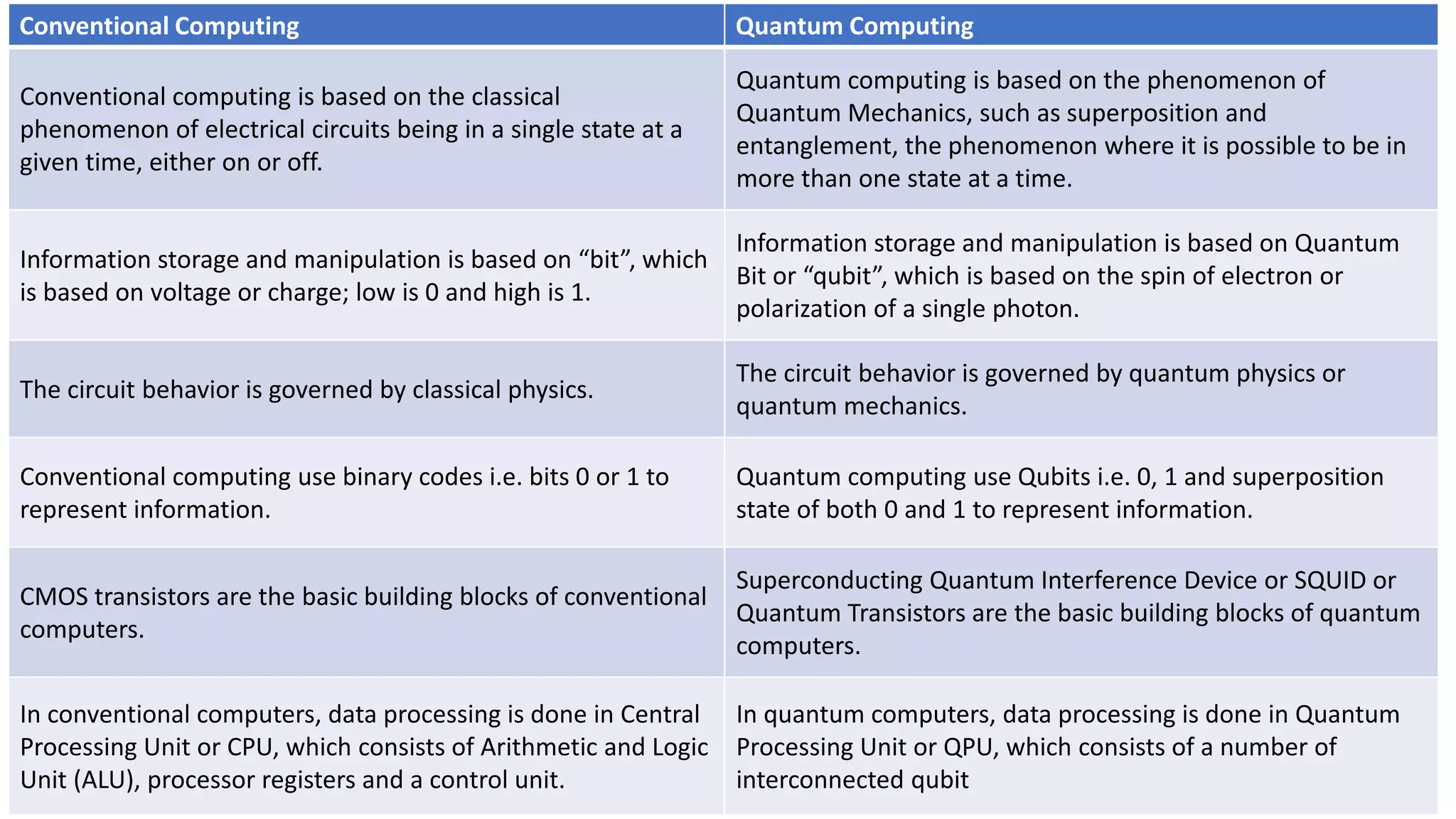
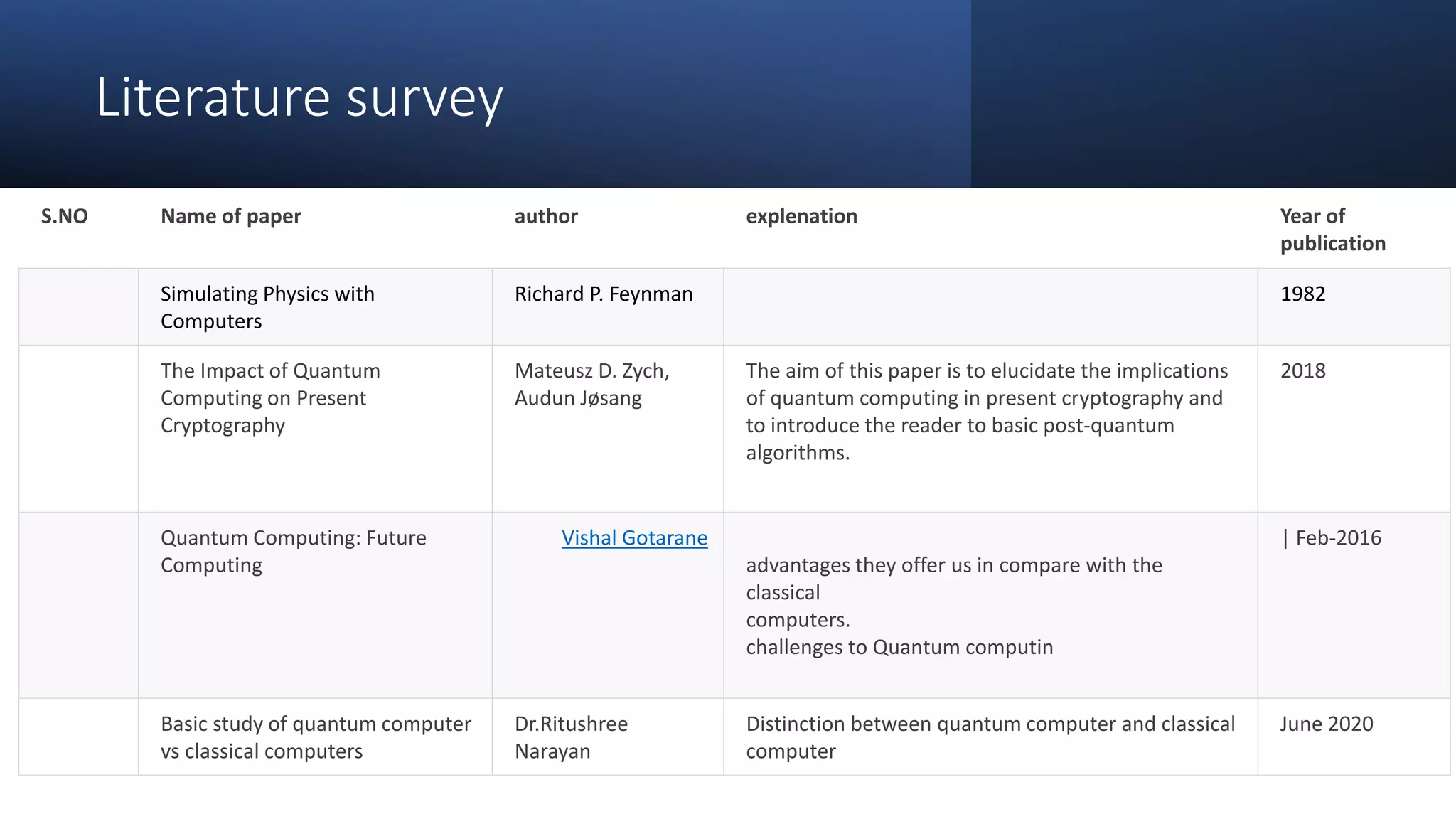
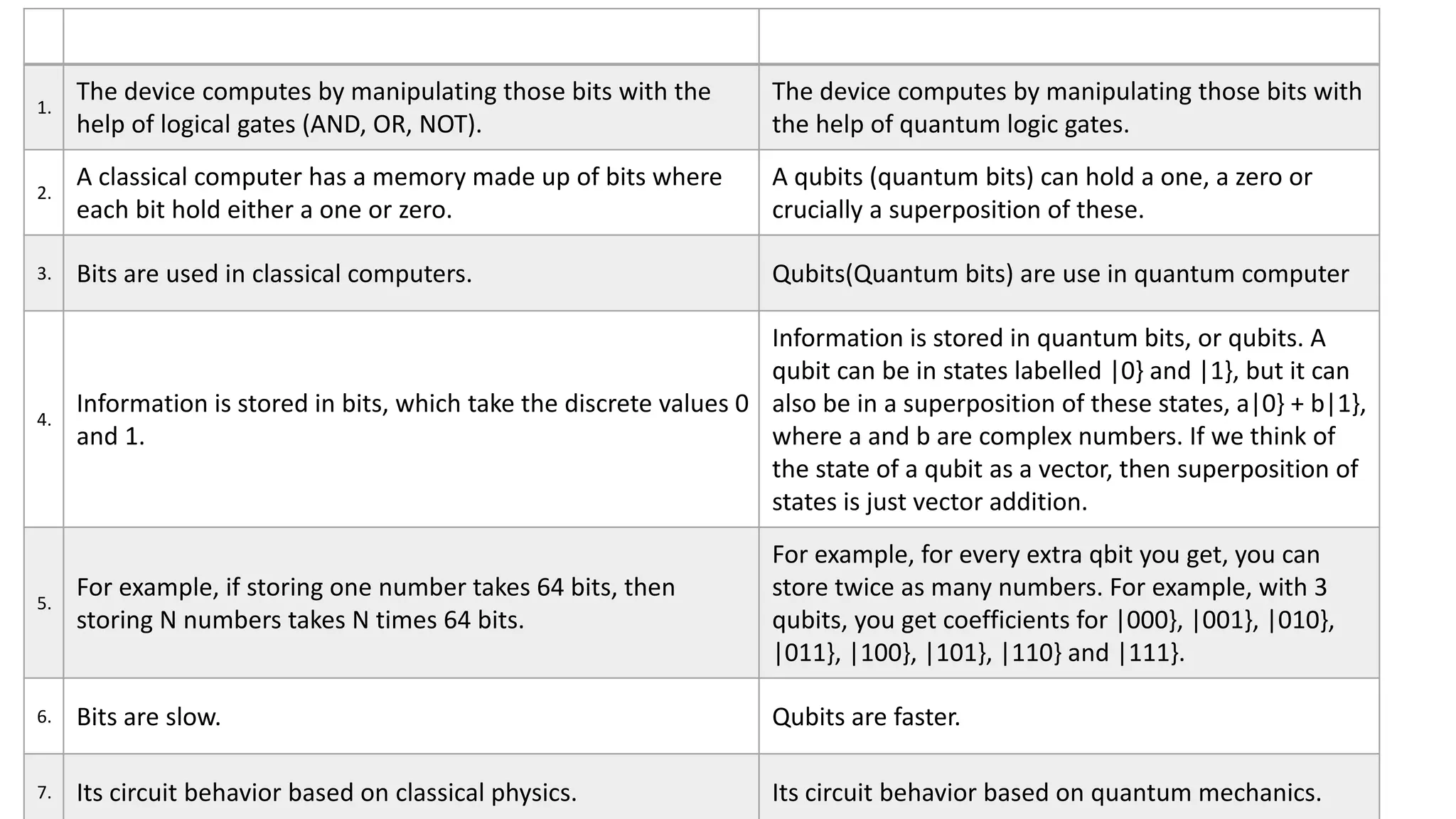
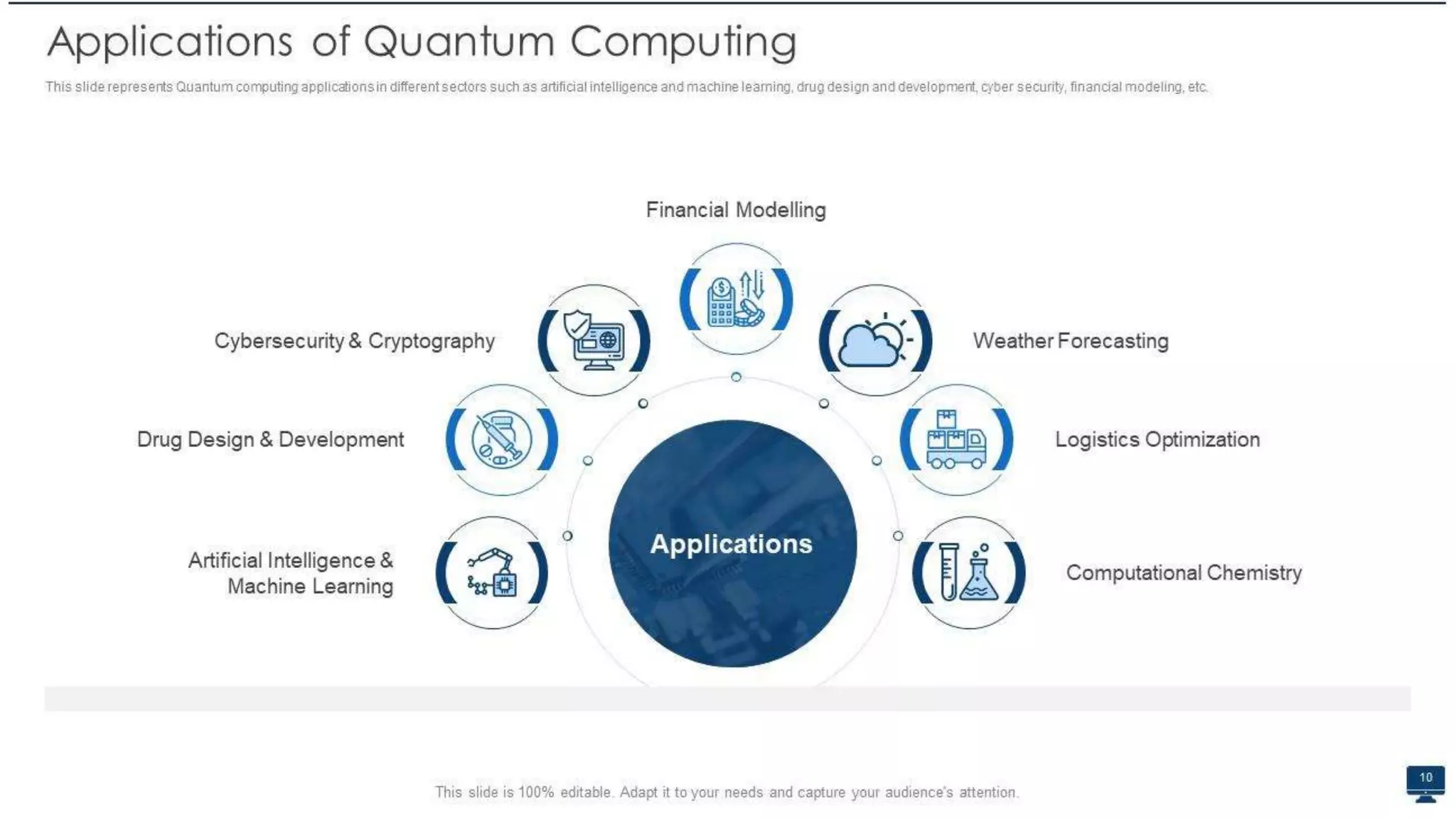
Quantum computing is a rapidly emerging technology that uses principles of quantum mechanics like superposition and entanglement to perform operations on quantum bits (qubits) and solve complex problems. It has the potential to vastly outperform classical computers for certain problems. The document discusses key aspects of quantum computing including how it differs from classical computing, what qubits are, how quantum computers work using elements like superconductors and Josephson junctions, and potential applications in areas like artificial intelligence, drug development, weather forecasting, and cybersecurity. It also covers advantages like speed and ability to solve complex problems, as well as current disadvantages like difficulty to build and susceptibility to errors.