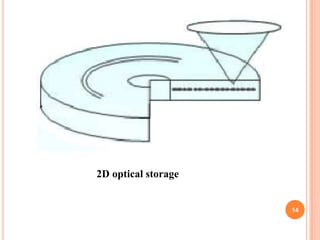
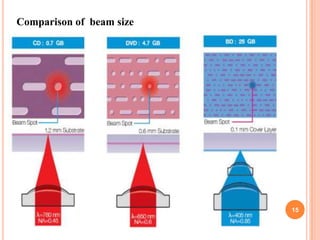
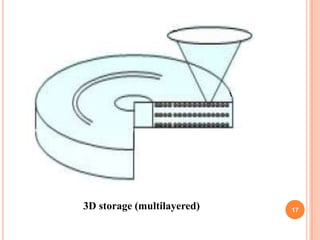
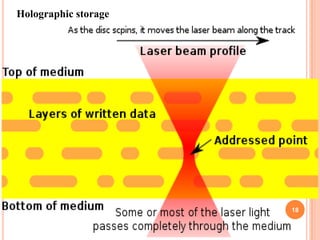
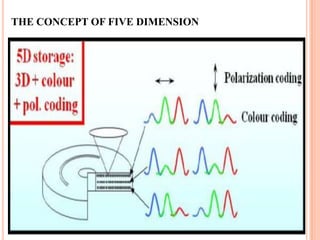
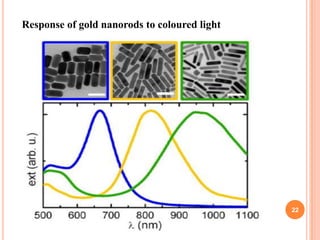
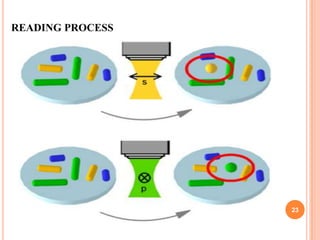
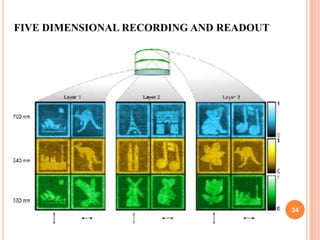
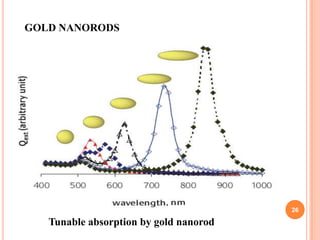
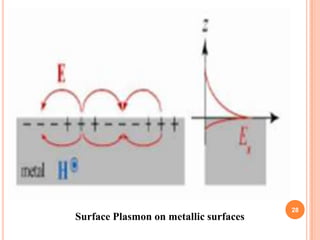
The document introduces a new 5D DVD technology that uses gold nanorods to store data across five dimensions - three spatial dimensions plus wavelength and polarization - allowing over 300 DVDs worth of data to be stored on a single disc. It works by exploiting the tunable light absorption of gold nanorods and their ability to support surface plasmons that can encode multiple layers of data at a single point. This would provide significantly higher storage densities compared to existing optical storage technologies.