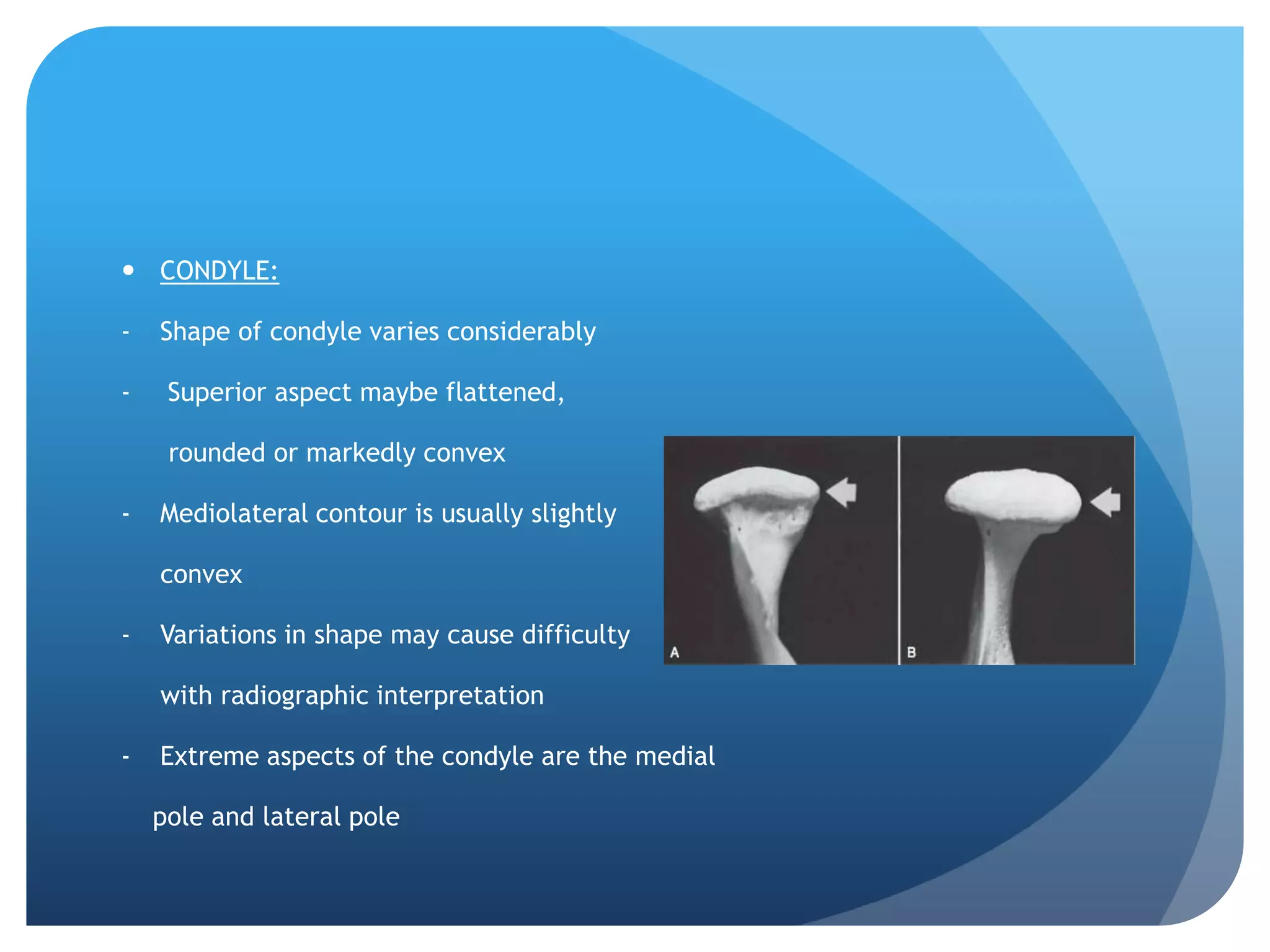
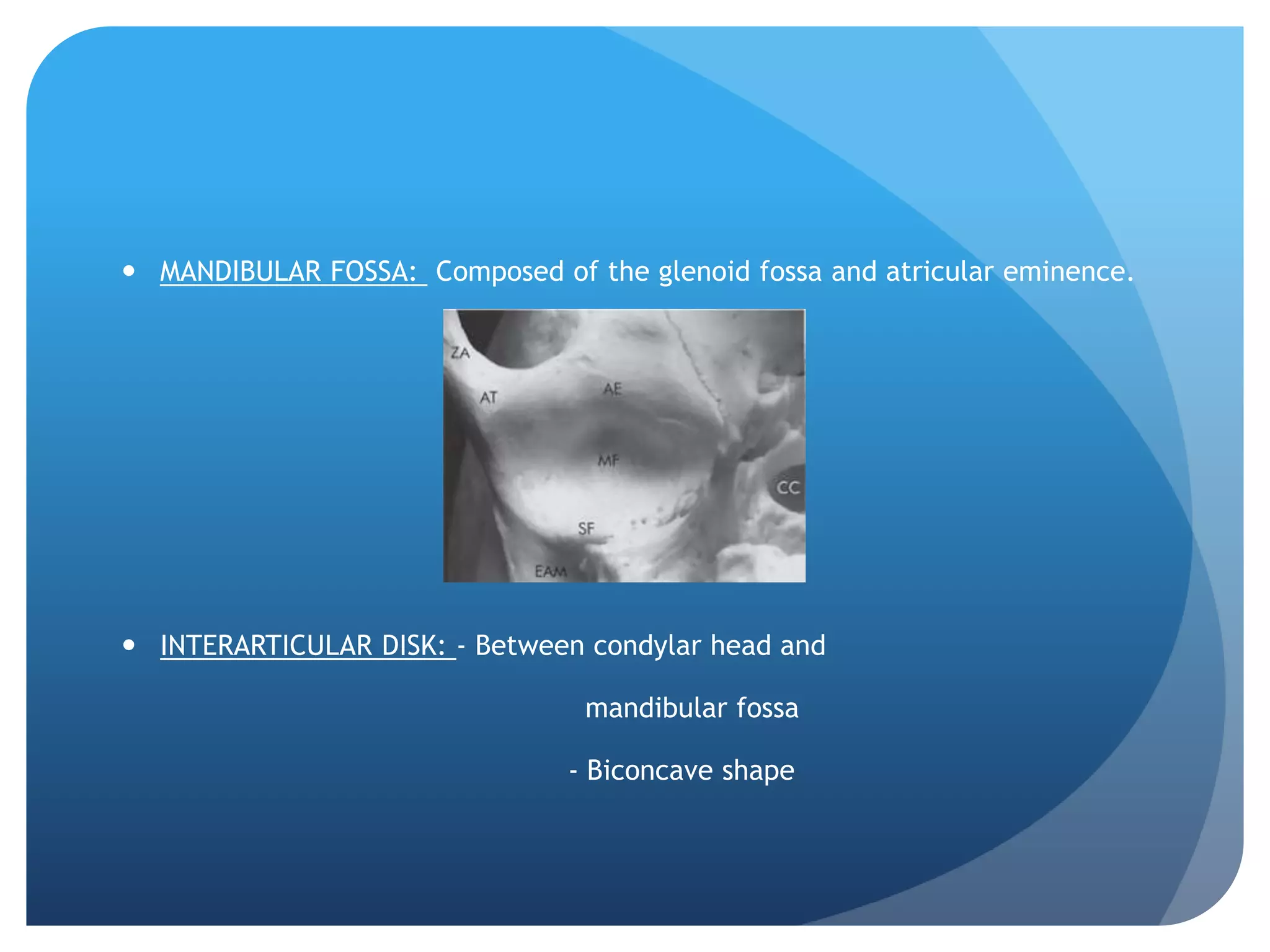
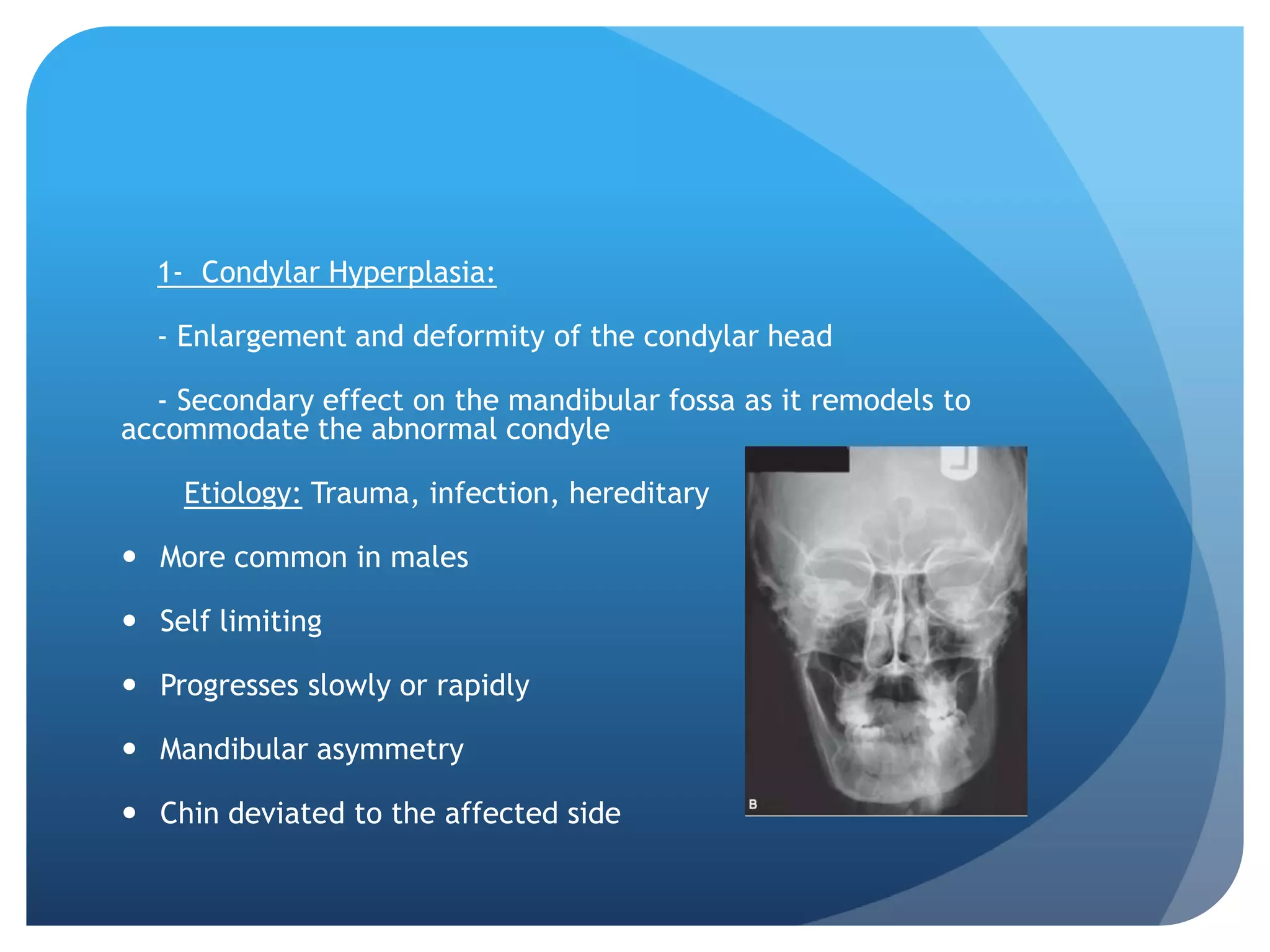
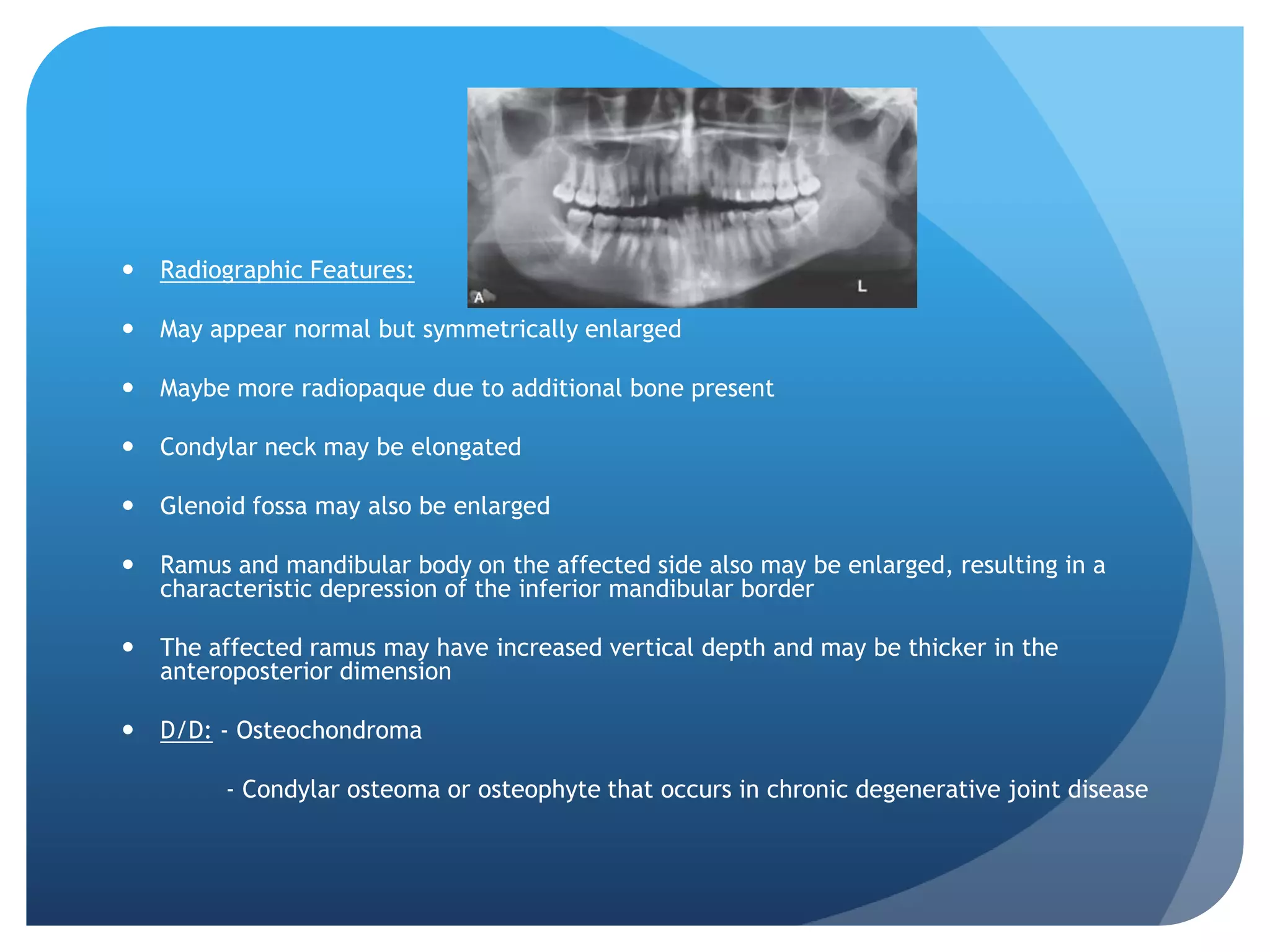
