This document provides an overview of quantum cryptography, including:
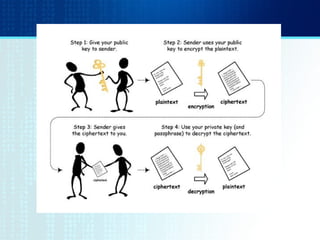
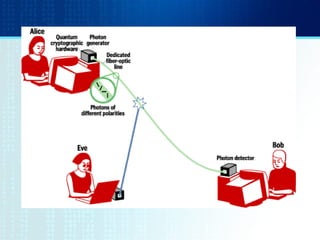
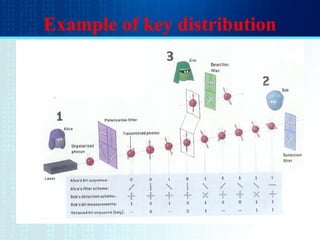
- The BB84 protocol allows Alice and Bob to generate a shared secret key by Alice sending encoded photons and Bob measuring them to discard mismatched results.
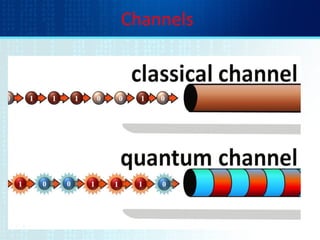
- Quantum cryptography derives security from photons being altered when read, preventing interception without detection.
- Milestones include the first bank transfer using quantum cryptography in 2004 and distribution over 148.7 km in 2007.
- Quantum cryptography has applications in secure broadcast, network, banking and email communications.