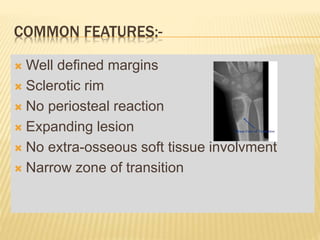
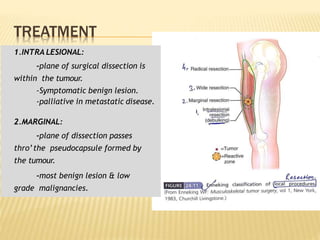
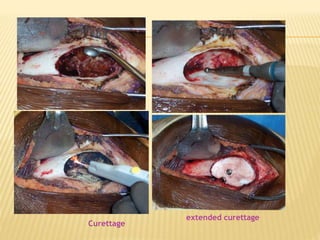
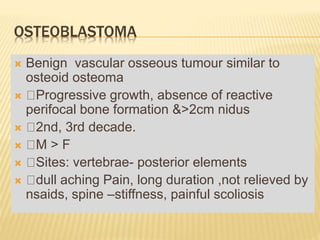
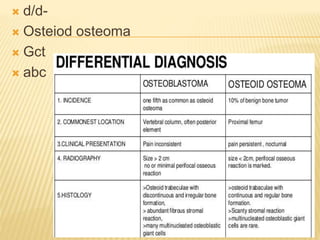
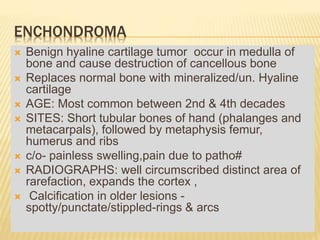
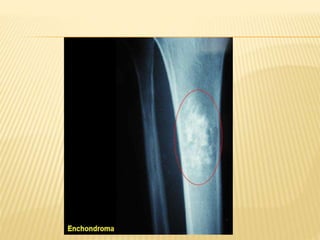
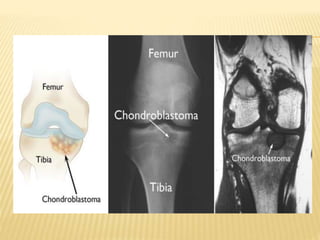
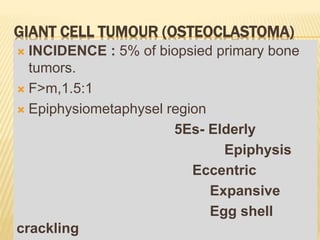
This document provides an overview of benign bone tumors. It discusses osteoma, osteoid osteoma, osteoblastoma, giant cell tumor (osteoclastoma), chondroblastoma, osteochondroma/exostosis, and enchondroma. For each tumor, it describes characteristics such as common locations, symptoms, radiological features, histopathology, differential diagnosis, and treatment options. Common features of benign bone tumors are also reviewed, including well-defined margins, sclerotic rims, and lack of soft tissue involvement. Treatment methods like curettage, extended curettage, and various reconstruction techniques are presented.




![OSTEOMA
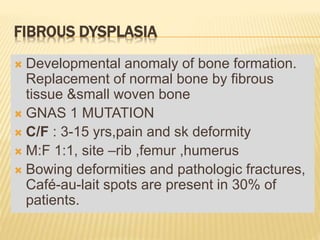
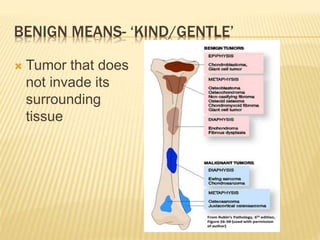
Benign bony outgrowth of membranous bones.
Multiple osteomas are associated with Gardner's
syndrome[multiple cut./subcut.lesion]
Highest incidence in the sixth decade
Male: female is 2:1
Asymptomatic,[sinonasal osteoma- sinusitis,
nasal discharge,headache]
Xray- 3-4cm homogenous round radiodense
mass
Excision if symptomatic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benignbonetumorppt-210610155904/85/Benign-bone-tumor-ppt-11-320.jpg)
![OSTEOID OSTEOMA
Commonest benign osseous tumour
Common in 1st& 2nd decade of life
10% of all benign bone tumours
M:F – 2:1
SITE: diaphysis, metaphysis of long bones [prox
femur mc>proximal tibia], posterior elements of
spine
On basis of CT/MRI-
subperiosteal,intracortical,endosteal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benignbonetumorppt-210610155904/85/Benign-bone-tumor-ppt-12-320.jpg)

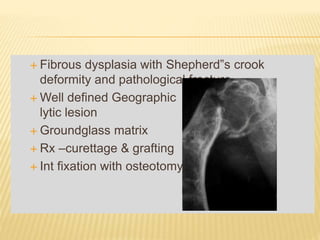
![Nidus –central well defined
hypervascular area of
rarefaction[reduction of density of
bone]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benignbonetumorppt-210610155904/85/Benign-bone-tumor-ppt-14-320.jpg)



![ xray/CT scan- radiolucent well
circumscribed lesion with central calcification
& thin peripheral shell of reactive
bone„[cotton wool‟ if calcified ]
Spine-spinous process,pedicle markedly
enlarged
t/t – intralesional curettage or en-
bloc resection
Neurologic involvement-
decompressive laminectomy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benignbonetumorppt-210610155904/85/Benign-bone-tumor-ppt-19-320.jpg)




