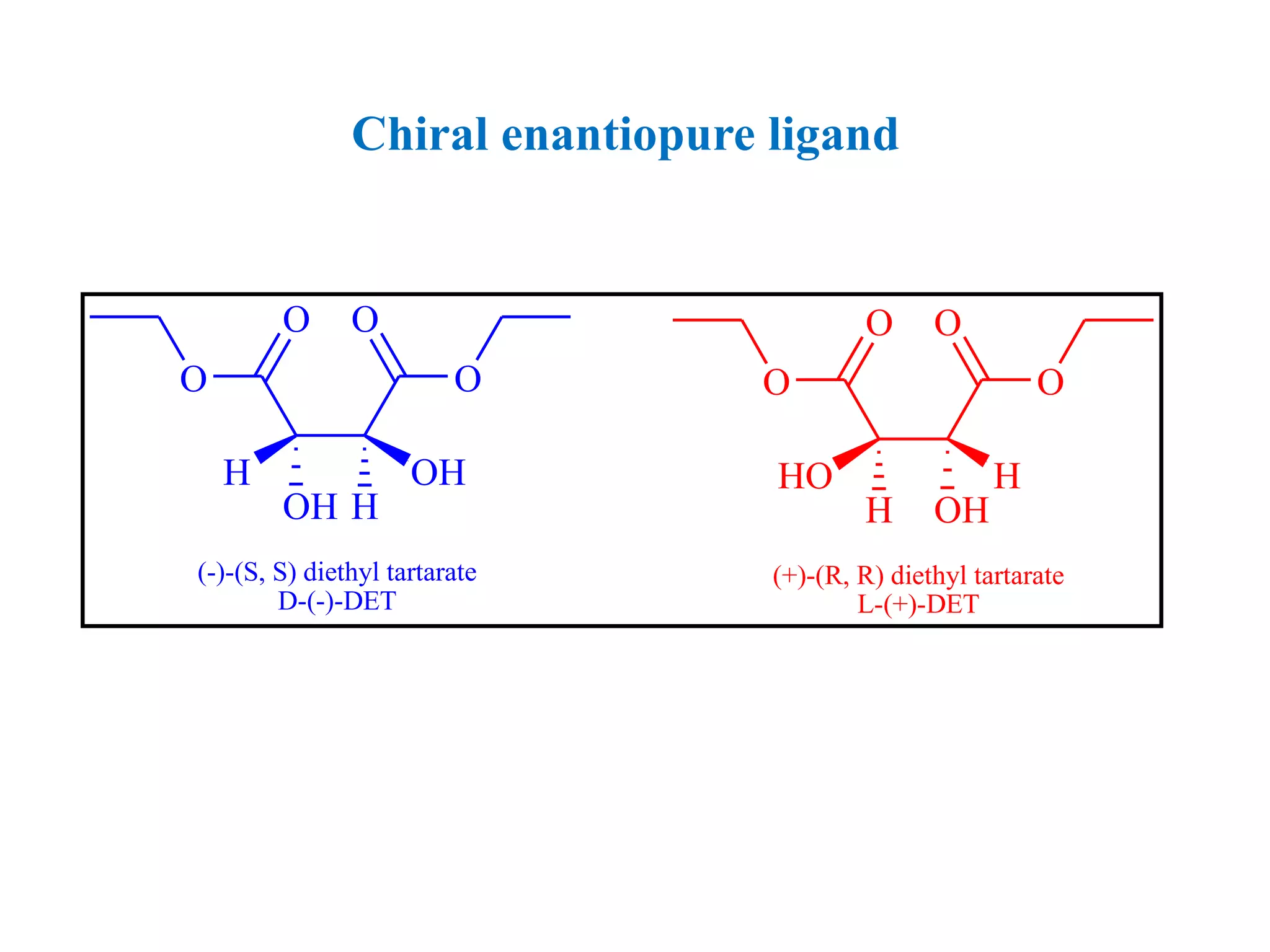