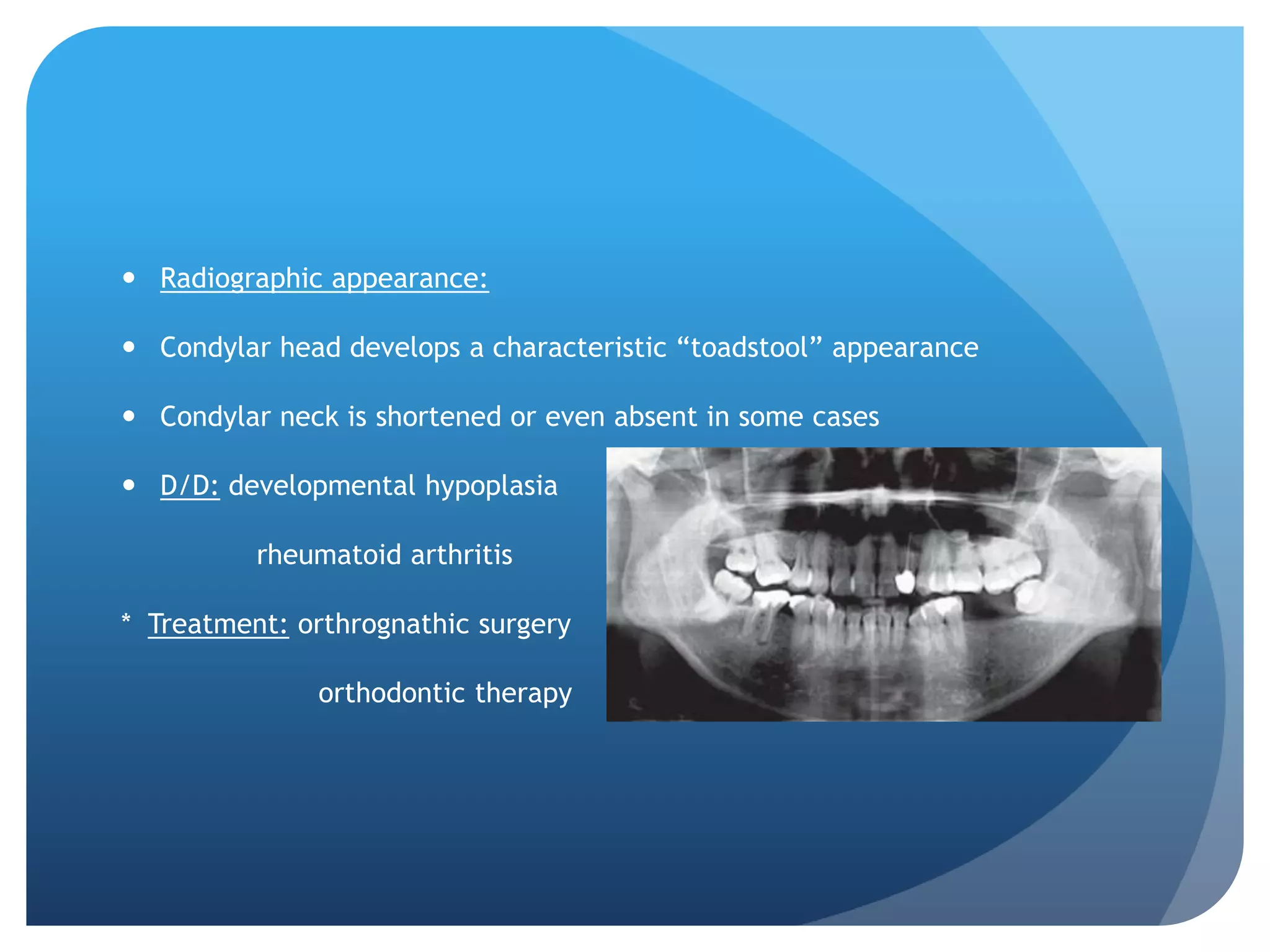
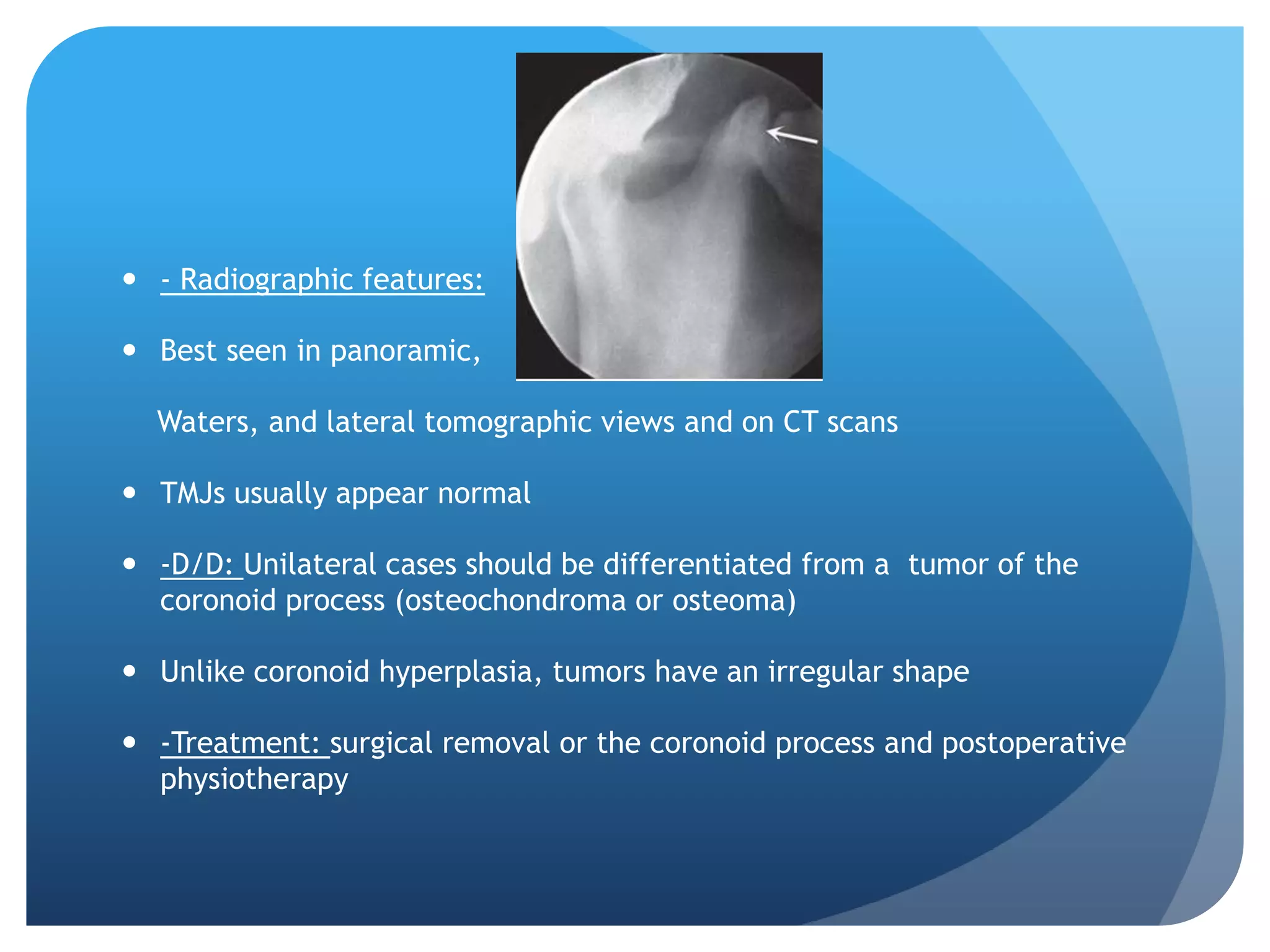
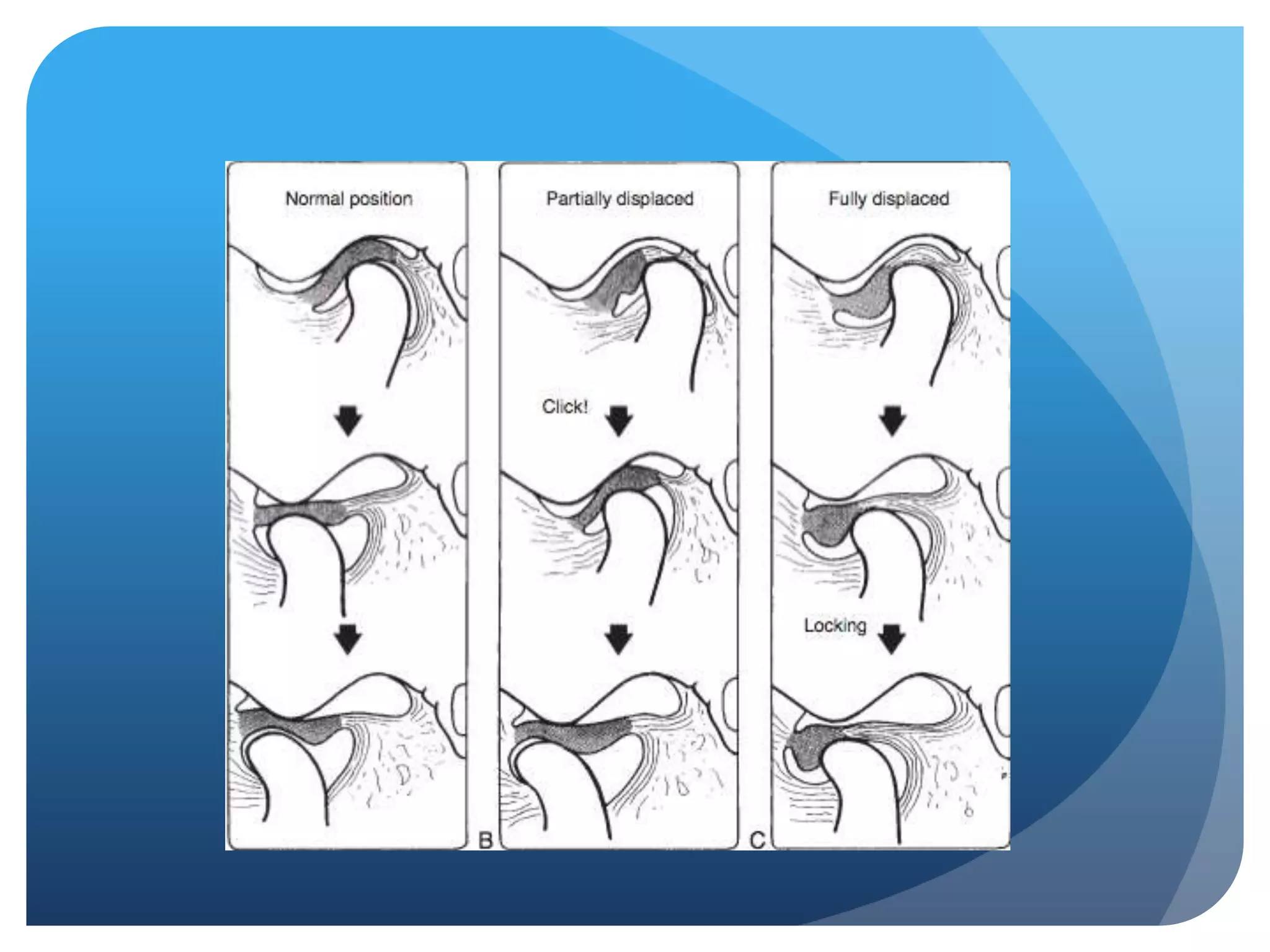
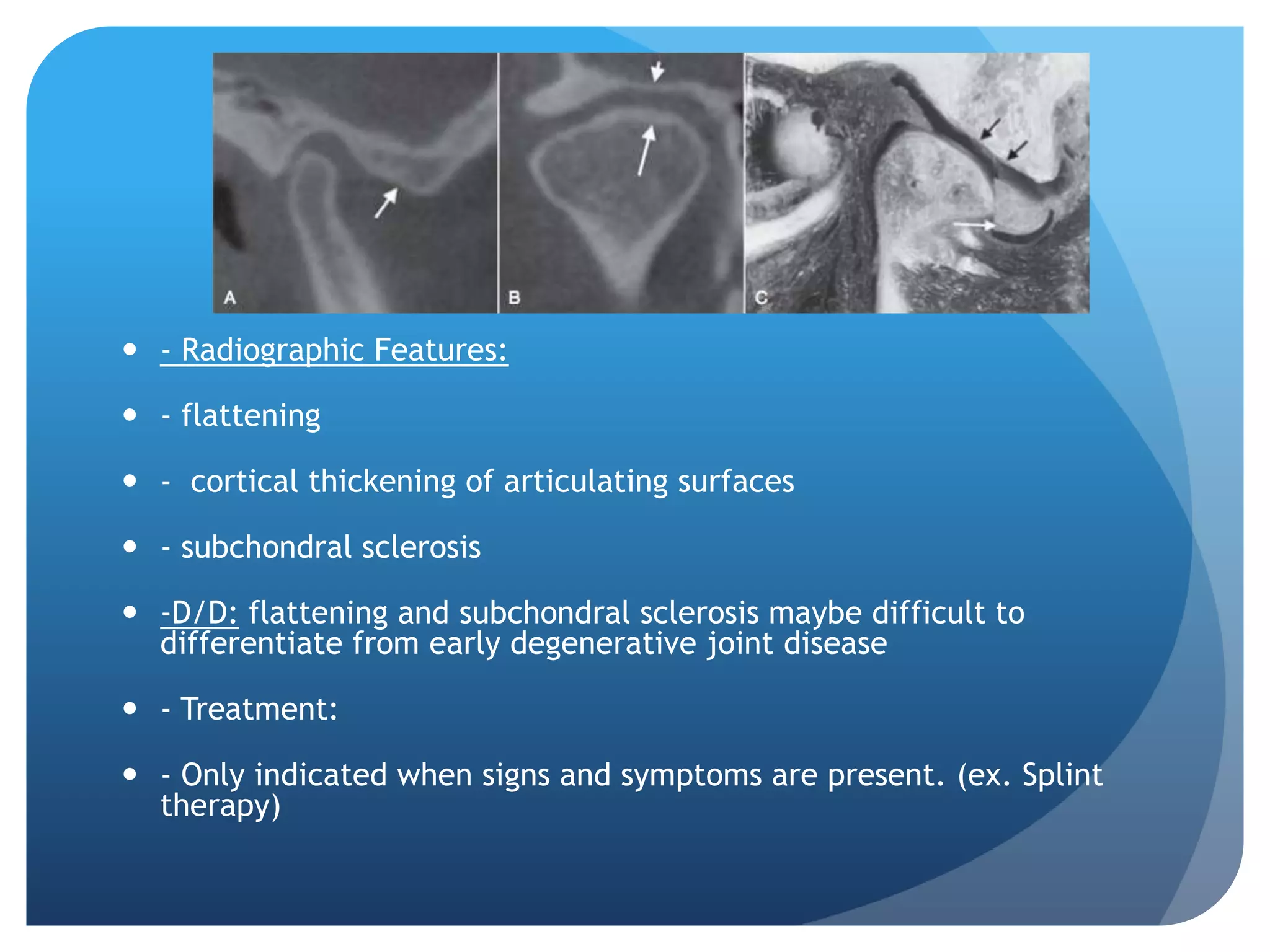
