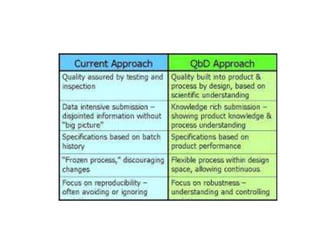
The document discusses Quality by Design (QbD), which is a systematic approach to pharmaceutical development that begins with predefined objectives and emphasizes product and process understanding and control based on sound science and quality risk management. It defines key QbD elements like Quality Target Product Profile, Critical Quality Attributes, Design Space, and Control Strategy. QbD aims to ensure final drug quality and has benefits like increased understanding, efficiency, and patient safety.







![Regulatory Control Guidelines Emphasising QbD: The
QbD approach which is based on scientific and
methodical product development was included in the
quality guidelines of ICH from 2005 onwards.
This approach includes, ICH
Q8: Pharmaceutical Development,
Q9: Quality Risk Management, and
Q10: Pharmaceutical Quality System guidelines.
The pharmaceutical products quality was also emphasised
in Process Analytical Technology [PAT] guidelines for new
pharmaceutical product development and quality.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qualitybydesignqbd-190202063119/85/Quality-by-design-QbD-8-320.jpg)


![ICH Q8: Pharmaceutical
Development:
It discusses the various element of Quality by
Design.
• Define the Quality Target Product Profile
• Identify the Quality Attributes
• Perform a Risk [Assessment] Analysis
• Determine the Critical Quality Attributes and
Critical Process Parameter
• Determine the Design Space
• Identify a Control Strategy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qualitybydesignqbd-190202063119/85/Quality-by-design-QbD-11-320.jpg)
![1. Quality Target Product Profile [QTPP]:
QTPP is “Prospective summary of the quality
characteristics of a drug product that ideally will be
achieved to ensure the desired quality, taking into
account safety and efficacy of the drug product”.
It is the quality characteristics that the drug product
should possess in order to reproducibly deliver the
therapeutic benefit promised in the label.
2. Quality Attributes: Once QTPP has identified, the next
step is to identify the relevant CQAs. A critical quality
attribute as defined by ICH is a physical, chemical,
biological, or microbiological characteristic that should be
within an appropriate limit, range, or distribution to
ensure the desired product quality.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qualitybydesignqbd-190202063119/85/Quality-by-design-QbD-12-320.jpg)
![For Drug Substance [Chemical] For Drug Product [Tablet]
Appearance
Particle size
Morphic forms
Water content
Residual solvents
Organic impurities
Inorganic impurities
Heavy metals
Residue on ignition
Assay
Appearance
Identification
Hardness
Uniformity of dosage
Physical form
Dissolution
Degradation products
Water content
Assay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qualitybydesignqbd-190202063119/85/Quality-by-design-QbD-13-320.jpg)
![ICH Q9: Quality Risk Management
[QRM]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qualitybydesignqbd-190202063119/85/Quality-by-design-QbD-14-320.jpg)