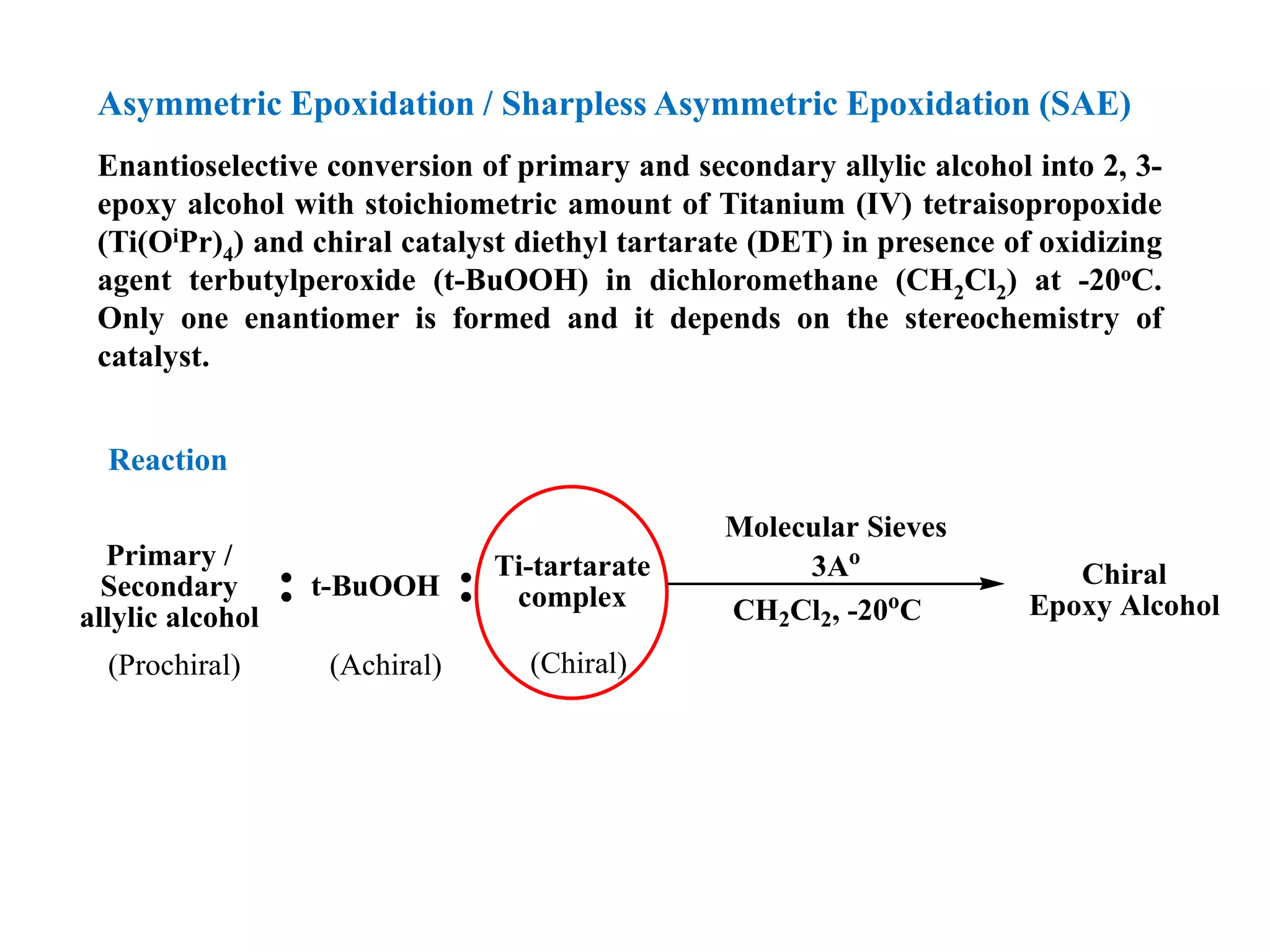