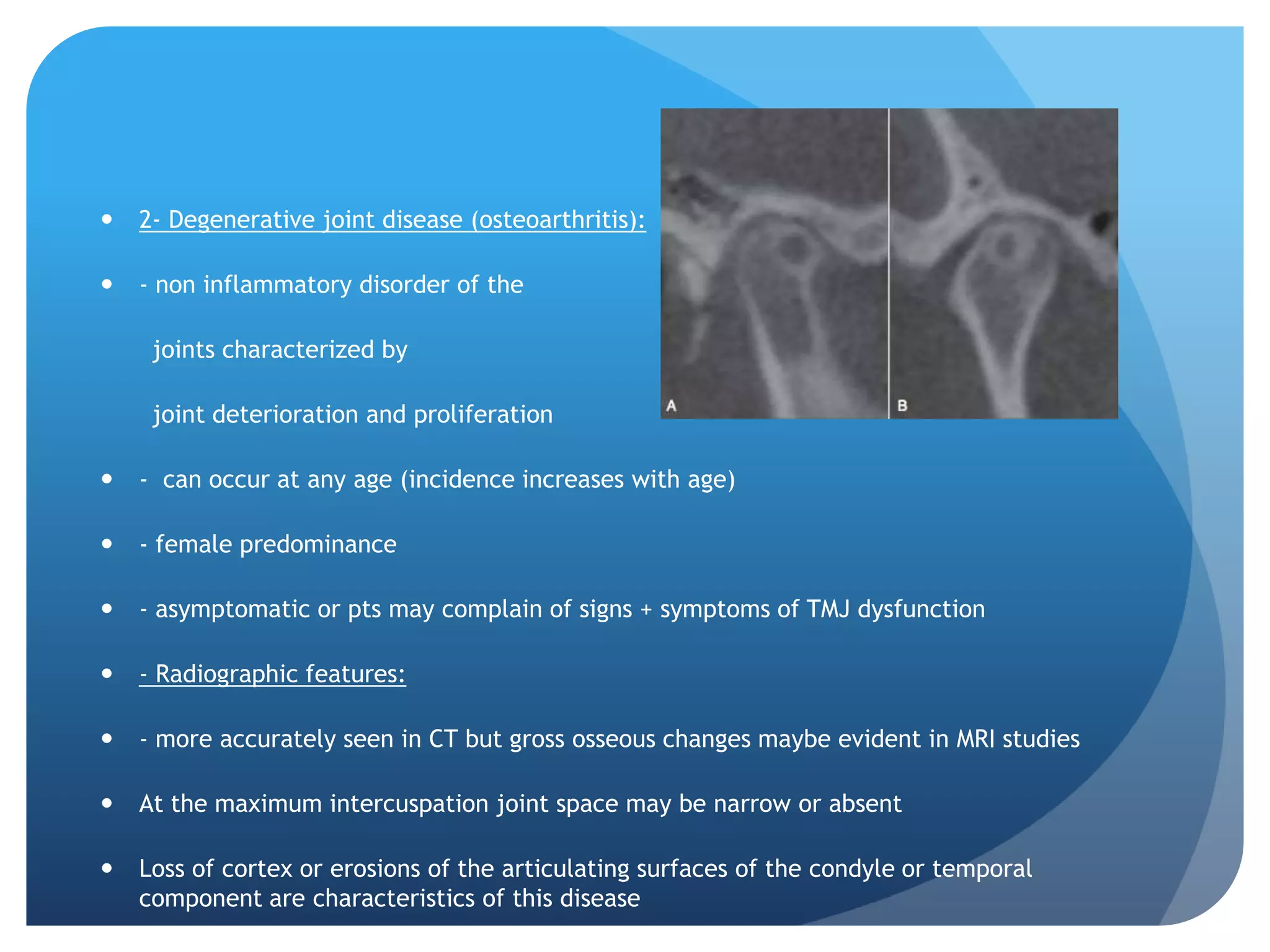
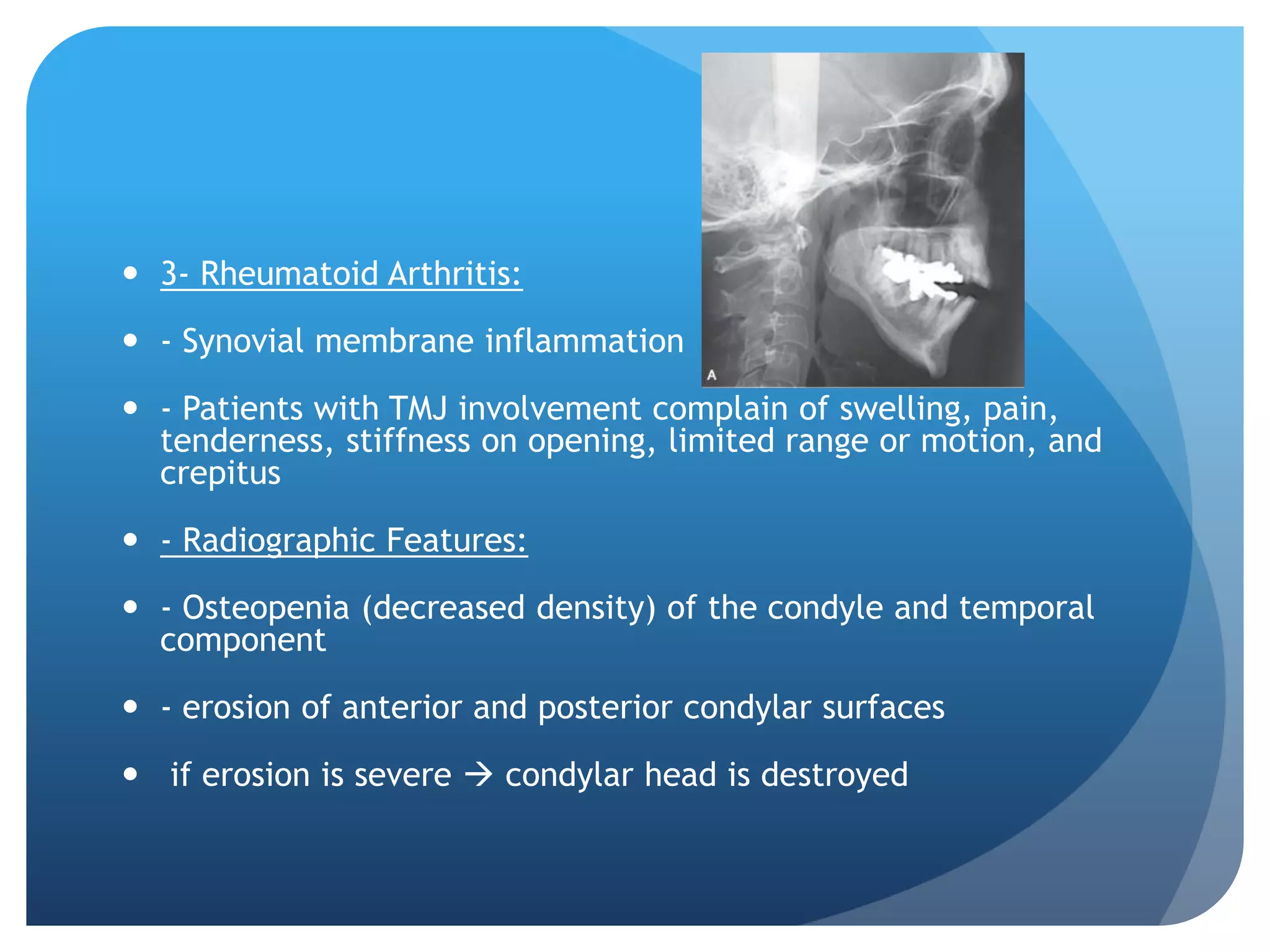
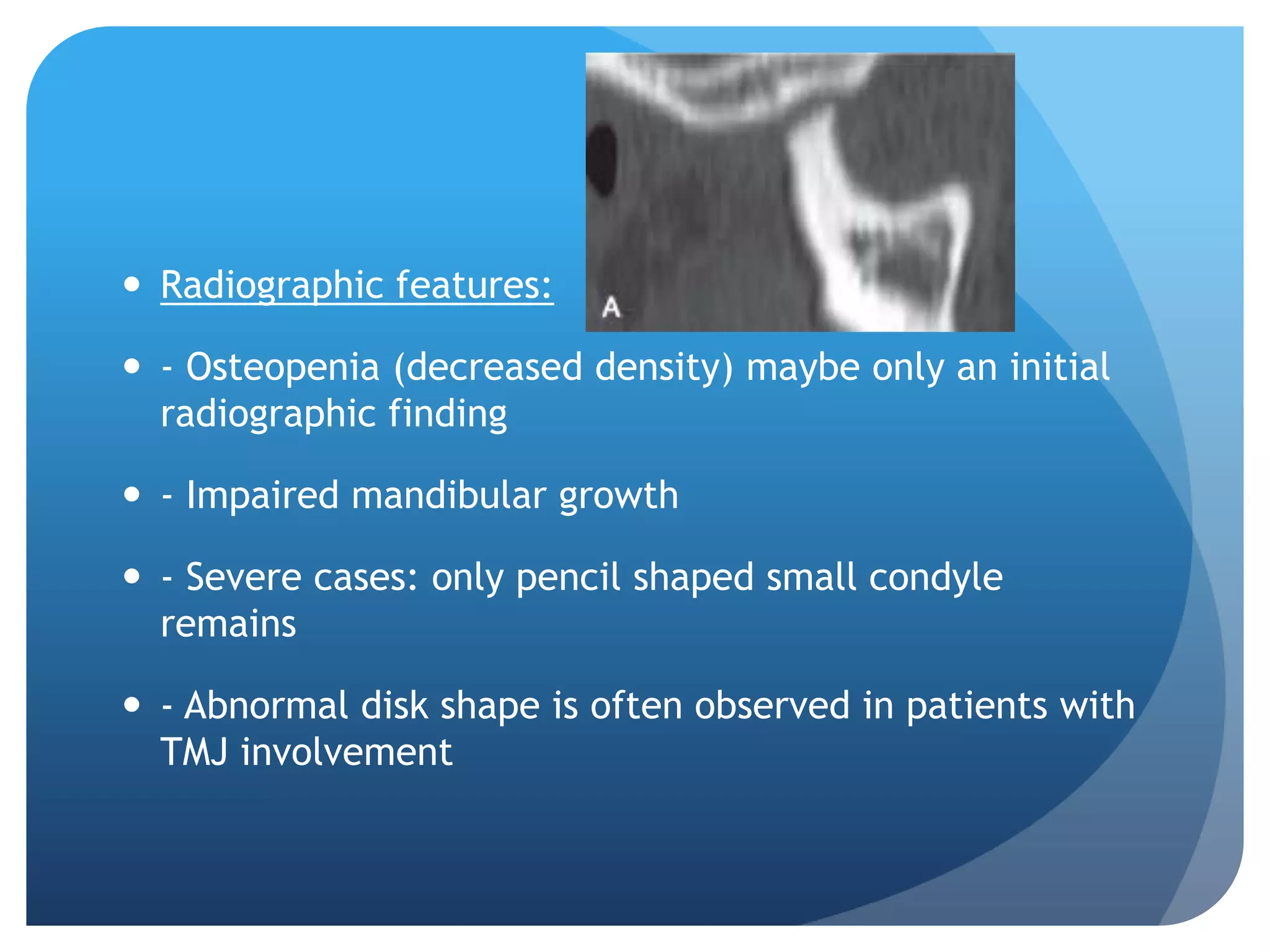
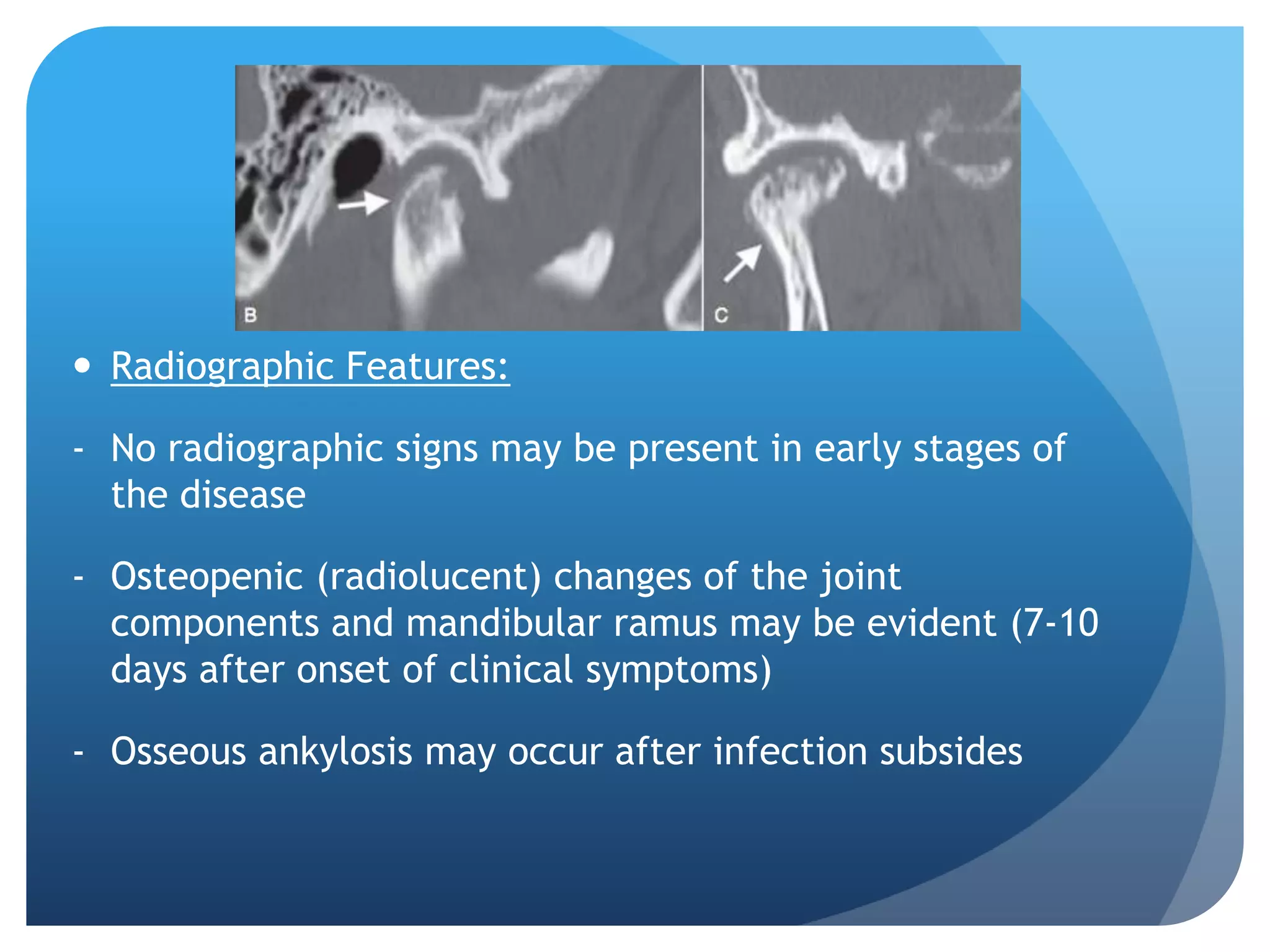