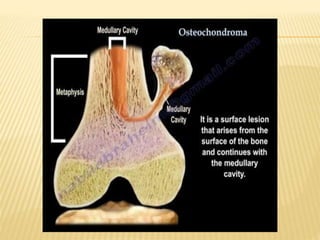

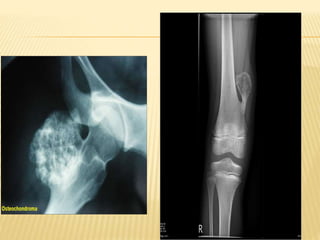

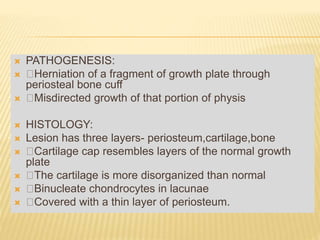


![HEREDITARY MULTIPLE EXOSTOSES (H.M.E)
Also known as: Multiple Exostoses, Diaphyseal
aclasis
Autosomal dominant hereditary disorder, 10% no
family history. EXT1,2,3 genes [EXT1 –severe dis]
Knees, ankles and shoulders are most frequently
affected.
Knobby appearance, Short stature
Forearm deformity, Tibio-fibular synostosis, Genu
valgum, Coxa valga
Rx - Excision of symptomatic exostosis
Correction of deformity and limb length discrepancy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benignbonetumorppt-210610155904/85/Benign-bone-tumor-ppt-34-320.jpg)




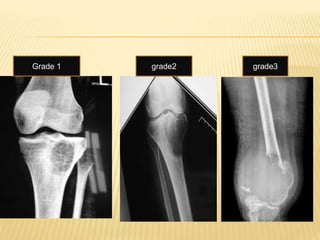
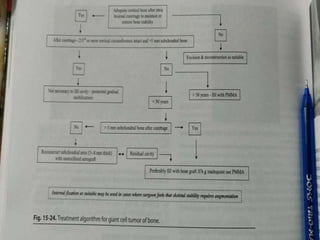
![ Campanacci Grading:
Grade I: Tumour associated with well defined
margins and thin rim of mature bone [cystic
lesion]
Grade II: Tumour is well defined but has no
radiopaque rim[thin cortex but no break in
cortex]
Grade III: Tumour has fuzzy borders [cortex
break & soft tissue extension]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benignbonetumorppt-210610155904/85/Benign-bone-tumor-ppt-42-320.jpg)
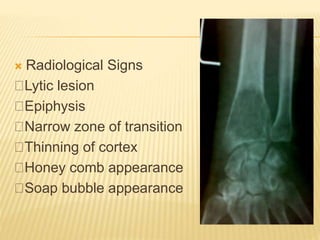




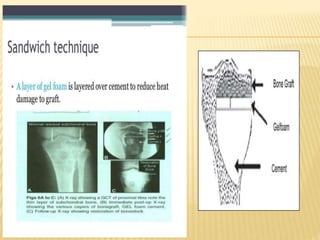
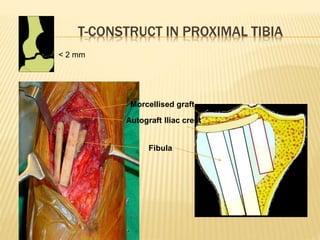

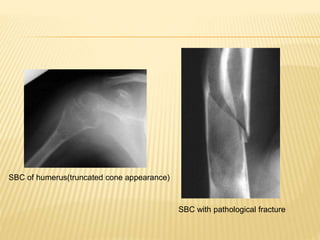
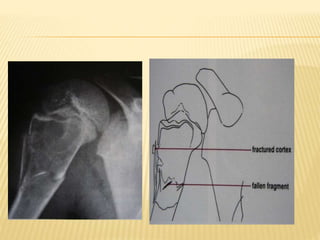
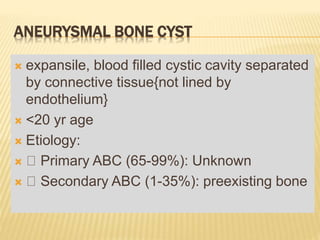

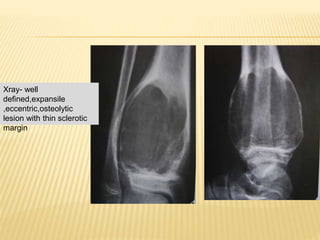
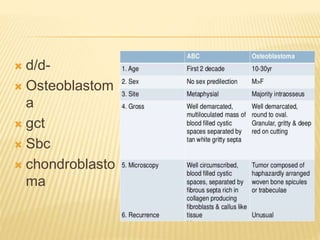
![ CT scan features: “blood filled sponge‟‟, fluid
levels due to sedimentation of blood.
MRI : Multiple cysts: Fluid – fluid levels [double
density fluid level & intralesional septa]sbc vs
abc
Nuclear study: “ donut sign ” i.e. peripheral
increased uptake.
Angiography: hypervascularity in the periphery
of the lesion.
Rx: Surgical curettage with bone grafting.
Recurrence rate is high](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benignbonetumorppt-210610155904/85/Benign-bone-tumor-ppt-58-320.jpg)