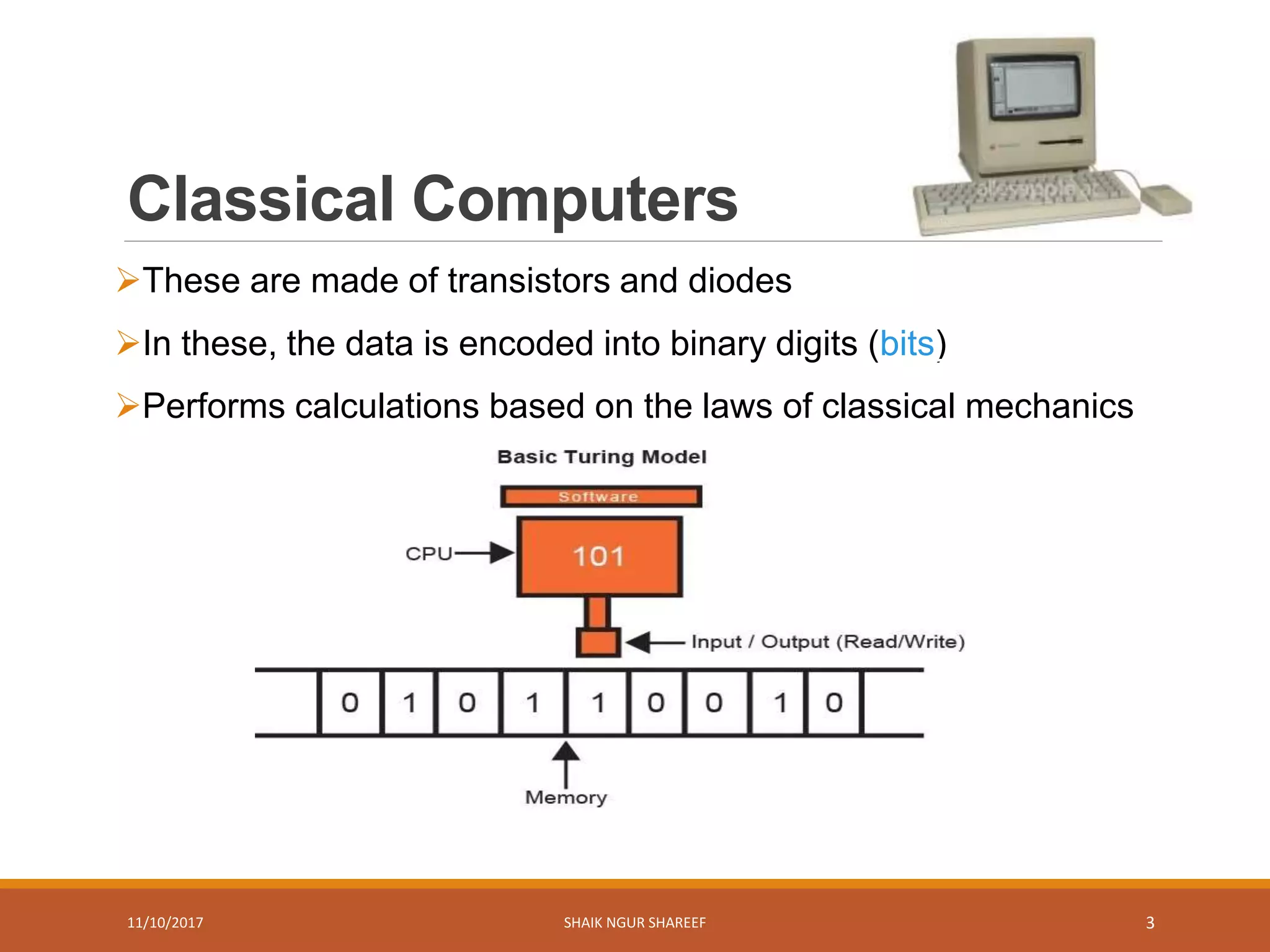
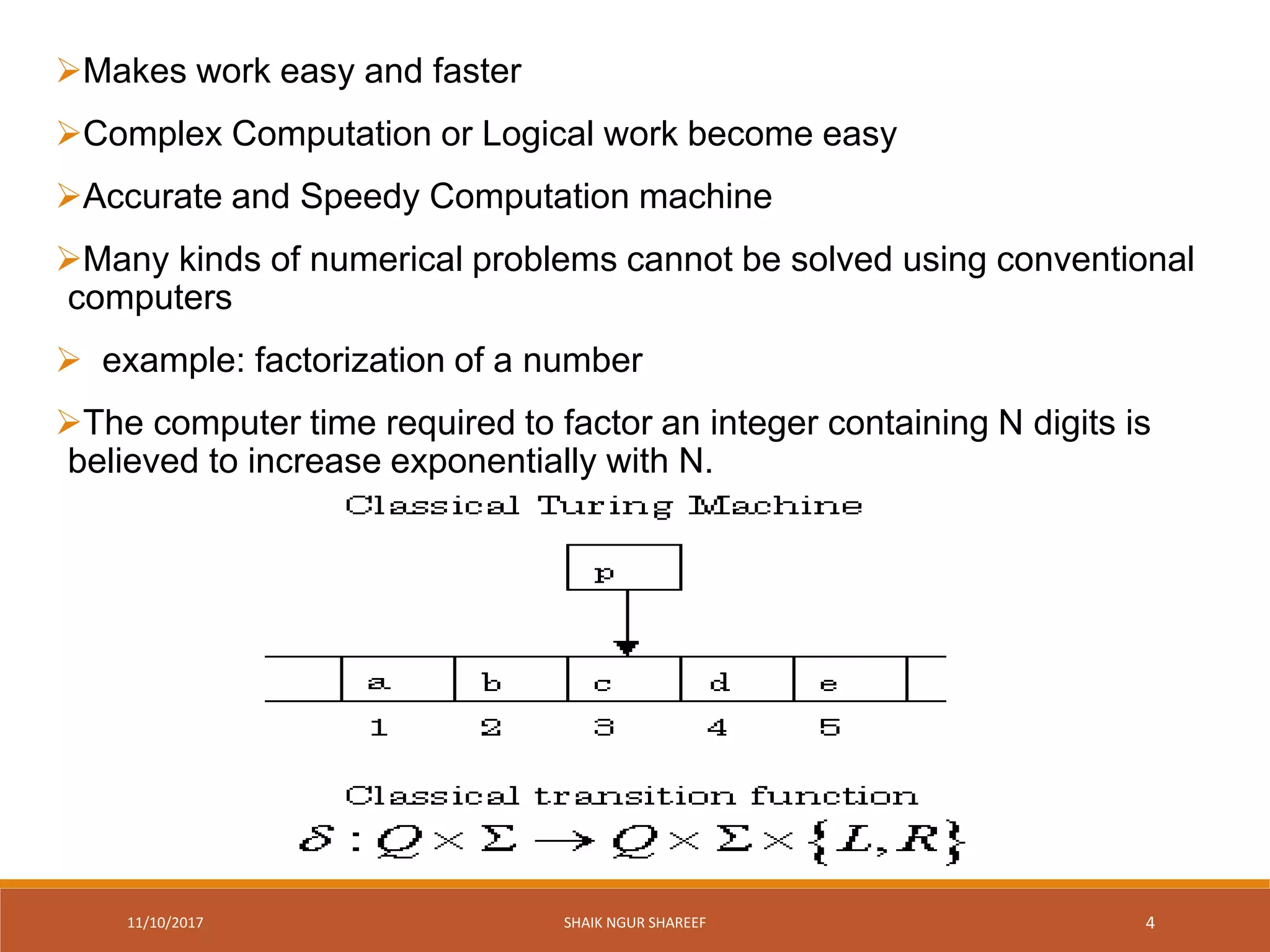
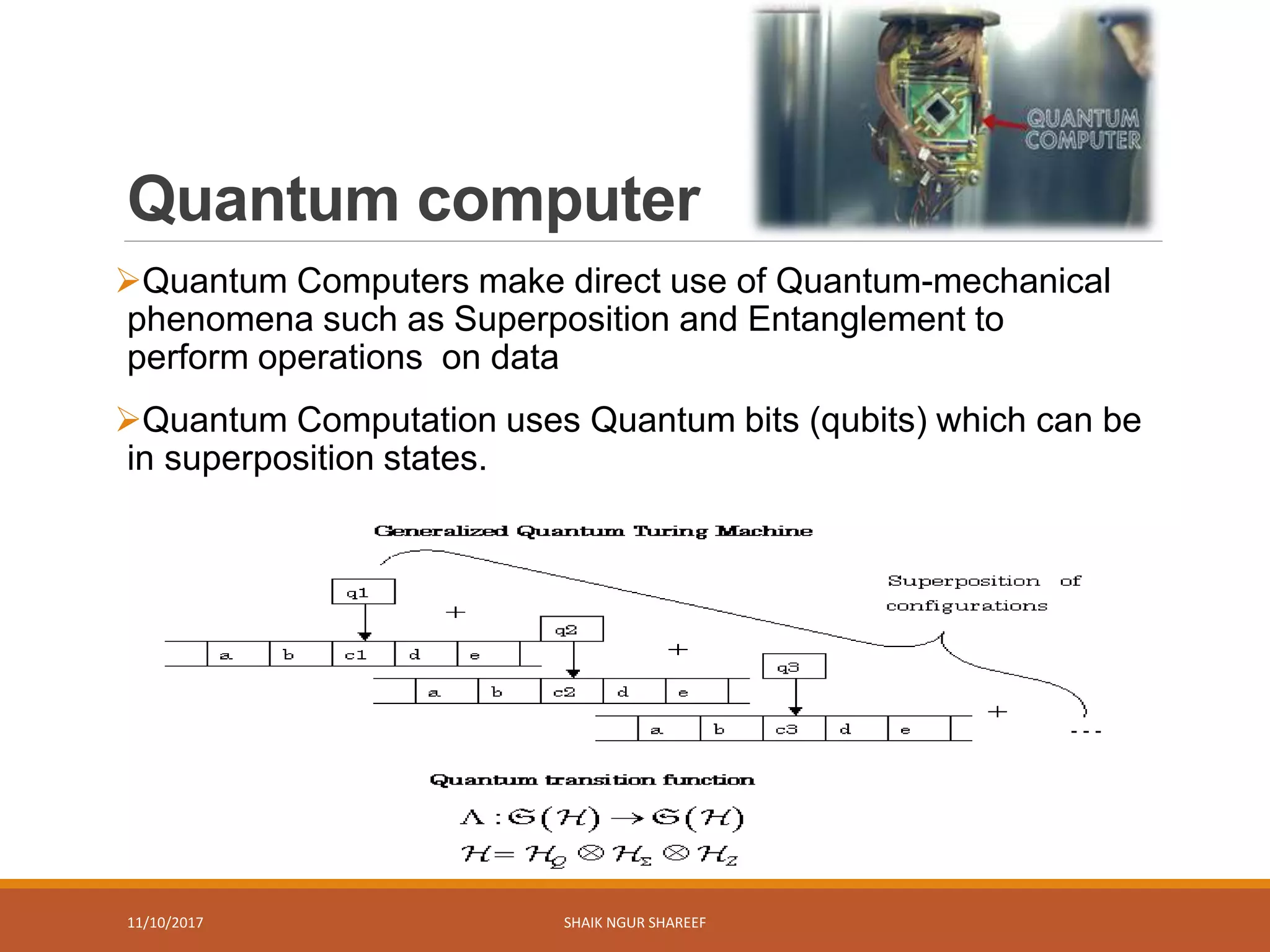
