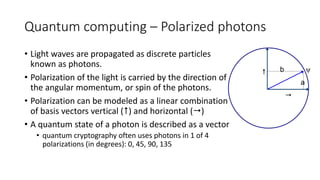
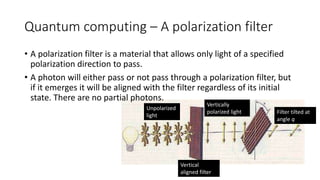
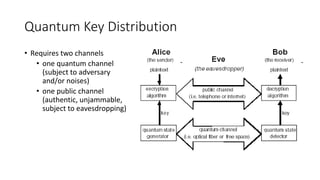
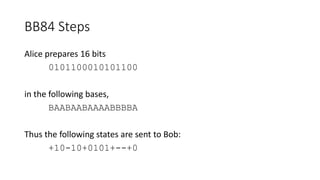
Quantum cryptography leverages quantum mechanical properties for cryptographic tasks, exemplified by quantum key distribution (QKD), which ensures secure key exchange despite eavesdropping. The process involves Alice sending photons of random polarizations to Bob, who measures them, while any eavesdropping can be detected through increased error rates. While quantum cryptography presents promising security benefits, its high cost and limitations, such as short transmission distances, prevent widespread adoption in the near future.