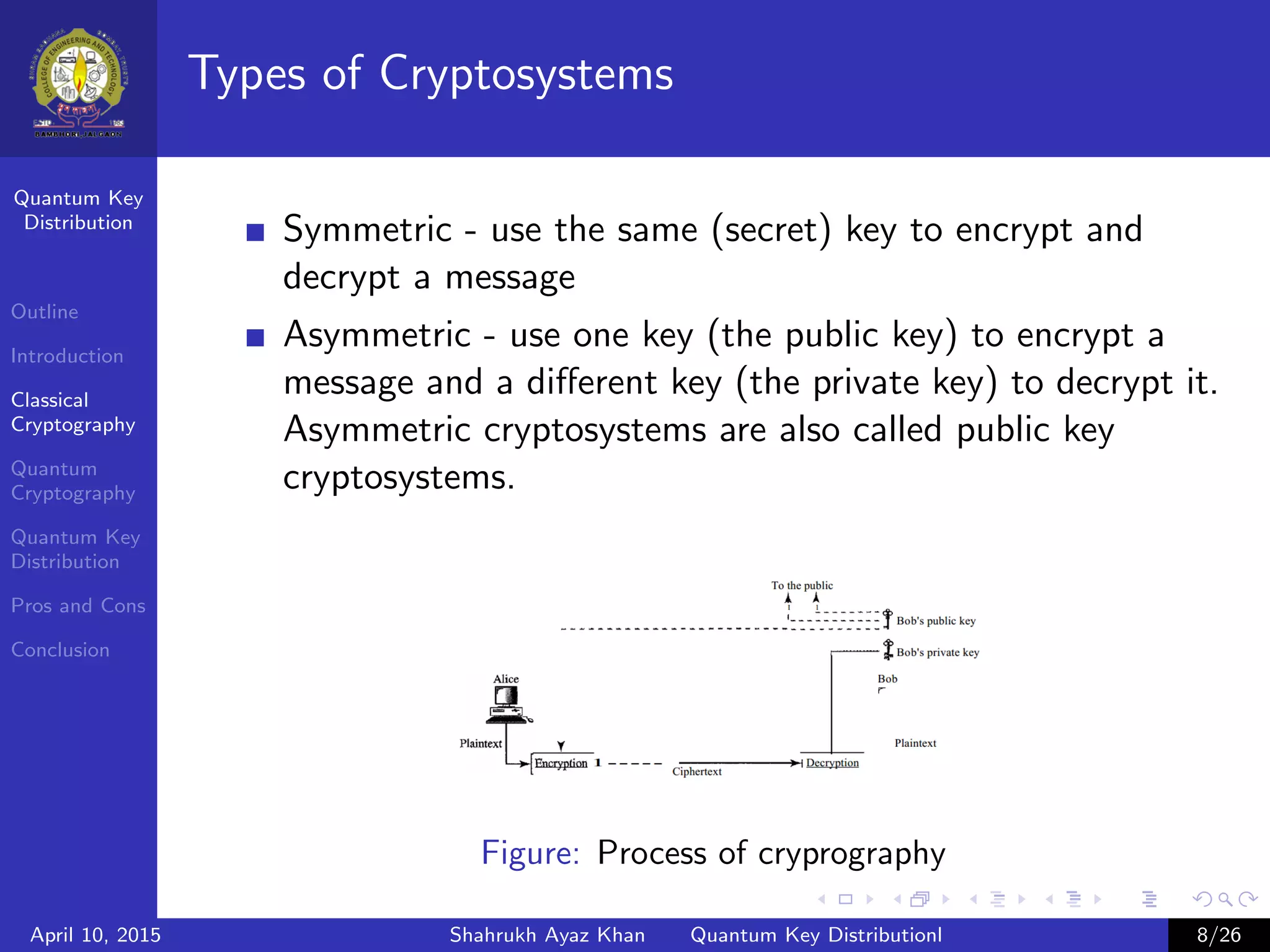
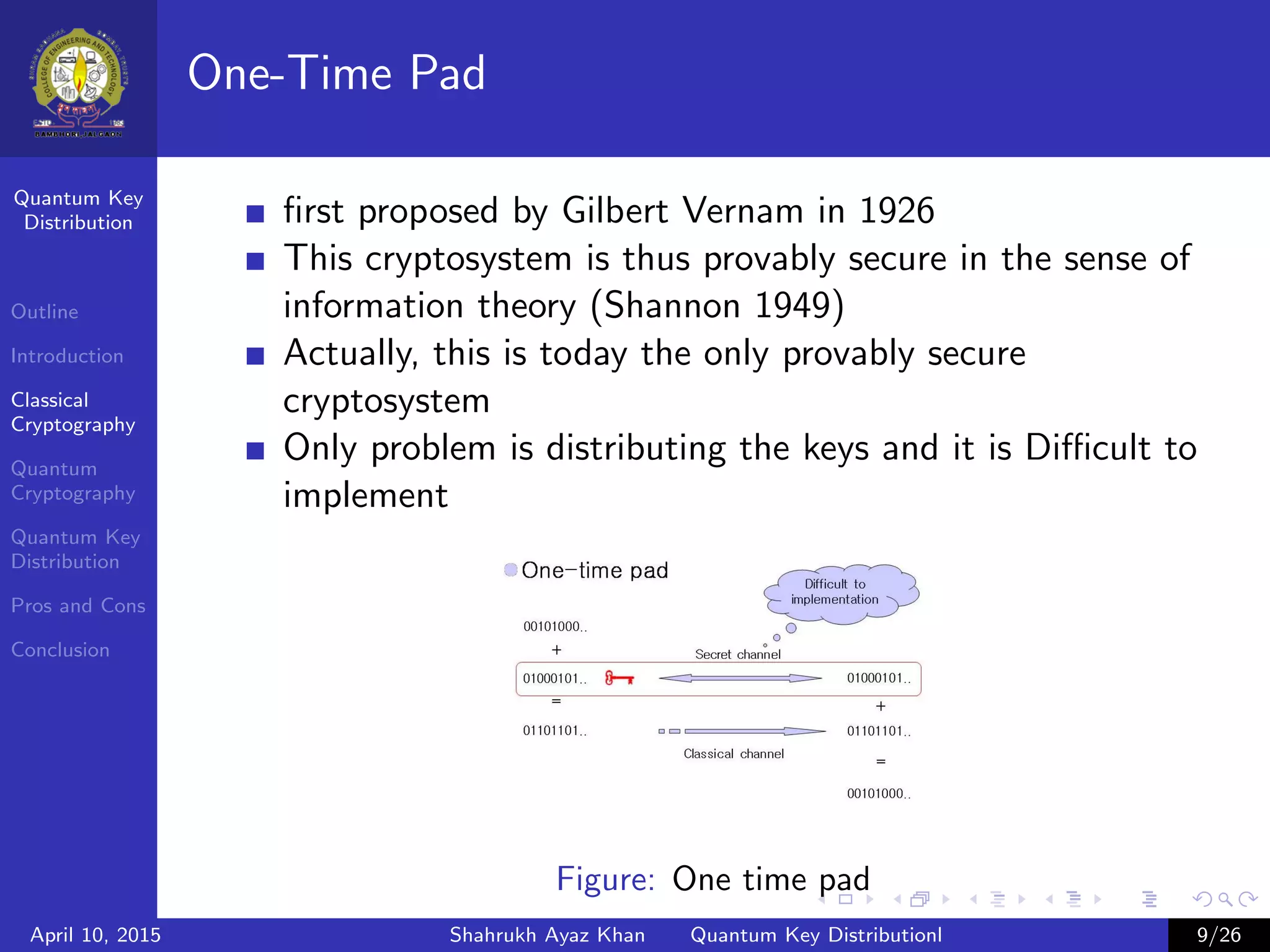
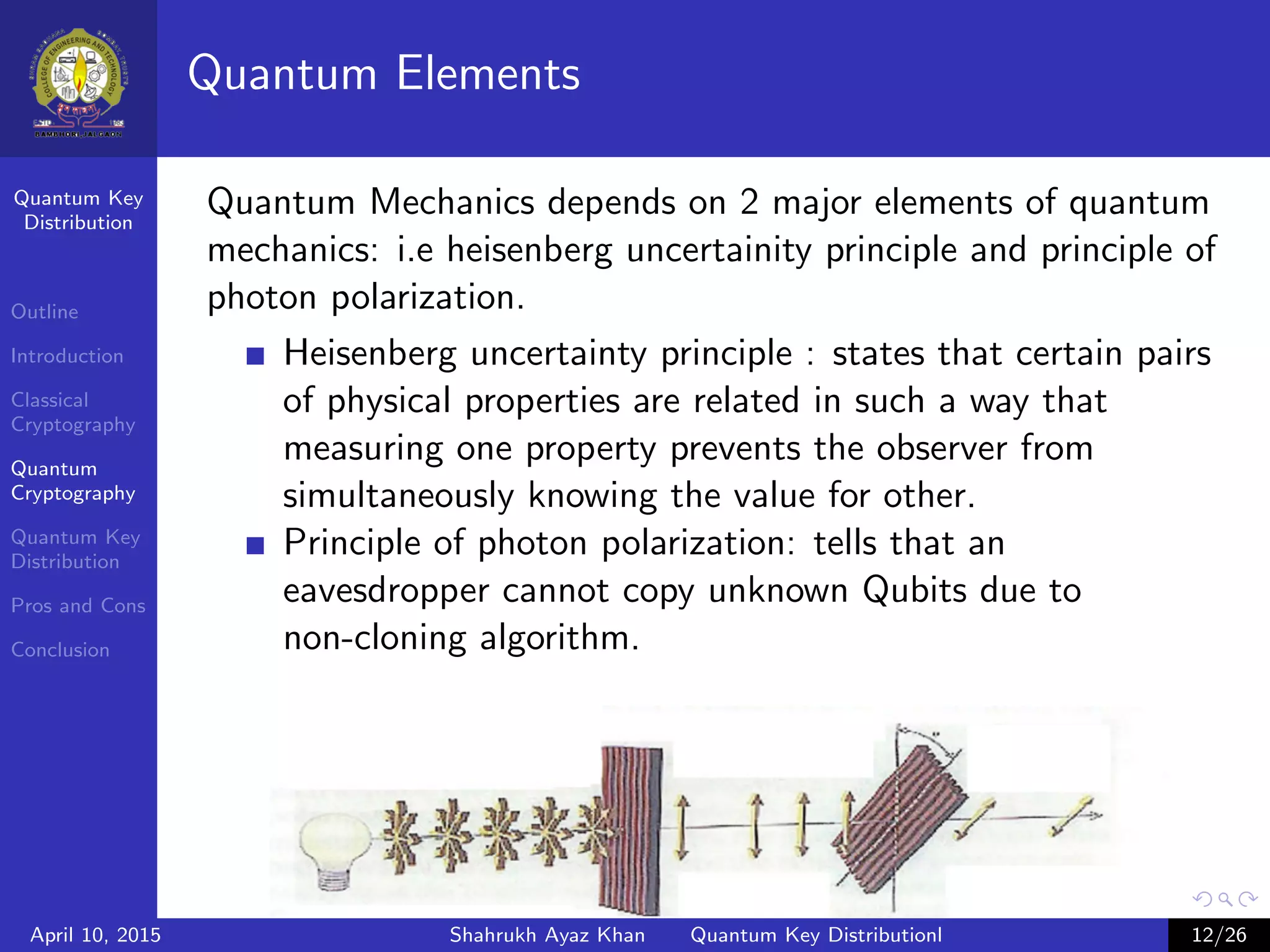
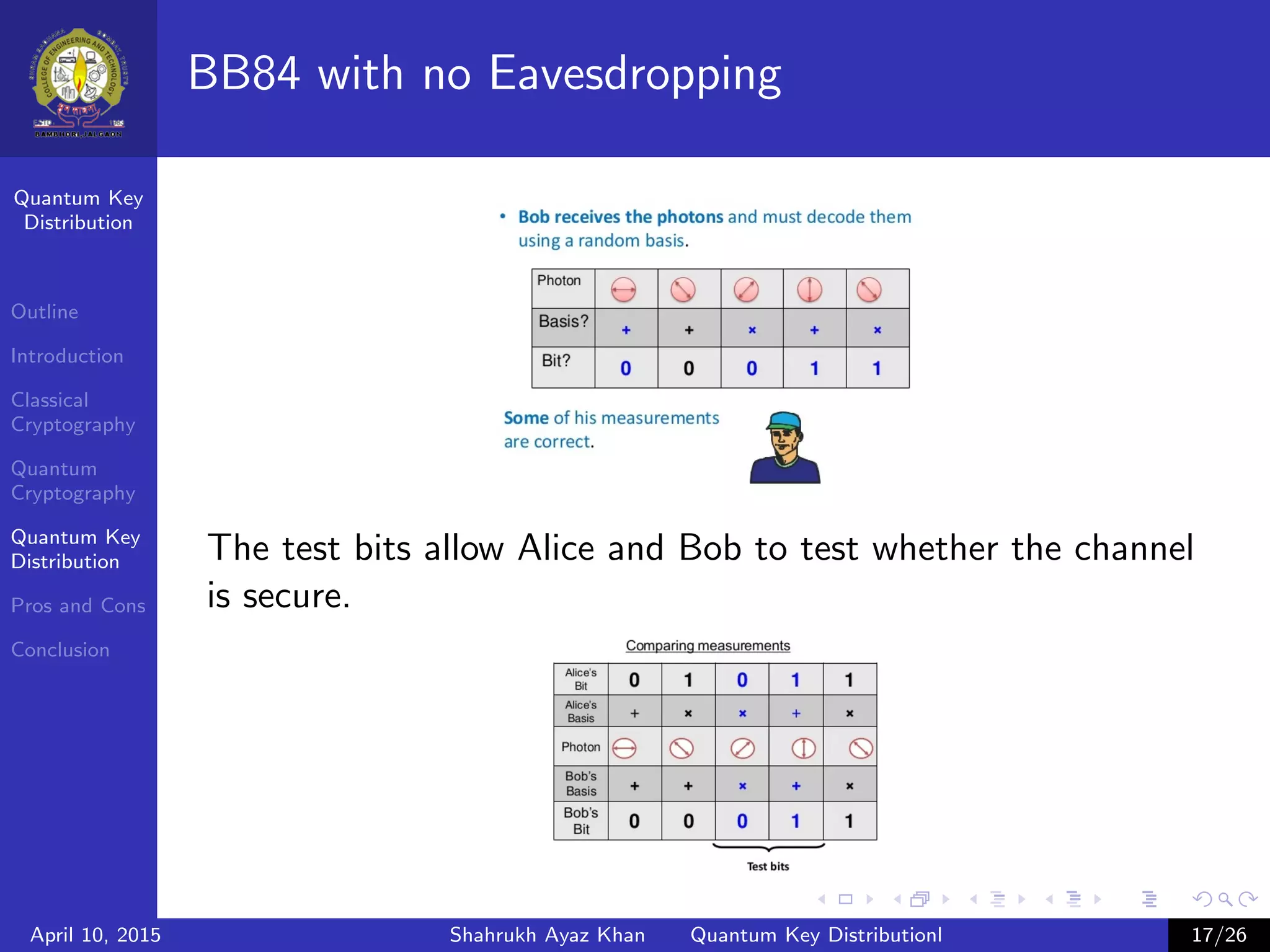
