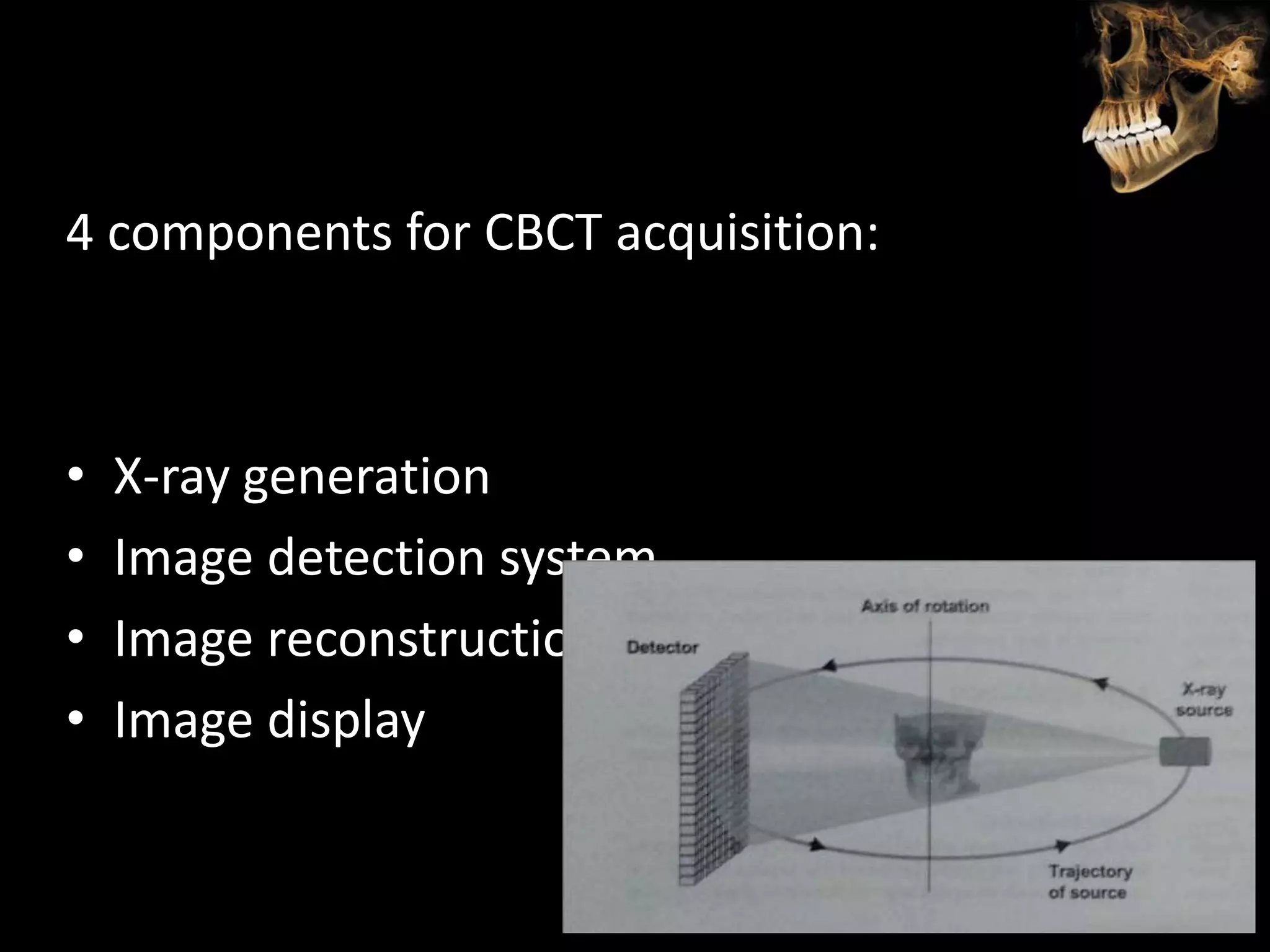
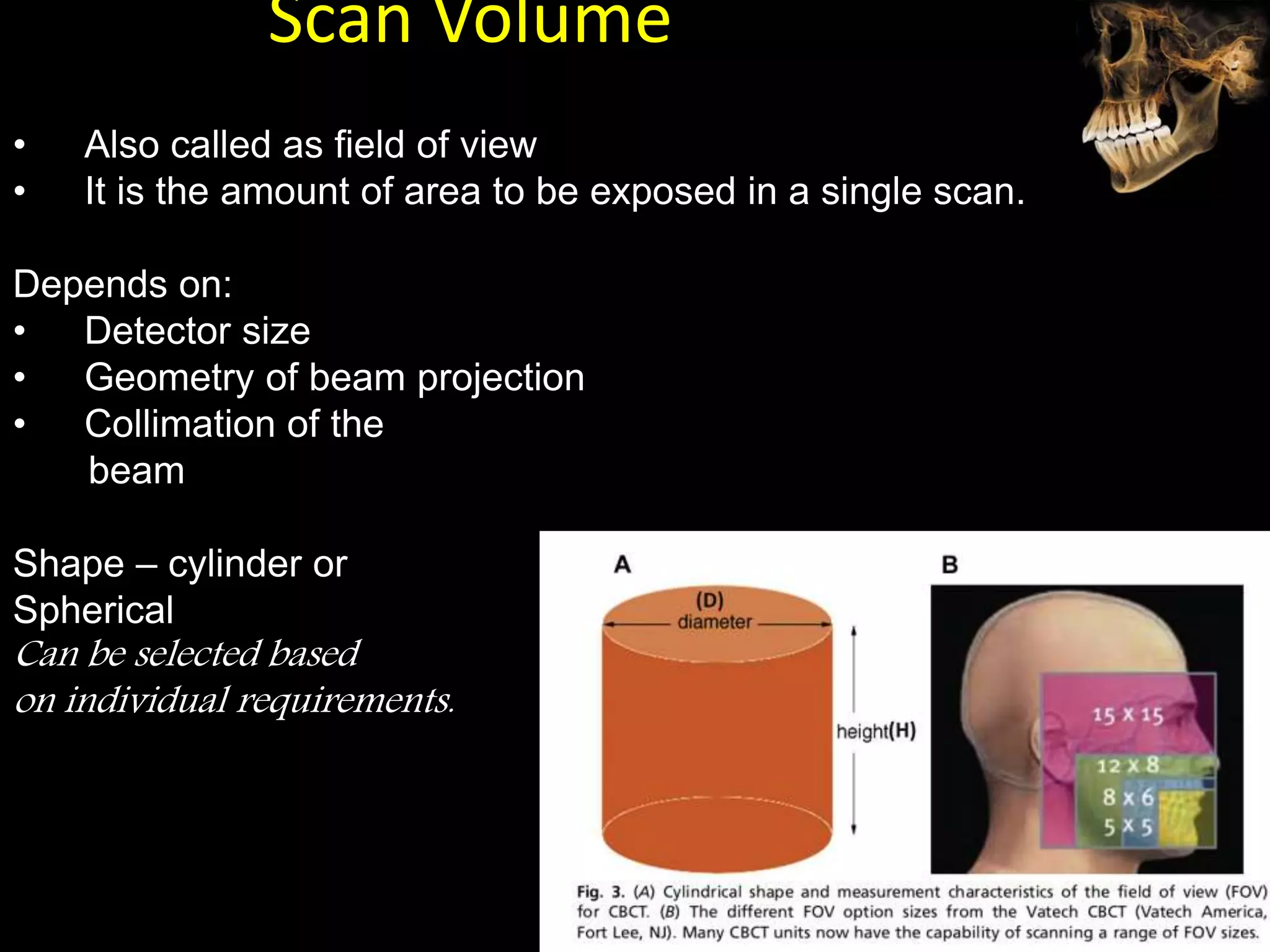
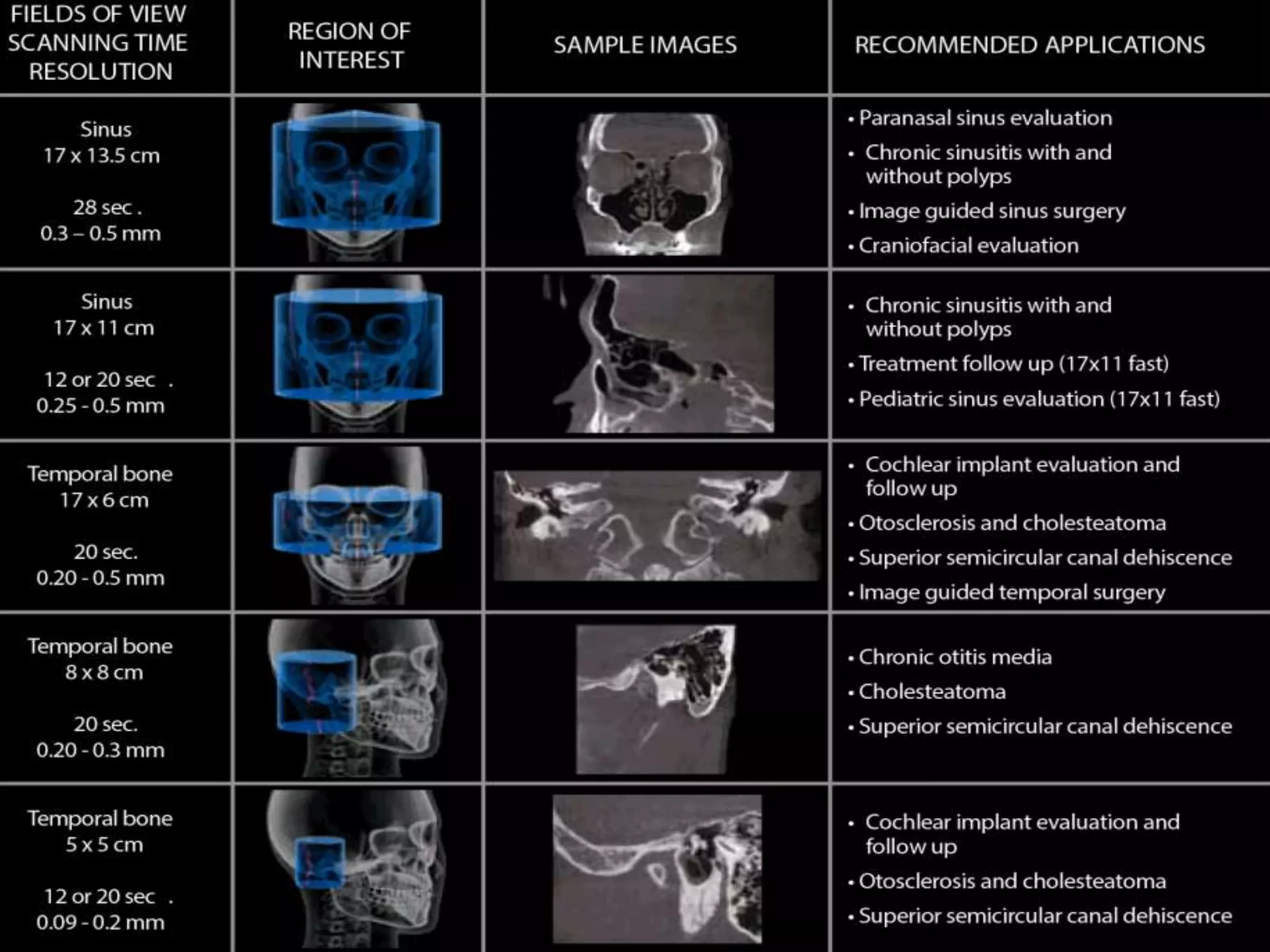
