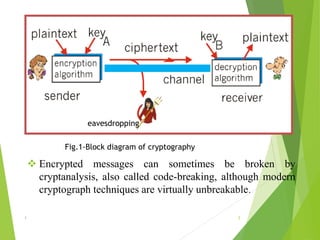
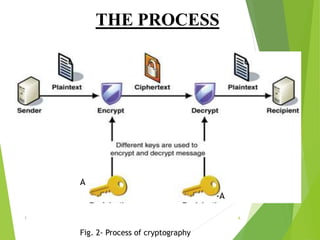
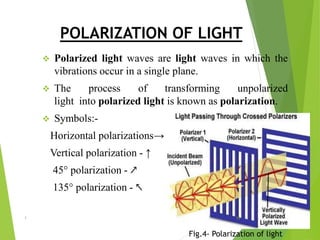
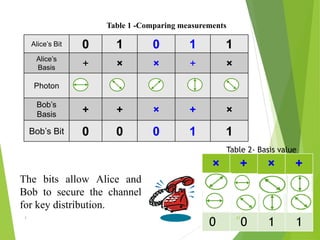
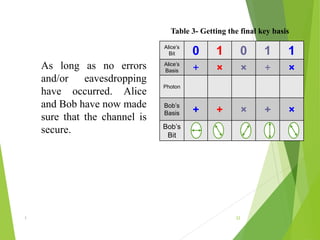
Naman Kumar presented on the topic of quantum cryptography. The presentation covered basic cryptography terms and techniques like encryption, decryption, and public key cryptography. It then discussed quantum key distribution and how it uses principles of quantum mechanics like photon polarization and Heisenberg's uncertainty principle to securely distribute encryption keys. The popular BB84 protocol was explained, which uses photon polarization to randomly generate and securely transmit encryption keys. Quantum cryptography provides unhackable secure communication up to 50km but has high setup costs. It could allow for perfectly secure transactions and communications in the future.