4 sheet. The data is encoded and printed densely, then retrieved by scanning and decoding the colors. While offering extremely low-cost and biodegradable storage, issues around color fading may lead to data loss over time.