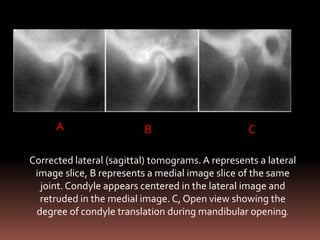
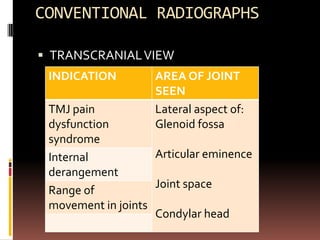
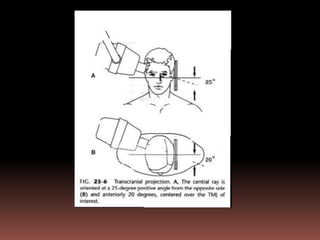
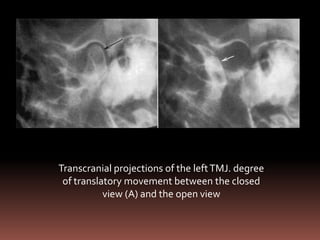
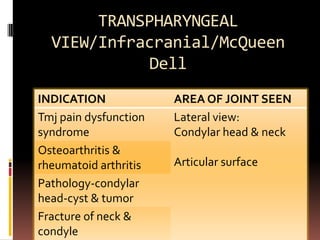
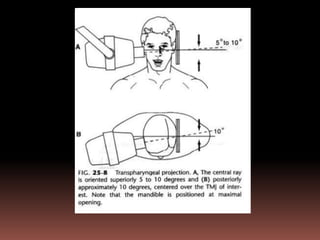
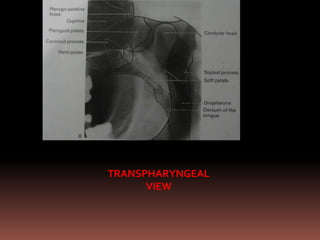
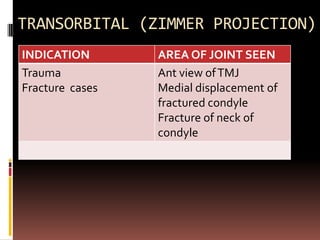
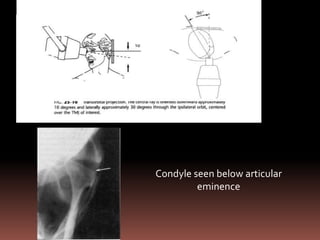
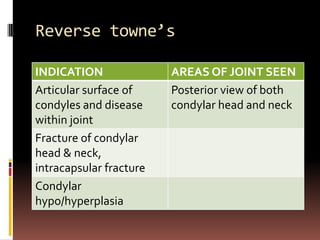
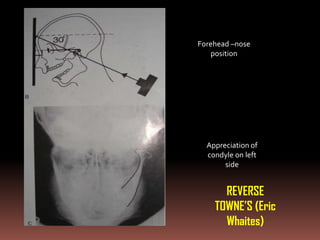
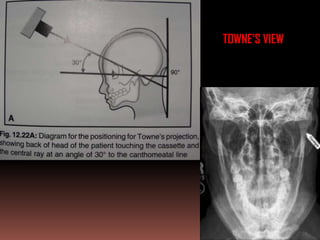
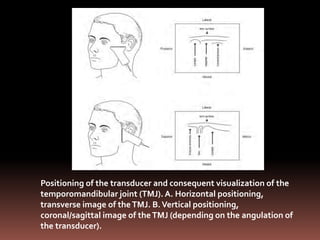
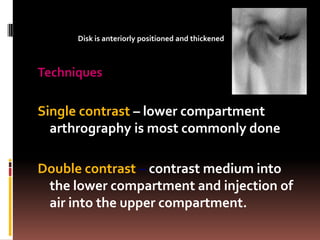
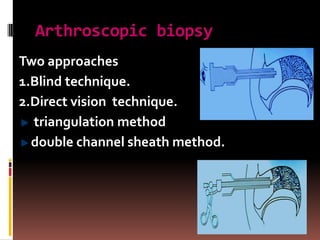
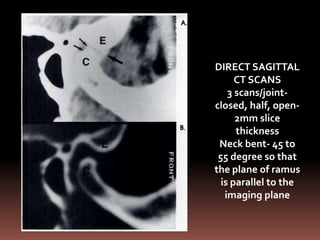
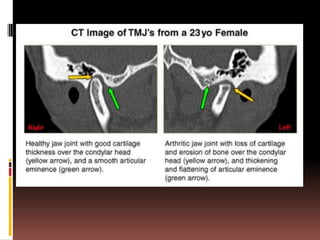
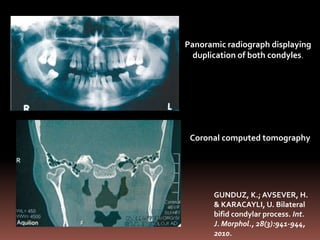
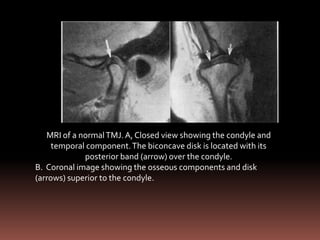
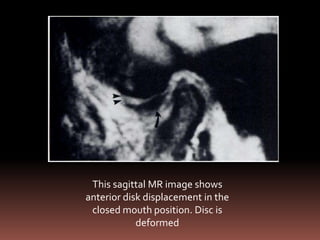
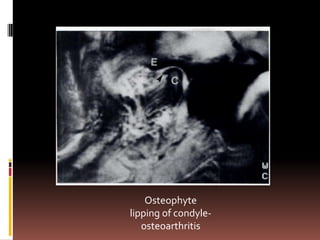
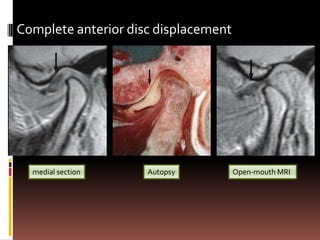
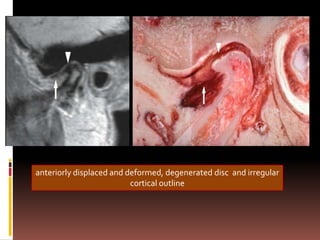
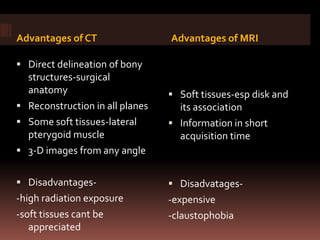
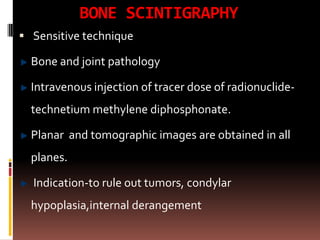
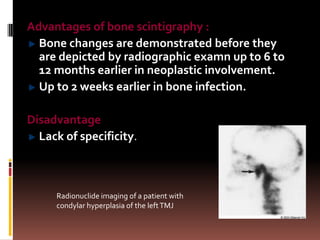
The document provides an extensive overview of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), focusing on its anatomy, various imaging modalities, and the techniques used for diagnosis and treatment of TMJ disorders. It discusses conventional radiography methods, including orthopantomograms and transcranial views, as well as advanced imaging techniques like CT and MRI, their indications, advantages, and limitations. Furthermore, it highlights the role of ultrasonography and arthrography in TMJ evaluation, emphasizing the need for accurate imaging to address complex pathologies associated with the joint.