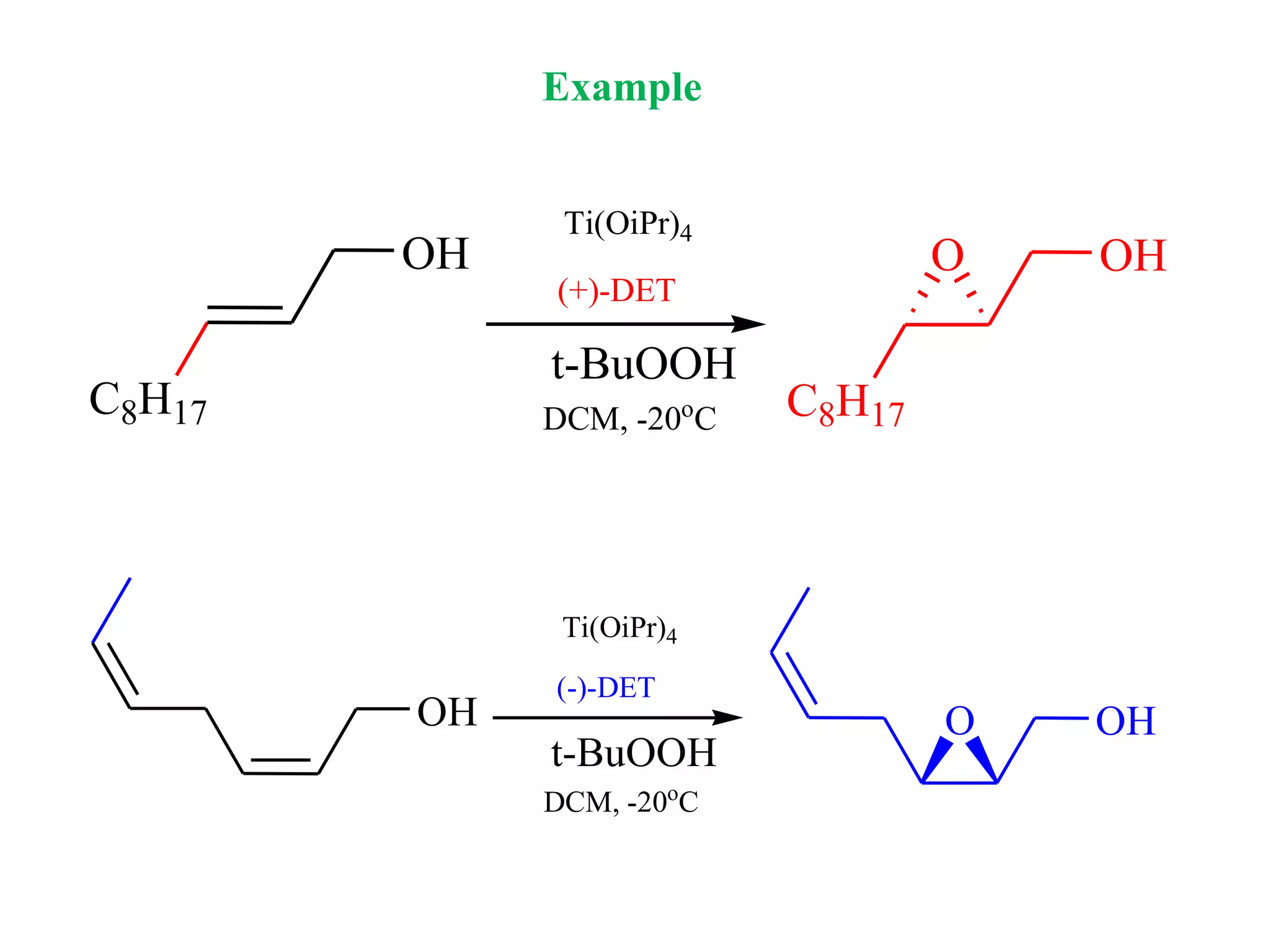
