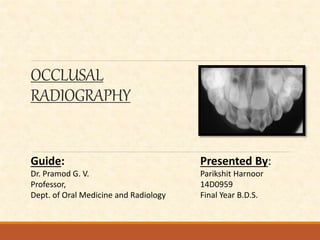
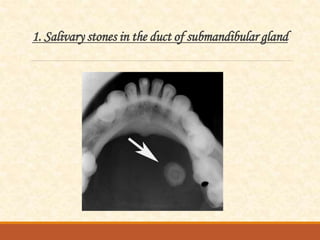
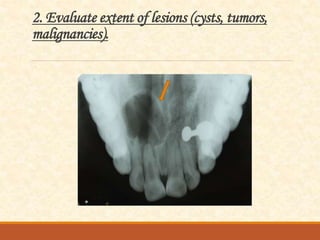
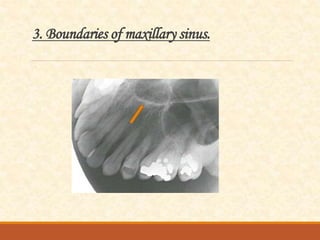
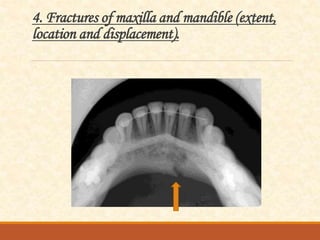
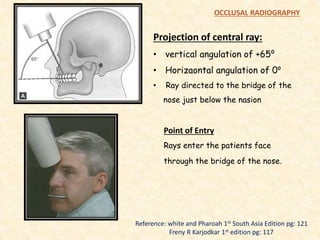
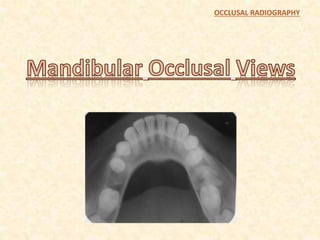
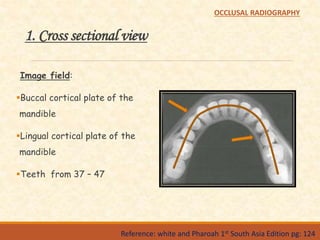
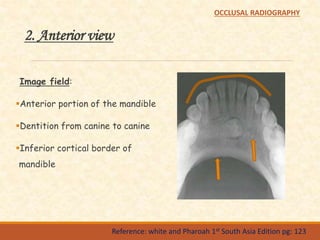
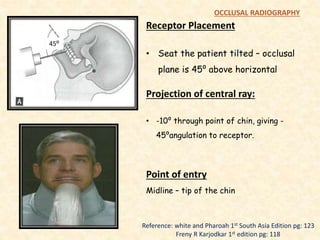
The document outlines the principles, classifications, and methods of occlusal radiography, which is used for examining large areas of the upper and lower jaws, including indications for its use. It details the types of occlusal views, positioning and angulation of radiographic films, and provides conclusions and references for further reading. Multiple choice questions at the end test knowledge on the subject matter.