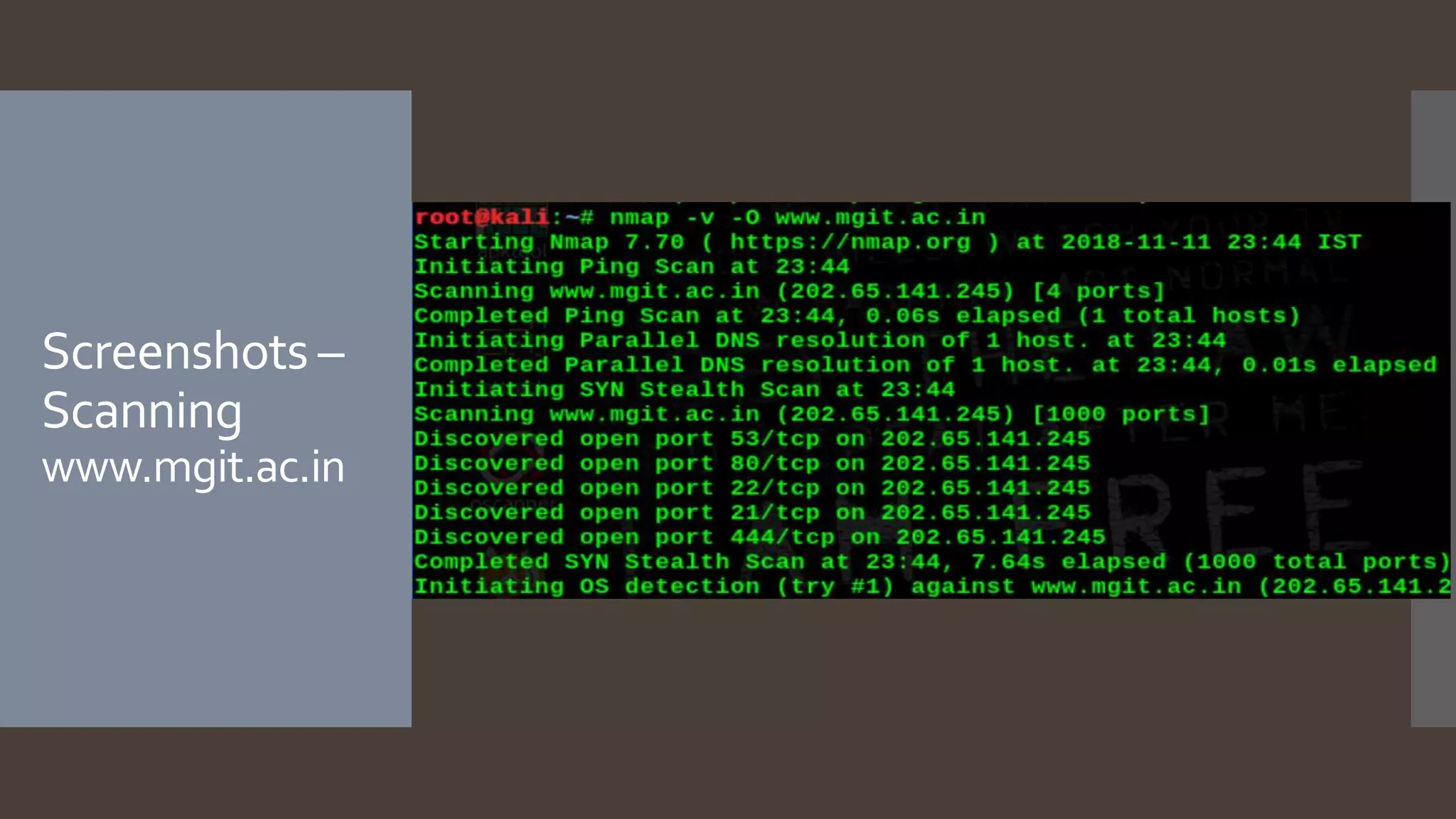
Nmap, developed by Gordon Lyon, is a free and open-source utility for network discovery and security auditing, useful for tasks like network inventory and monitoring service uptime. It features a range of capabilities including host and service detection, operating system identification, and the ability to evade packet filters. With various tools included in the Nmap suite, users can customize scans for accuracy and speed, making Nmap a preferred tool for network scanning.