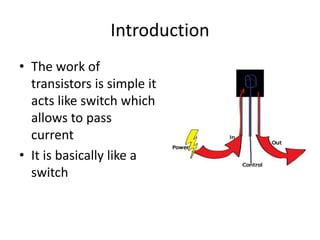
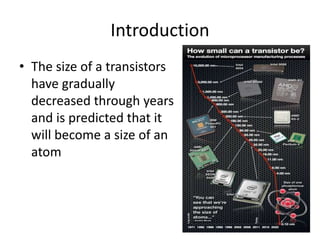
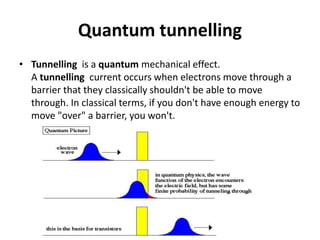
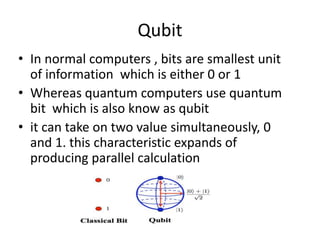
A quantum computer uses quantum mechanics phenomena like superposition and entanglement to perform calculations exponentially faster than classical computers. It uses quantum bits (qubits) that can be in superposition of states 0 and 1, allowing massive parallelism. However, quantum computers are very difficult to build due to challenges like decoherence where external noise disrupts the fragile quantum states. If developed further, quantum computers could break current encryption methods and vastly accelerate tasks like database searching and optimization problems.