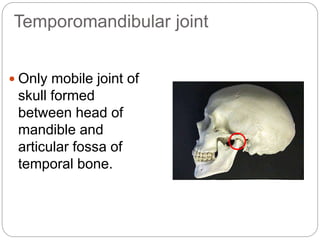
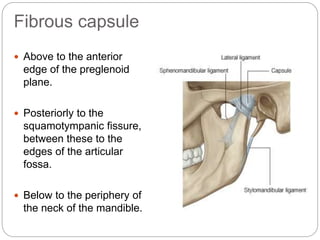
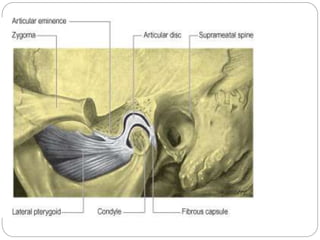
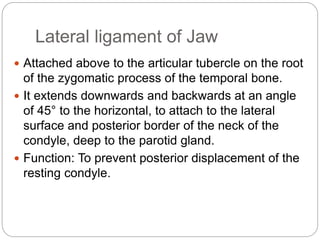
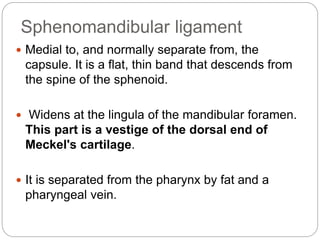
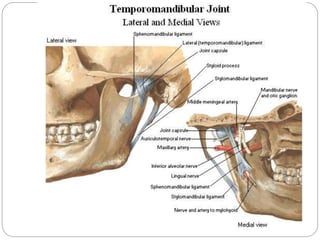
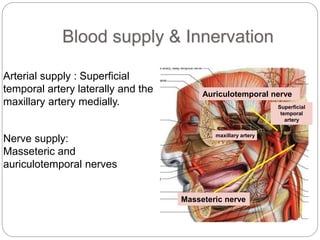
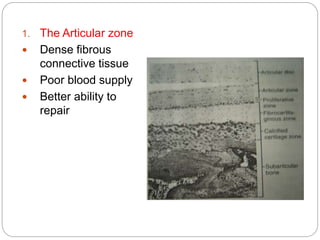
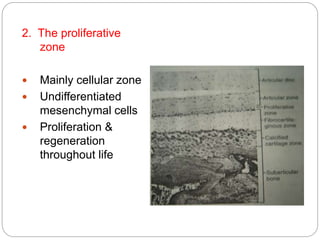
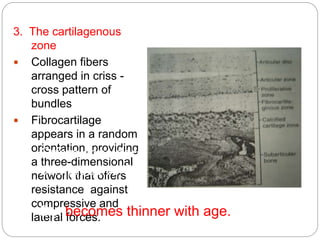
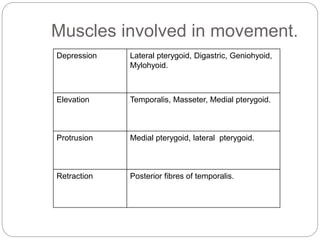
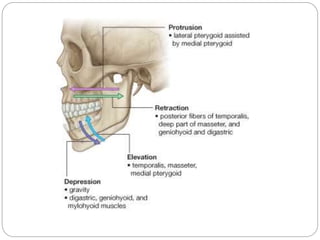
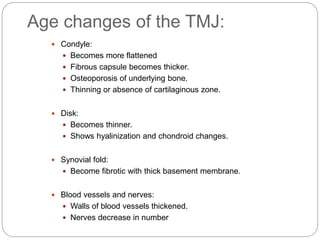
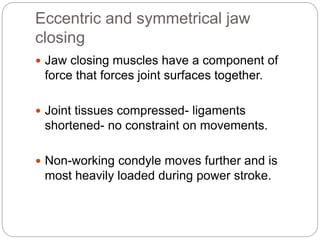
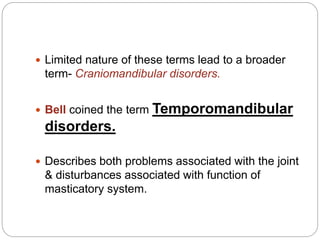
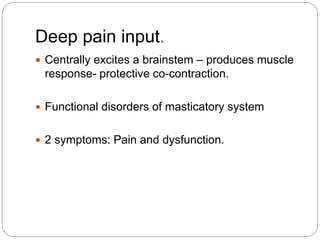
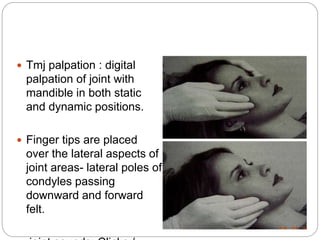
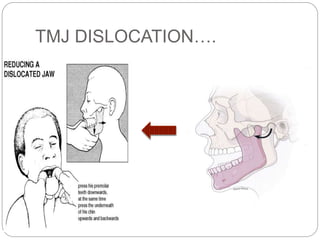
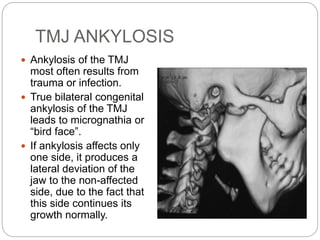
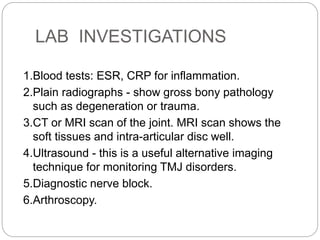
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a bilateral joint that allows for hinge-like and gliding motions of the mandible. It is formed between the head of the mandible and the articular fossa of the temporal bone. The TMJ is unique in that it contains an articular disc that divides the joint cavity into upper and lower compartments. Common functions of the TMJ include mastication and speech. Temporomandibular disorders (TMD) refer to a group of medical conditions involving the muscles of mastication and TMJ. Major etiological factors for TMD include occlusal condition, trauma, emotional stress, deep pain input, and parafunctional activities.