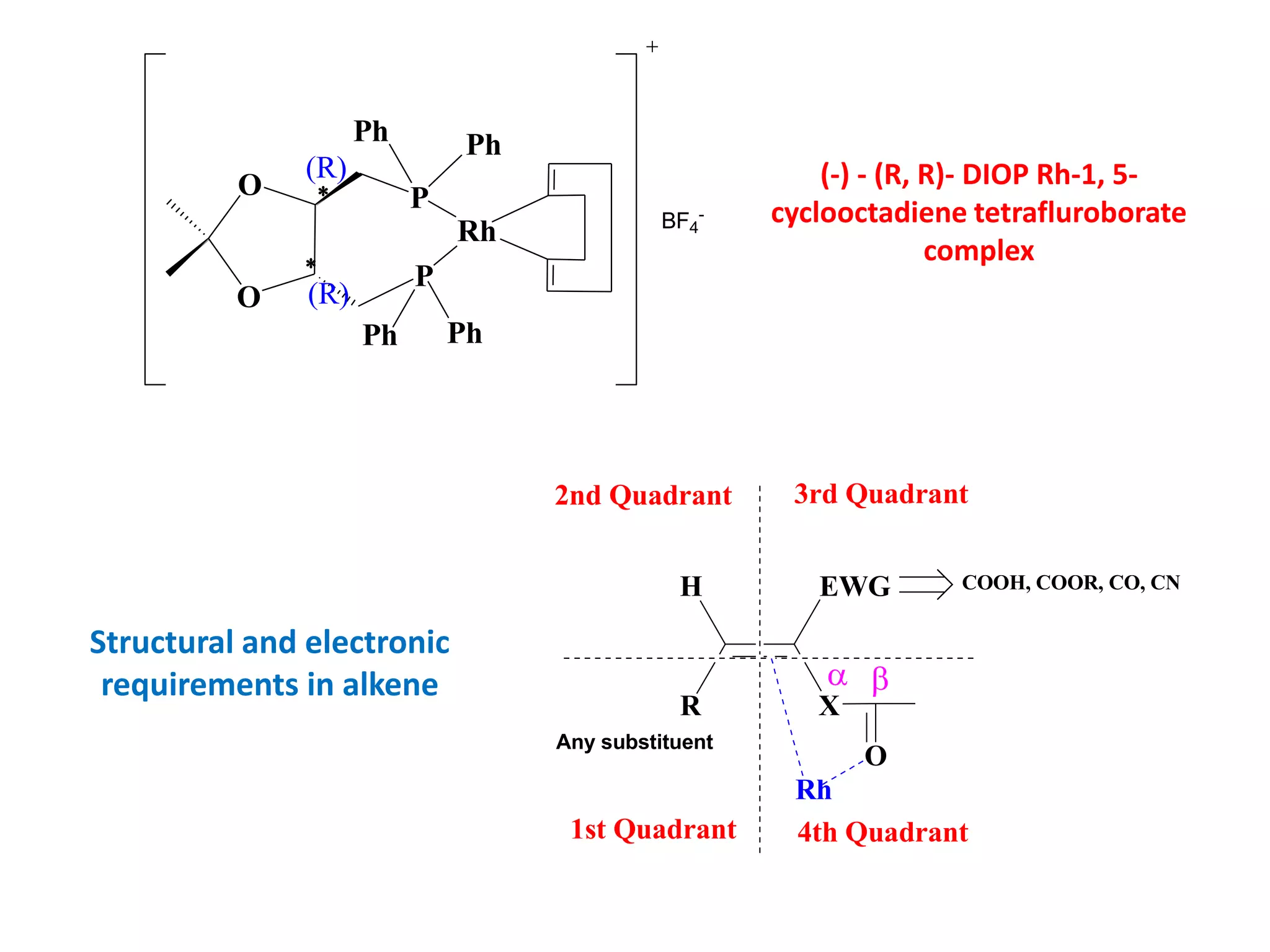
