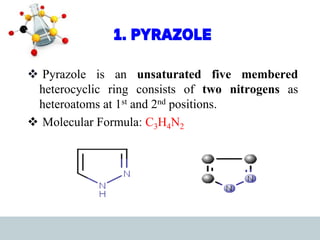
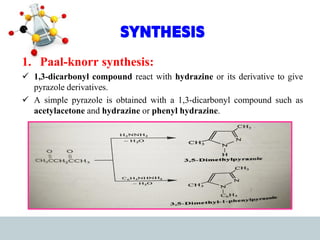
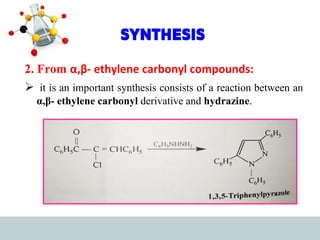
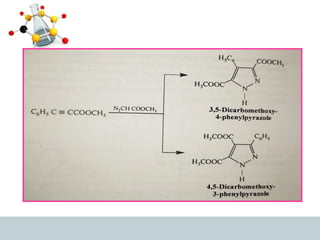
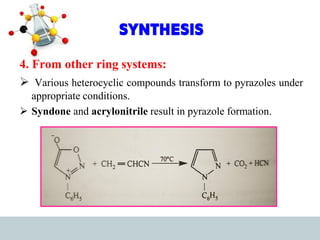
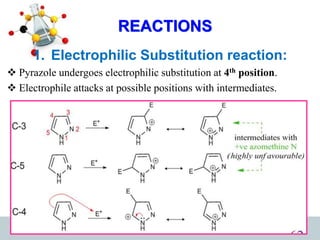
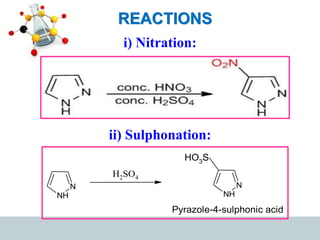
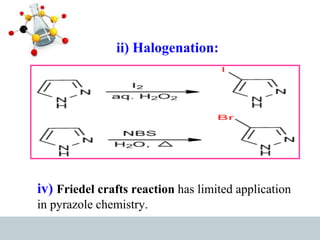
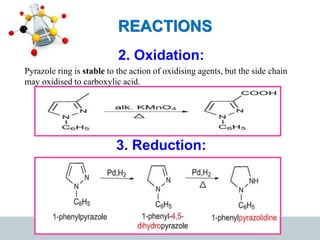
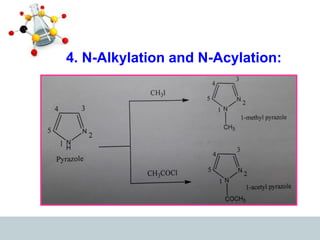
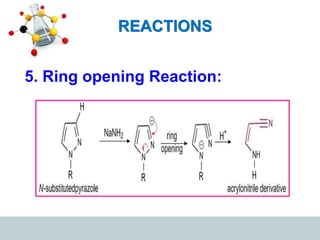
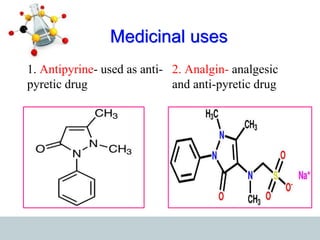
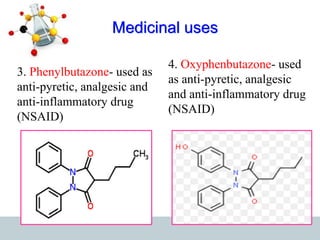
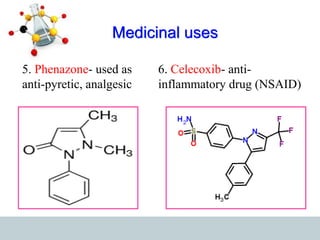
This document discusses heterocyclic compounds, specifically pyrazoles. It describes pyrazoles as a 5-membered heterocyclic ring containing two nitrogen atoms at the 1st and 2nd positions. Several common synthesis routes for pyrazoles are outlined, including the Paal-Knorr synthesis using 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds and hydrazines. The document also reviews reactions that pyrazoles undergo, such as electrophilic substitution, oxidation, and reduction. Finally, some medicinal uses of pyrazoles are provided, including their use as anti-pyretic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory drugs.