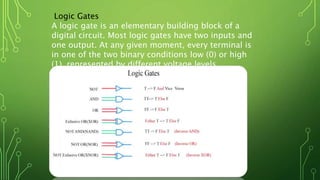
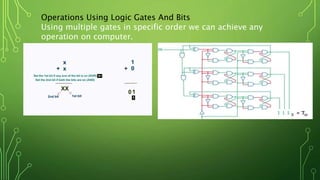
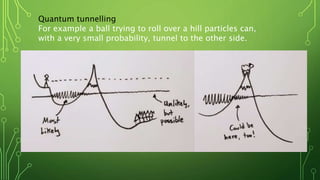
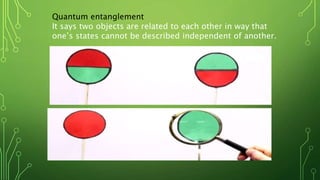
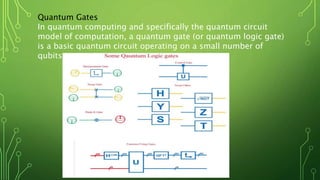
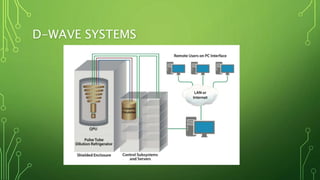
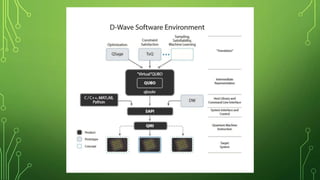
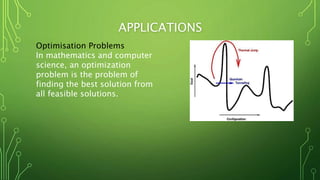
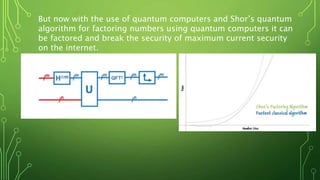
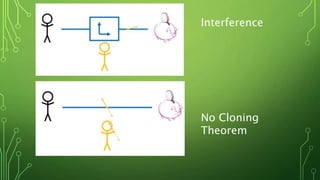
Quantum computing is a field focused on developing technology based on quantum mechanics principles, using qubits that can represent multiple states simultaneously. This technology has applications in areas such as quantum cryptography and optimizations in complex computational tasks. It has the potential to revolutionize computing capabilities and security, enabling solutions to previously unsolvable problems.