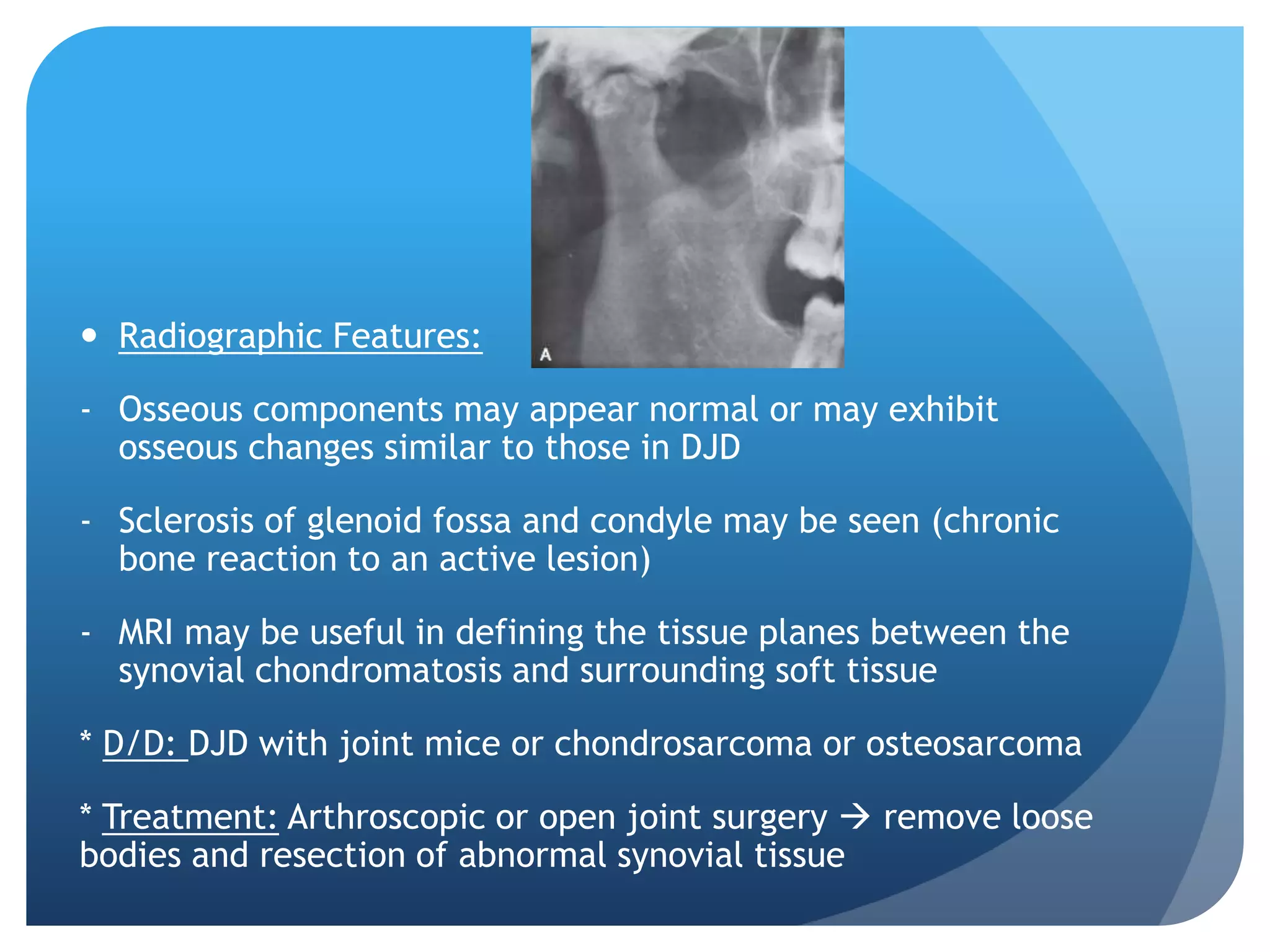
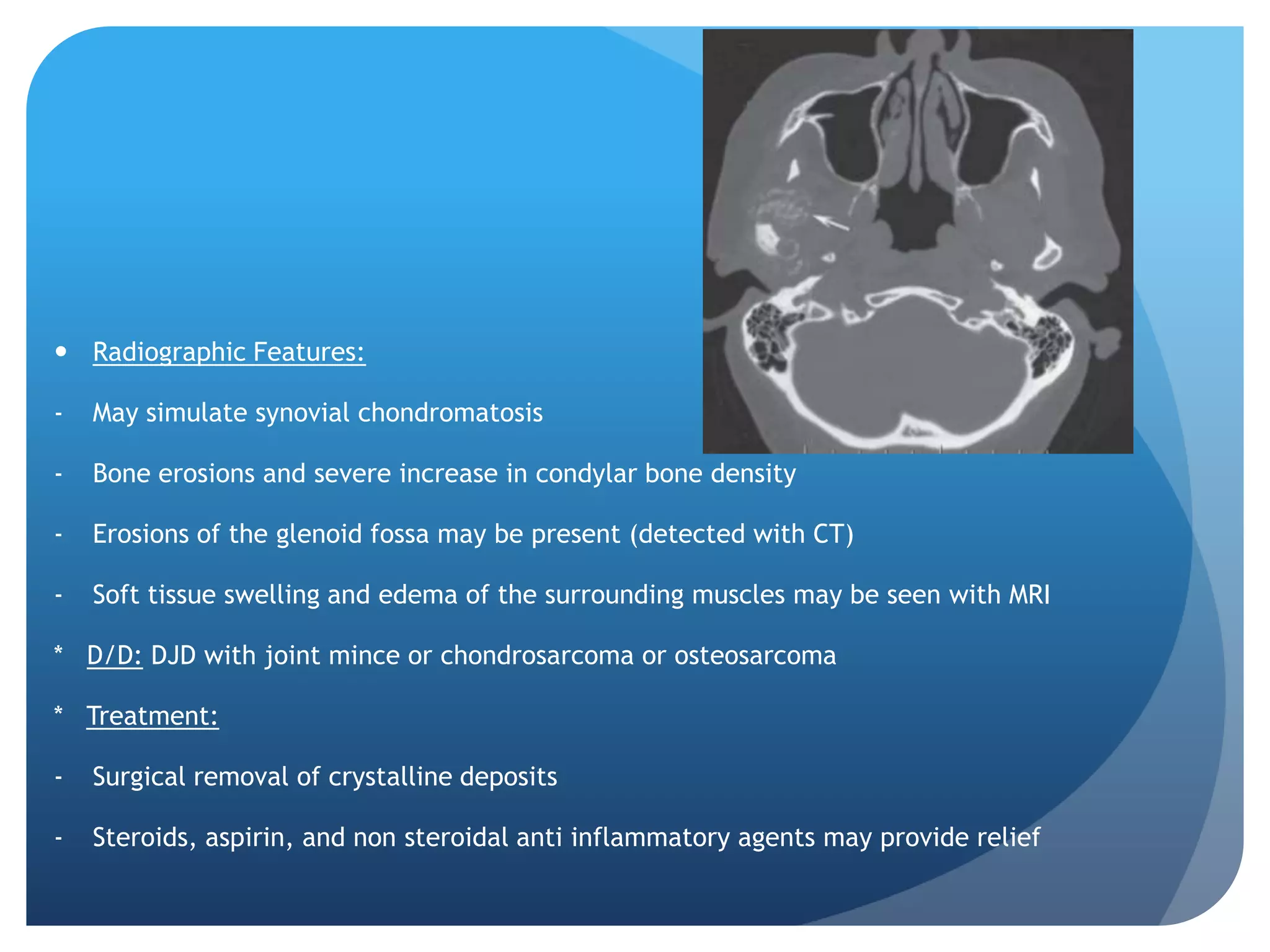
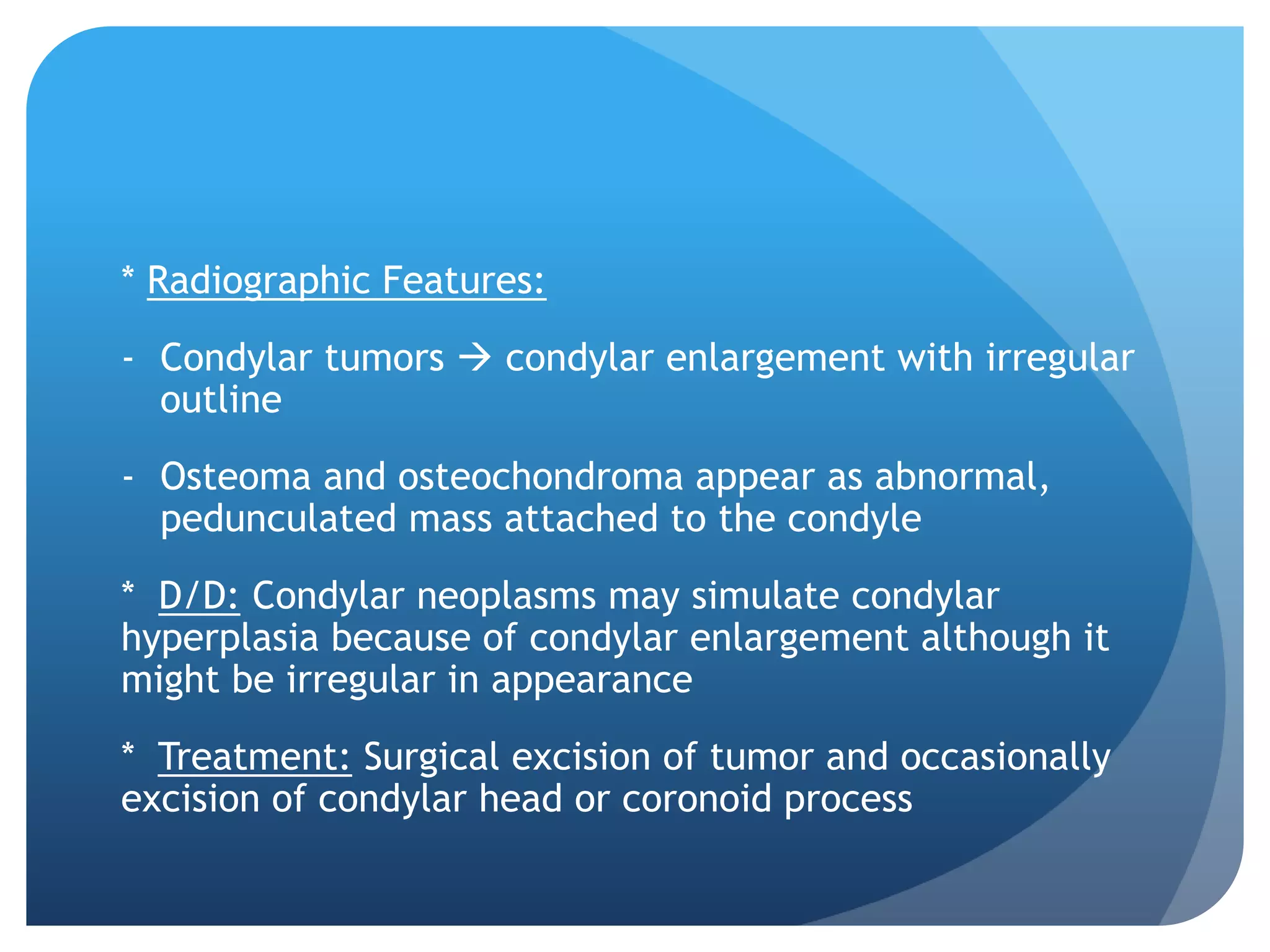
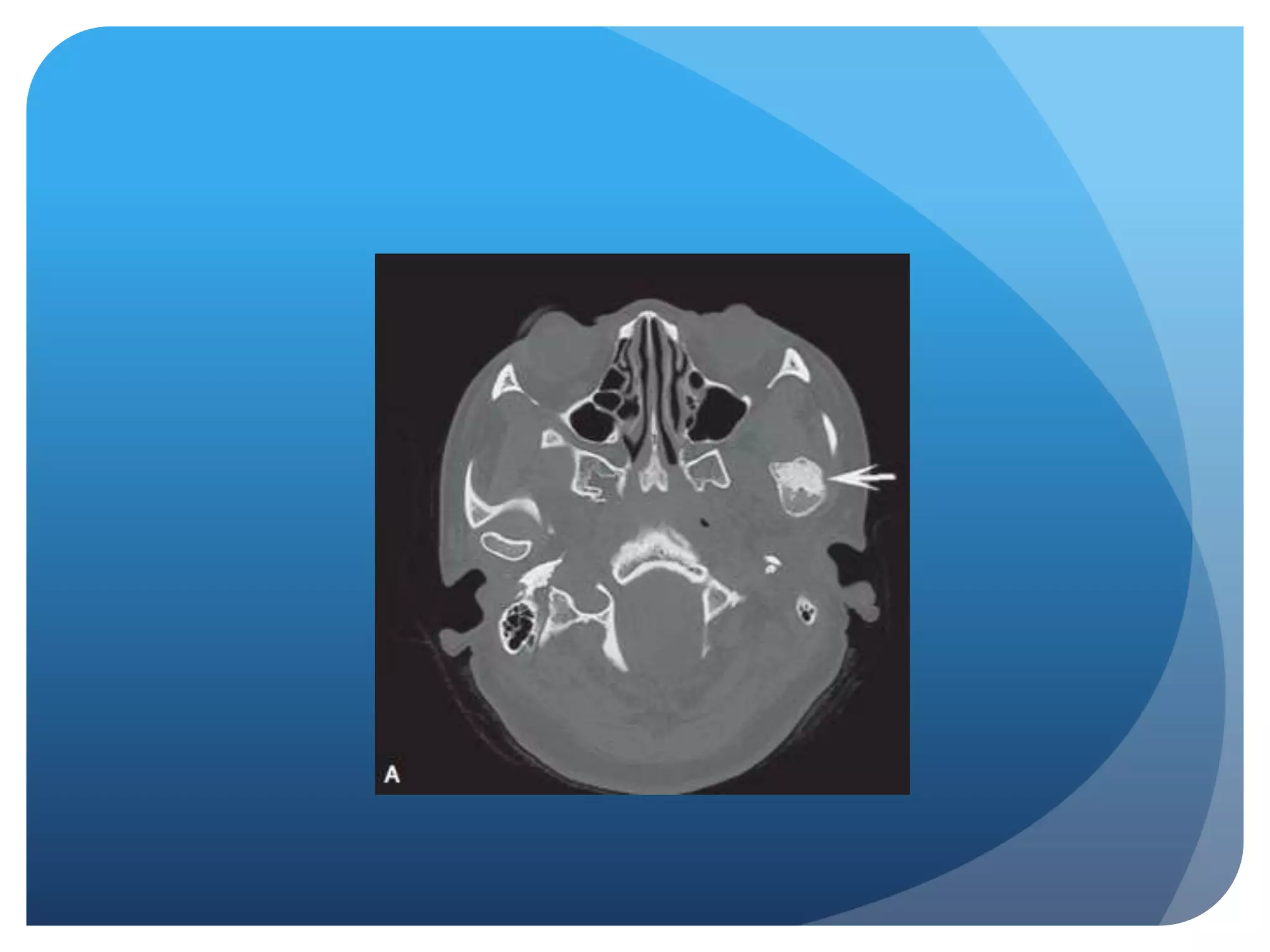