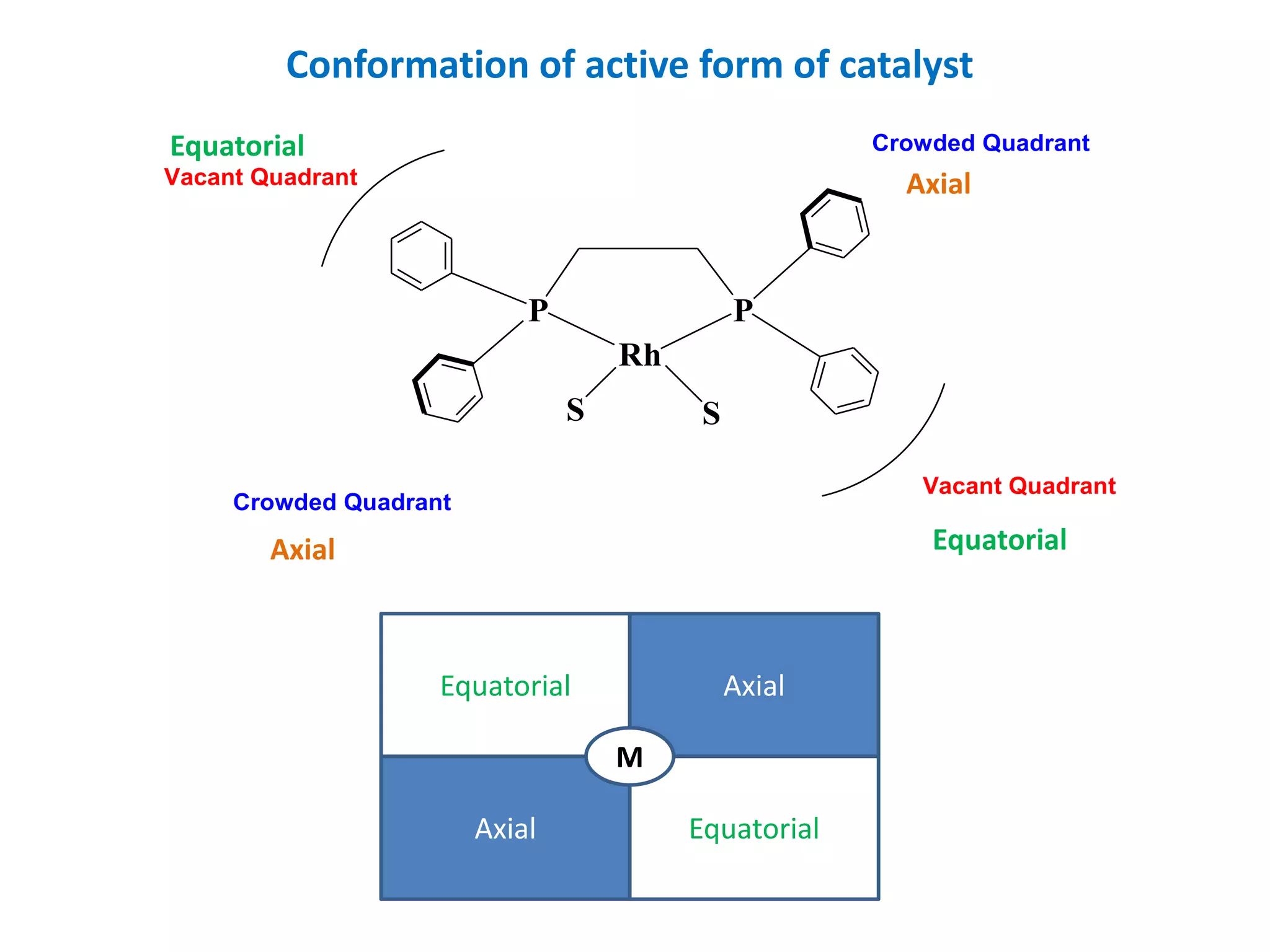
