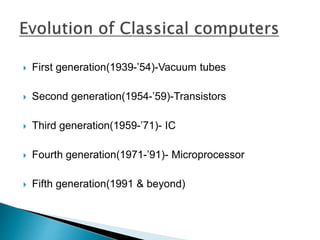
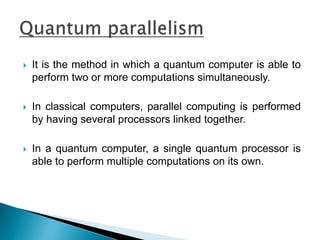
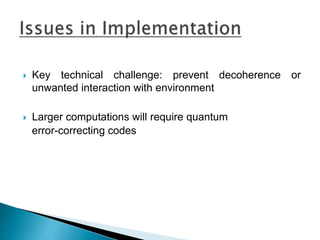
The document discusses the history and progression of computer generations from vacuum tubes to microprocessors. It then covers the concepts of quantum computing, including quantum bits that can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously, quantum entanglement, and how quantum computers could solve problems like integer factorization exponentially faster than classical computers. Some applications proposed include networking, simulation, and cryptography, but challenges remain in scaling up quantum systems and preventing decoherence.