The document outlines the basics of quantum cryptography including:
- The need for quantum cryptography due to limitations of classical cryptography in the face of quantum computers.
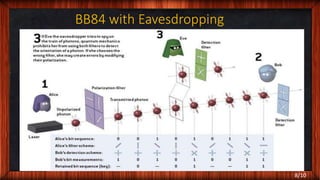
- The BB84 quantum key distribution protocol which uses photon polarization to randomly generate and distribute encryption keys between two parties in a way that can detect eavesdropping.
- How the BB84 protocol works including key generation and verification steps to detect if the transmitted quantum states were accessed or copied without authorization during transmission.
- Examples of real-world deployments of quantum cryptography networks to securely distribute keys for applications such as voting machines.