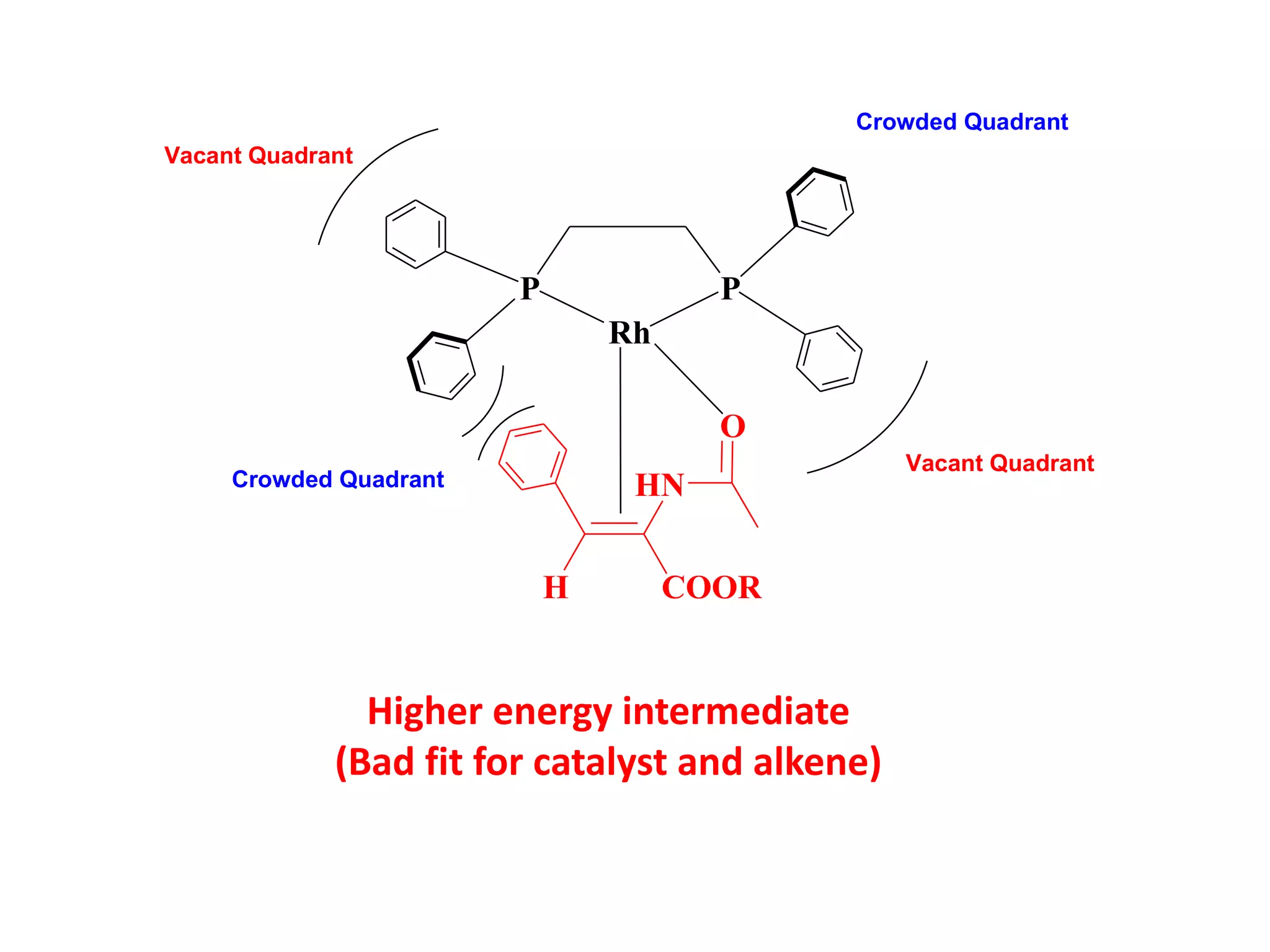
