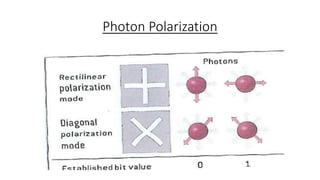
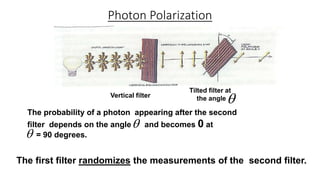
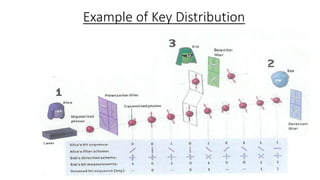
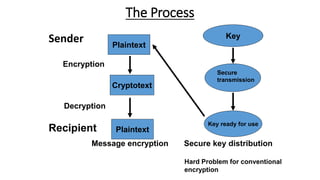
This document discusses quantum cryptography and its advantages over traditional cryptography. It begins by defining cryptography as restricting access to transmitted information even if intercepted. Then it explains the key distribution problem in traditional cryptography. Quantum cryptography solves this using photons and their quantum properties. The document outlines how photons can encode information and how their polarization allows secure key distribution between two parties via the BB84 protocol. It discusses current implementations of quantum cryptography over fiber and free space, as well as challenges like noise and distance. In conclusion, quantum cryptography promises virtually unhackable secure communication based on fundamental physics.




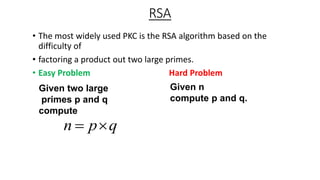
![Factoring A Product Of Two Large Primes
• The best known conventional algorithm requires the solution time
proportional to:
])ln(ln)(lnexp[)( 3/23/1
nncnT
For p & q 65 digits long T(n) is approximately
one month using cluster of workstations.
For p&q 200 digits long T(n) is astronomical.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quantumcryptography-200404164736/85/Quantum-cryptography-7-320.jpg)
![Quantum Computing Algorithm For Factoring.
• In 1994 Peter Shor from the AT&T Bell Laboratory showed that in
principle a quantum computer could factor a very long product
of primes in seconds.
• Shor’s algorithm time computational complexity is
])[(ln)( 3
nOnT
Once a quantum computer is built the RSA
method would not be safe.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quantumcryptography-200404164736/85/Quantum-cryptography-8-320.jpg)