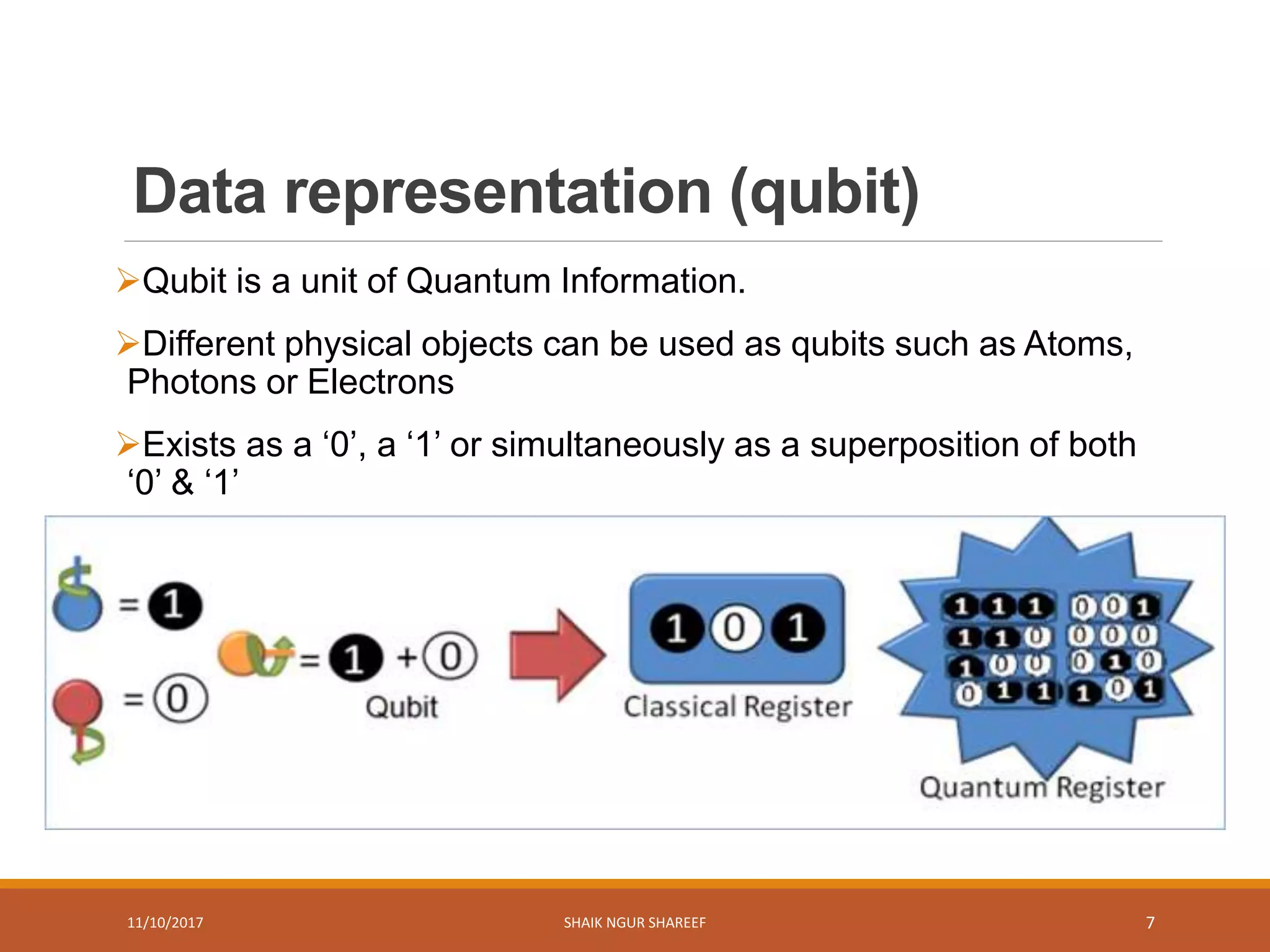
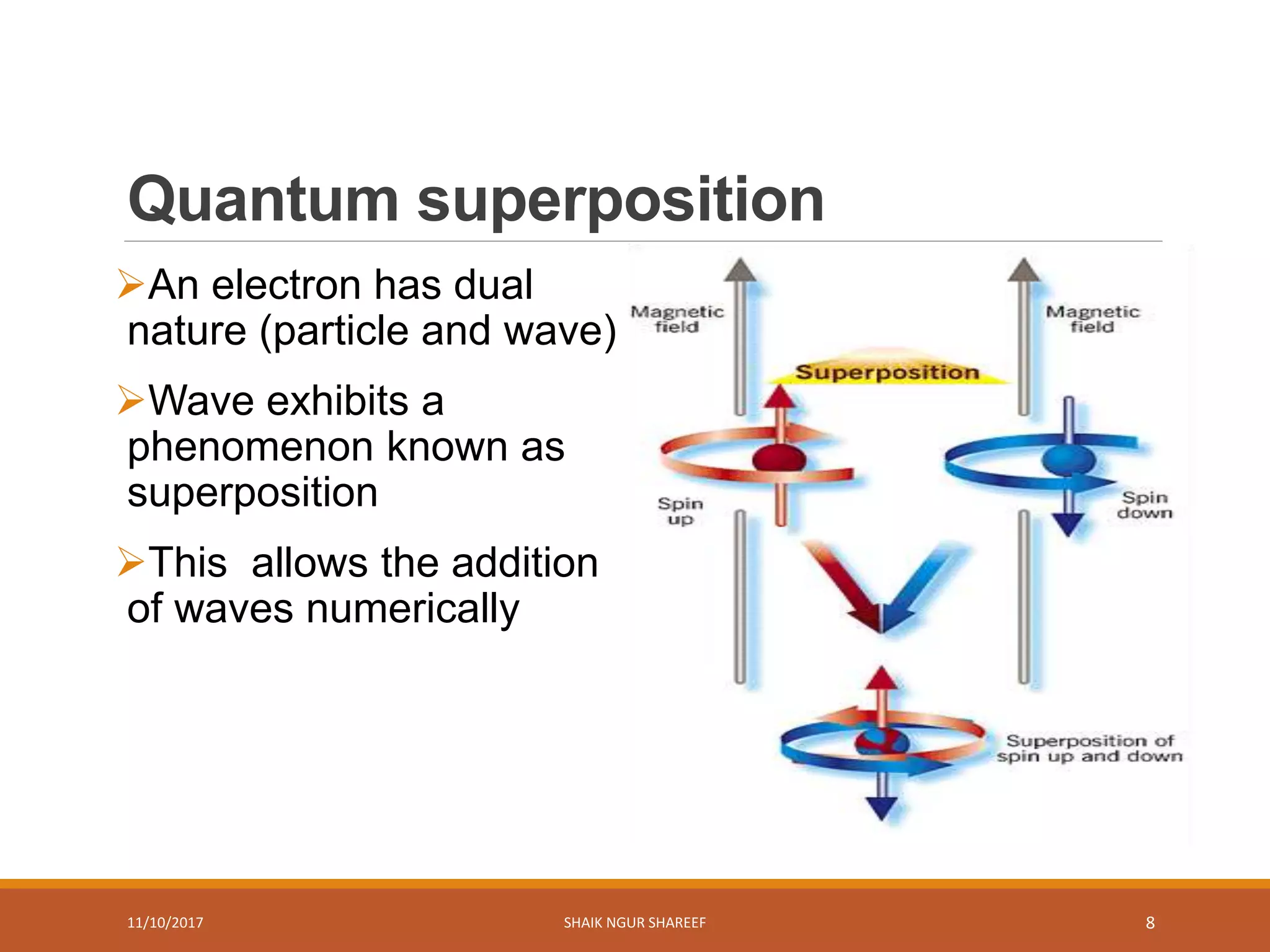
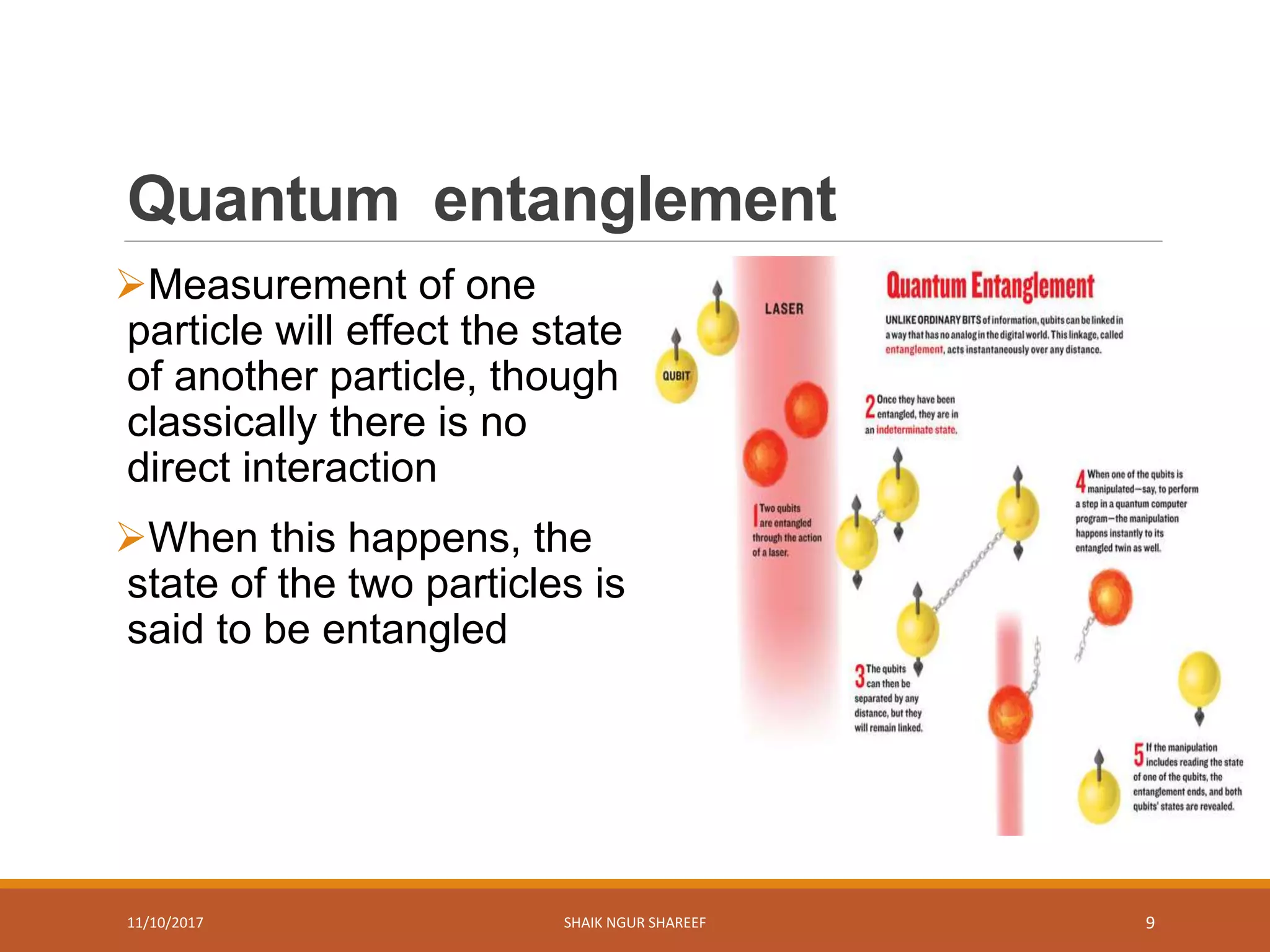