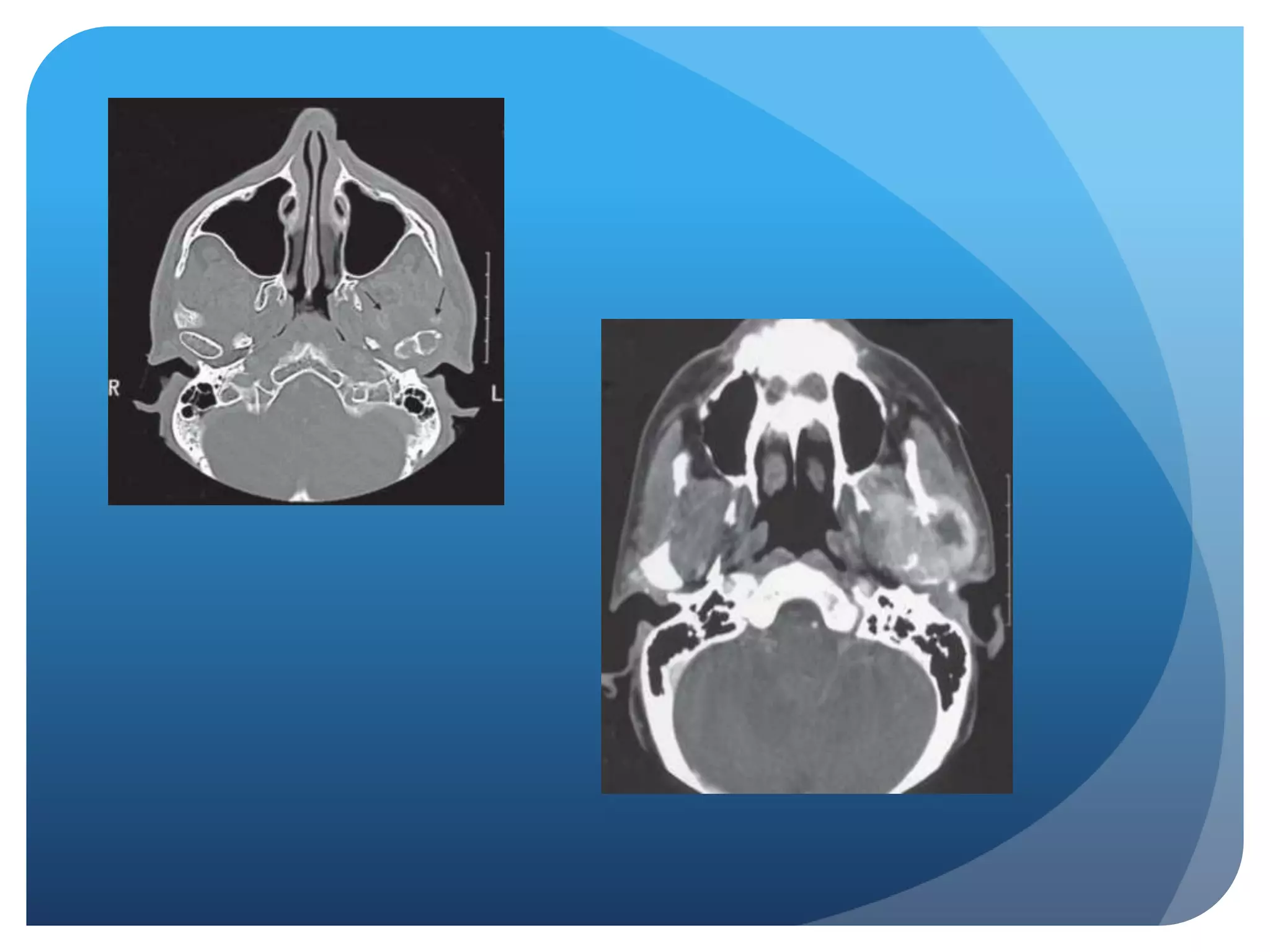
This document summarizes diagnostic imaging techniques for disorders of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). It describes the anatomy of the TMJ and its components. It then discusses various disorders including developmental abnormalities like condylar hyperplasia and hypoplasia, soft tissue abnormalities like internal derangements, remodeling and different types of arthritis. It also covers trauma-related conditions, tumors, and diagnostic features seen on imaging for each disorder. A wide range of TMJ pathologies are described with an emphasis on radiographic presentations.