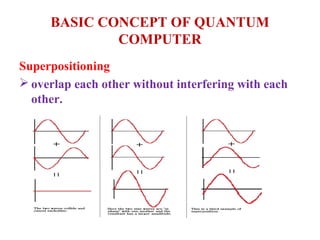
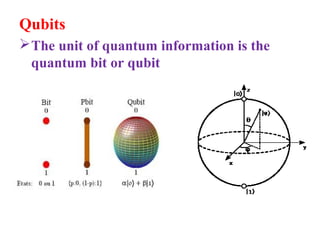
This document provides an overview of quantum computing, including its history, basic concepts, applications, advantages, difficulties, and future directions. It discusses how quantum computing originated in the 1980s with the goal of building a computer that is millions of times faster than classical computers and theoretically uses no energy. The basic concepts covered include quantum mechanics, superpositioning, qubits, quantum gates, and how quantum computers could perform calculations that are intractable on classical computers, such as factoring large numbers. The document also outlines some of the challenges facing quantum computing as well as potential future advances in the field.