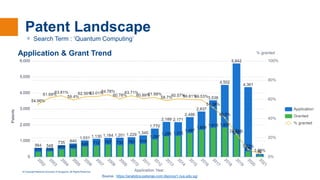
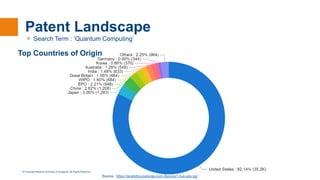
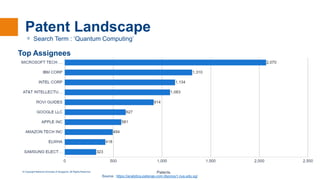
The document discusses quantum computing, explaining its basics such as superposition and entanglement, and how these principles distinguish quantum computers from classical ones. It covers the capabilities of quantum computing in various fields, including optimization, cryptography, and simulation, as well as current technological advancements and challenges in the field. Lastly, it outlines future prospects, including advancements in quantum algorithms and potential to break existing encryption methods.