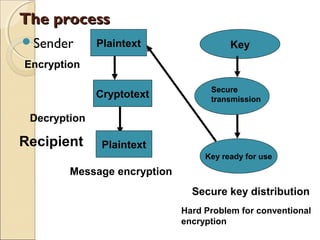
This document provides an introduction to quantum cryptography. It discusses how quantum cryptography solves the key distribution problem faced by conventional cryptography through the use of polarized photons and quantum properties like the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. The document summarizes the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol developed by Bennett and Brassard, in which Alice and Bob use randomly polarized photons to generate an encryption key. It also discusses some challenges for practical quantum cryptography implementations, like developing single photon sources and detectors and transmitting photons over long distances.





![Factoring a product of two large primesFactoring a product of two large primes
The best known conventional algorithm
requires the solution time proportional to:
])ln(ln)(lnexp[)( 3/23/1
nncnT =
For p & q 65 digits long T(n) is
approximately
one month using cluster of workstations.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptquant-150316041718-conversion-gate01/85/quantum-cryptography-7-320.jpg)
![Quantum Computing algorithm forQuantum Computing algorithm for
factoring.factoring.
In 1994 Peter Shor from the AT&T Bell
Laboratory showed that in principle a
quantum computer could factor a very long
product of primes in seconds.
Shor’s algorithm time computational
complexity is
])[(ln)( 3
nOnT =
Once a quantum computer is built
the RSA method
would not be safe.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cryptquant-150316041718-conversion-gate01/85/quantum-cryptography-8-320.jpg)



