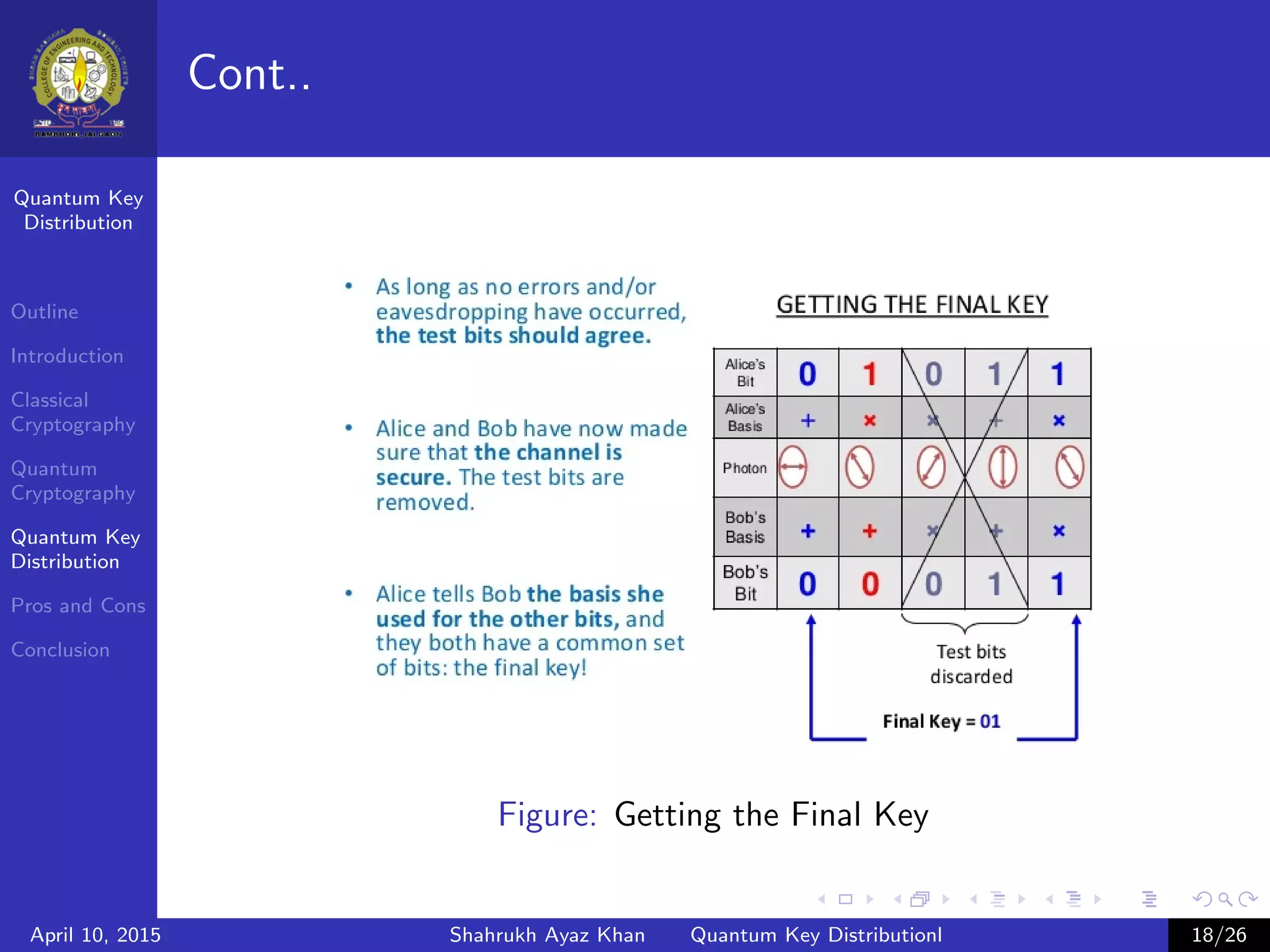
This document outlines a presentation on quantum key distribution. The presentation covers an introduction to cryptography, classical cryptography techniques like the one-time pad, quantum cryptography concepts like photon polarization, and quantum key distribution protocols like BB84. Quantum key distribution allows two parties to detect an eavesdropper attempting to gain knowledge of an encrypted key by exploiting quantum effects. The document provides context and details for each topic that will be covered in the presentation.