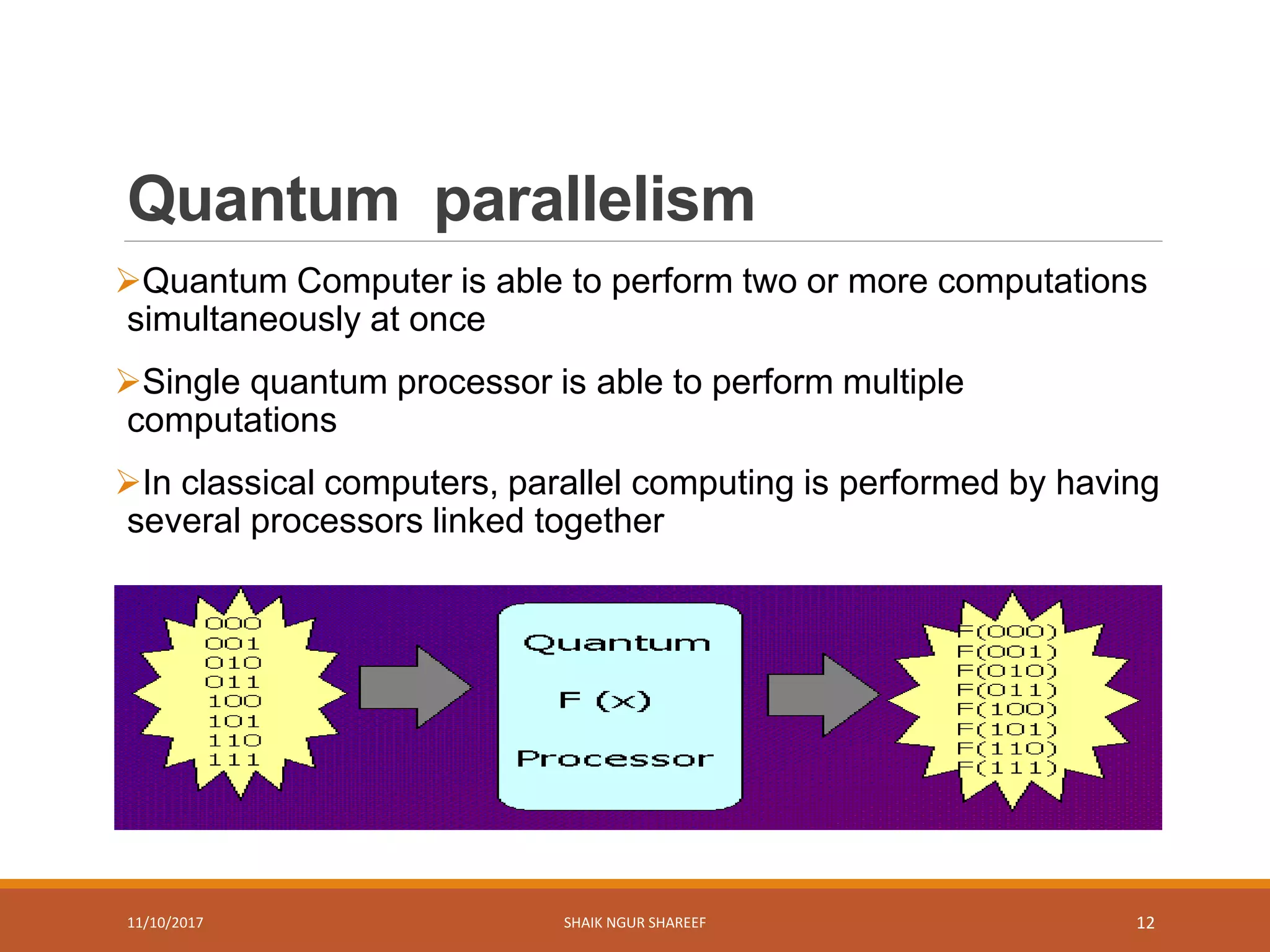
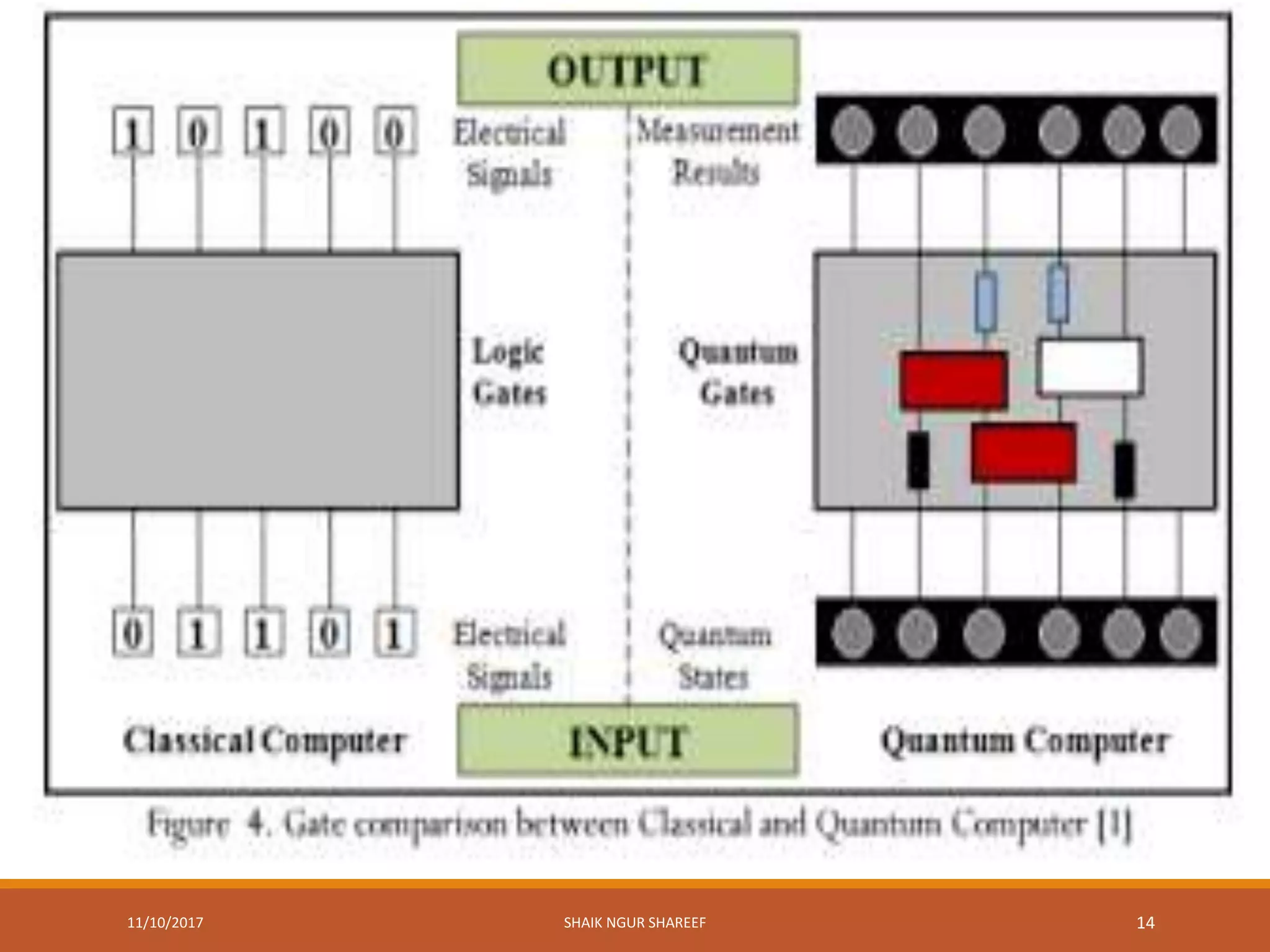
This document discusses quantum computers and their advantages over classical computers. It begins by describing classical computers and how they operate based on classical mechanics. It then defines quantum computers, explaining that they use quantum bits that can exist in superposition and entanglement, allowing them to perform multiple computations simultaneously. The document outlines the history of quantum computing development. It also discusses quantum computing concepts like superposition and entanglement. Finally, it reviews some applications of quantum computing like simulation, encryption, and factorization algorithms.