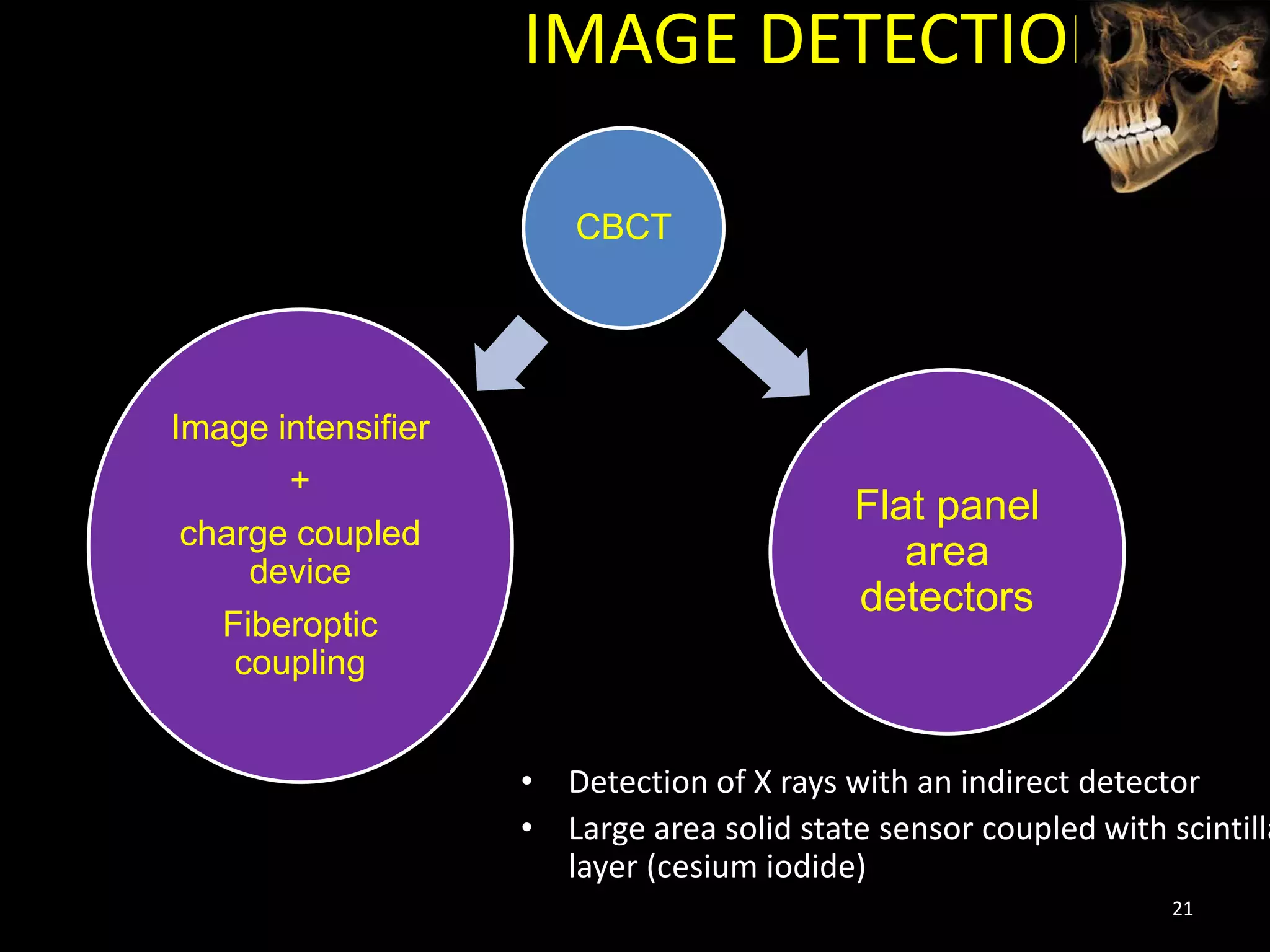
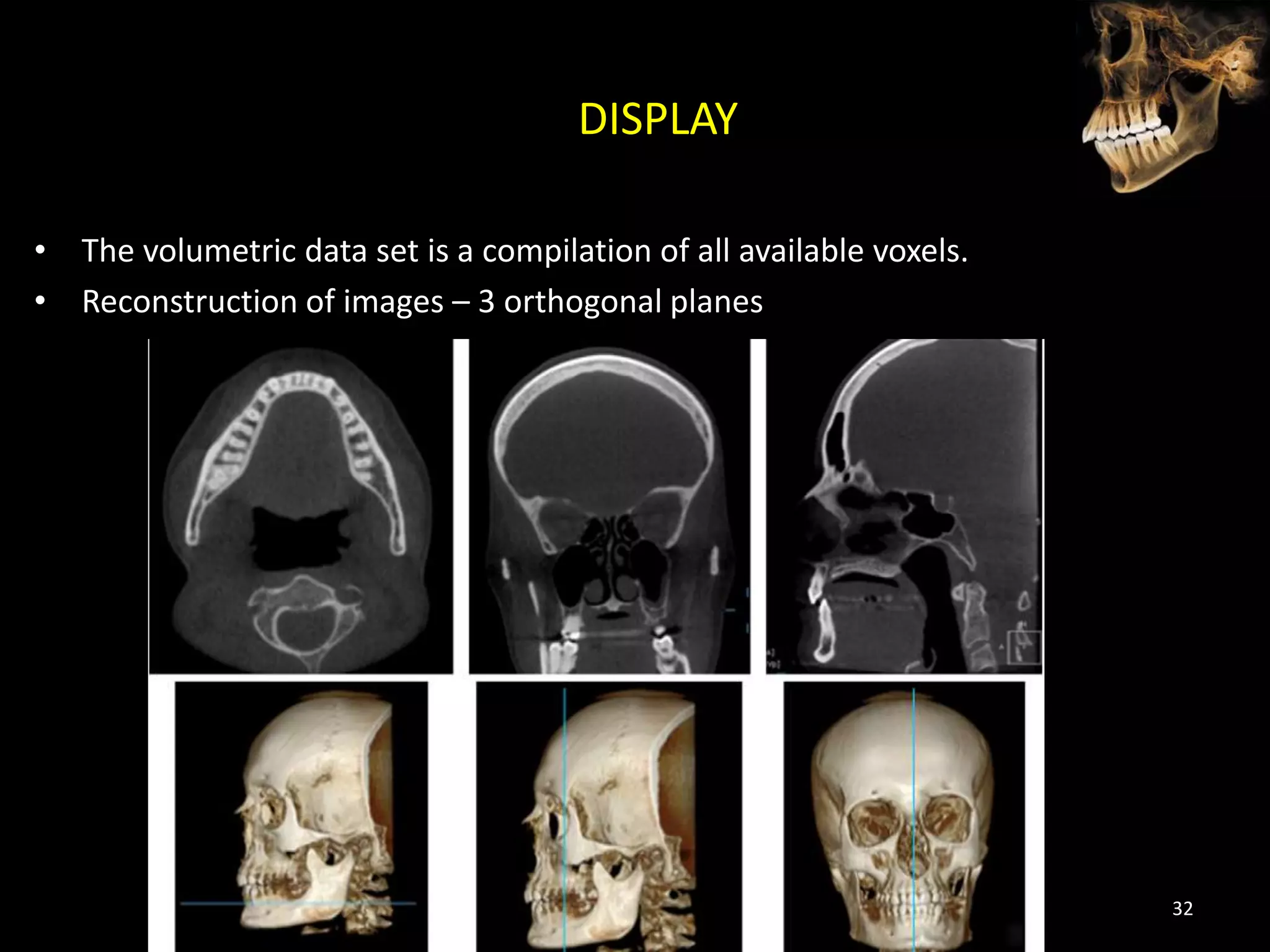
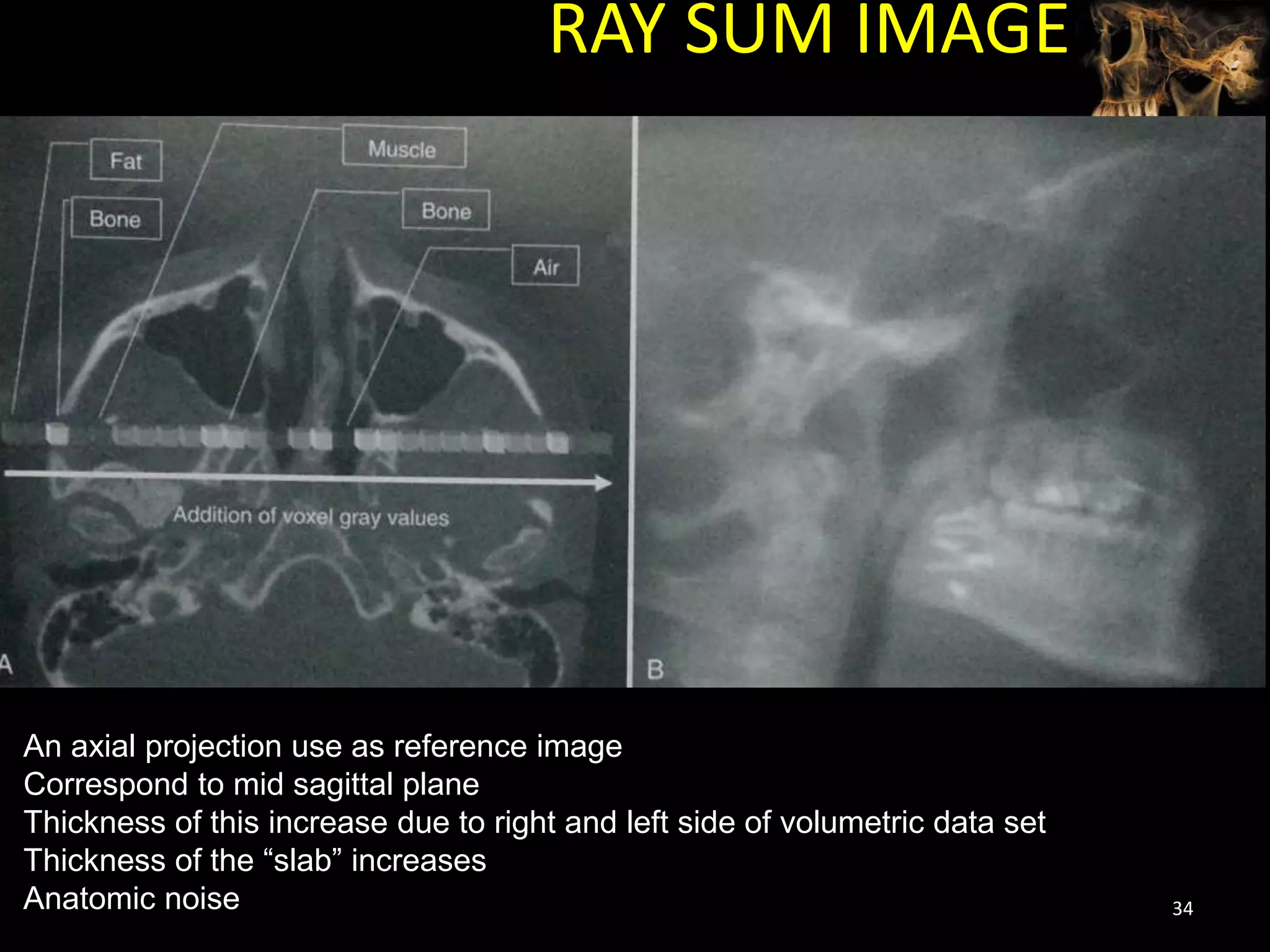
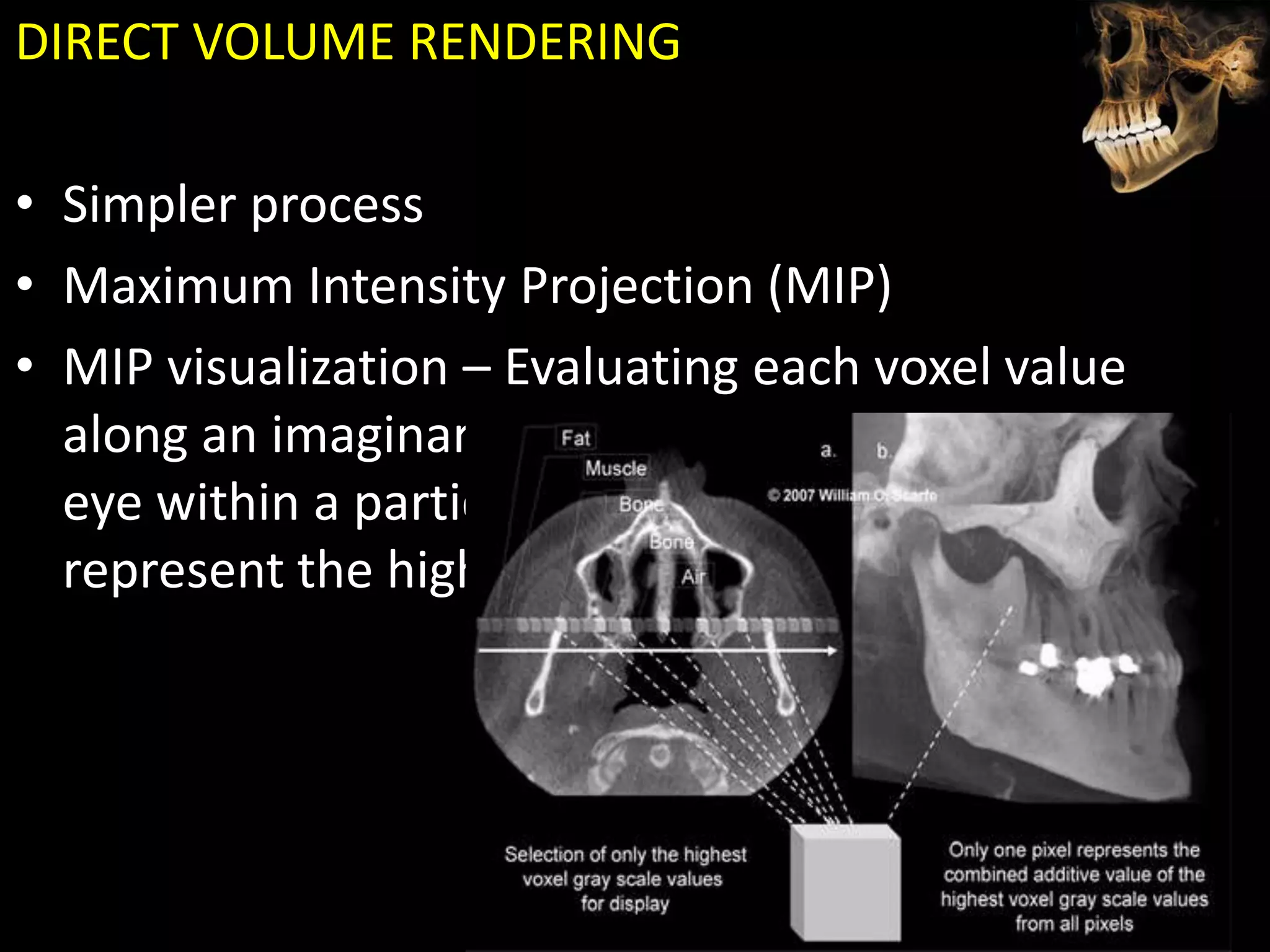
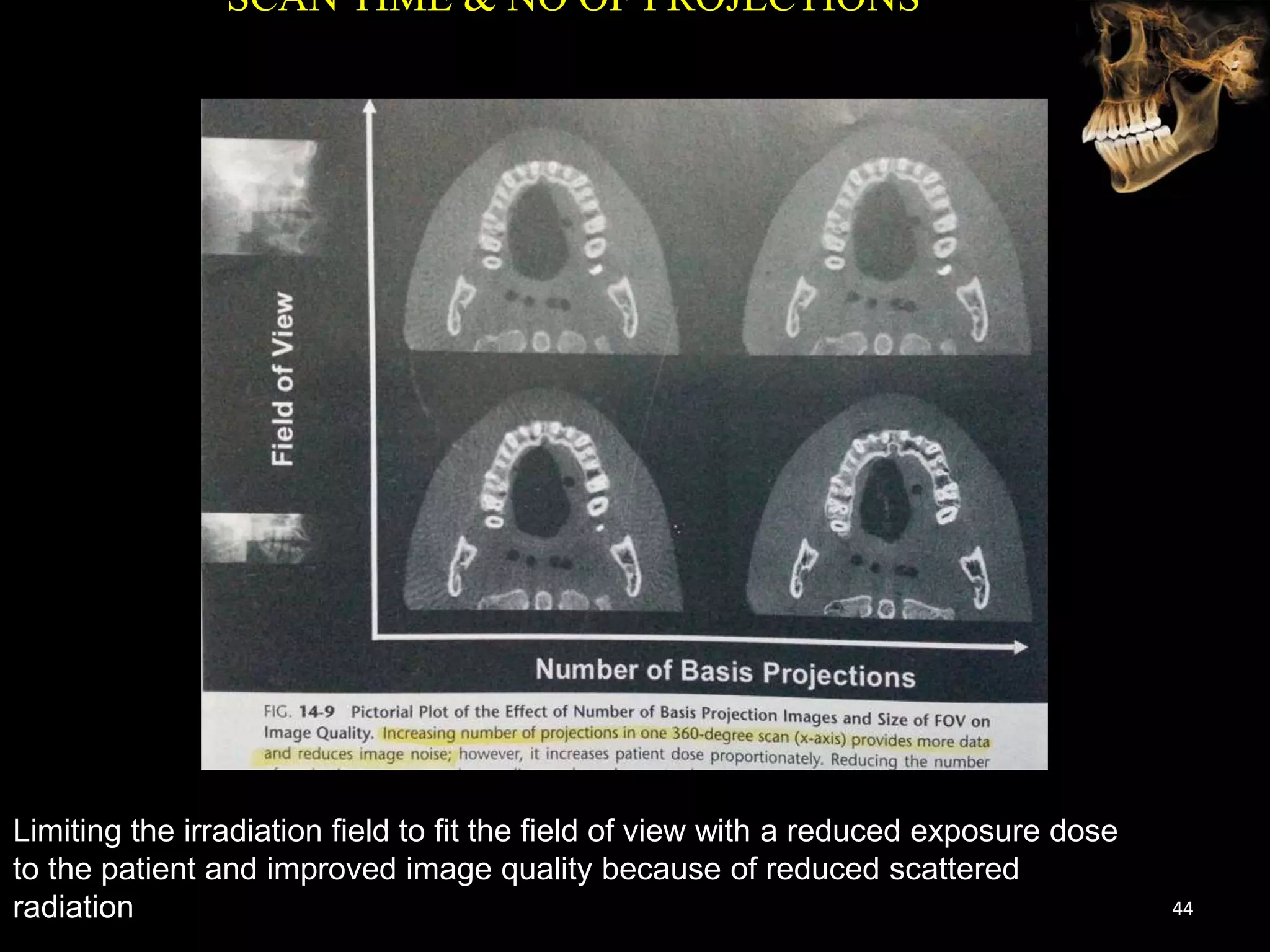
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) uses a cone-shaped x-ray beam projected through the area of interest and a 2D detector to acquire multiple 2D radiographic images at different angles. These images are then used to reconstruct 3D volumetric images. CBCT has applications in dentistry for implant planning, endodontics, orthodontics and TMJ imaging due to its ability to provide high contrast images of bony structures at a lower radiation dose compared to medical CT. Some limitations include artifacts from metallic restorations, lower soft tissue contrast and isotropic resolution compared to medical CT.