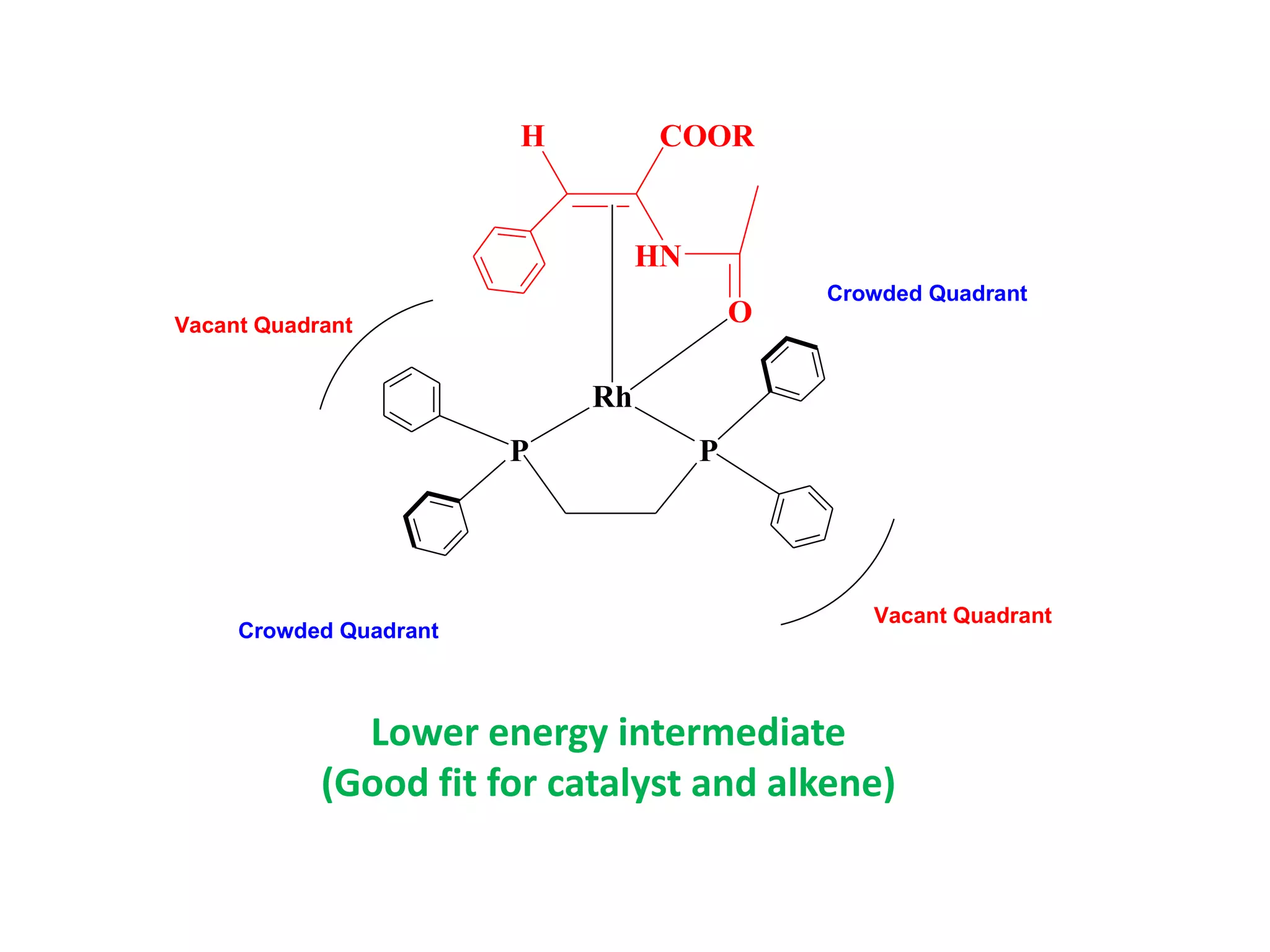
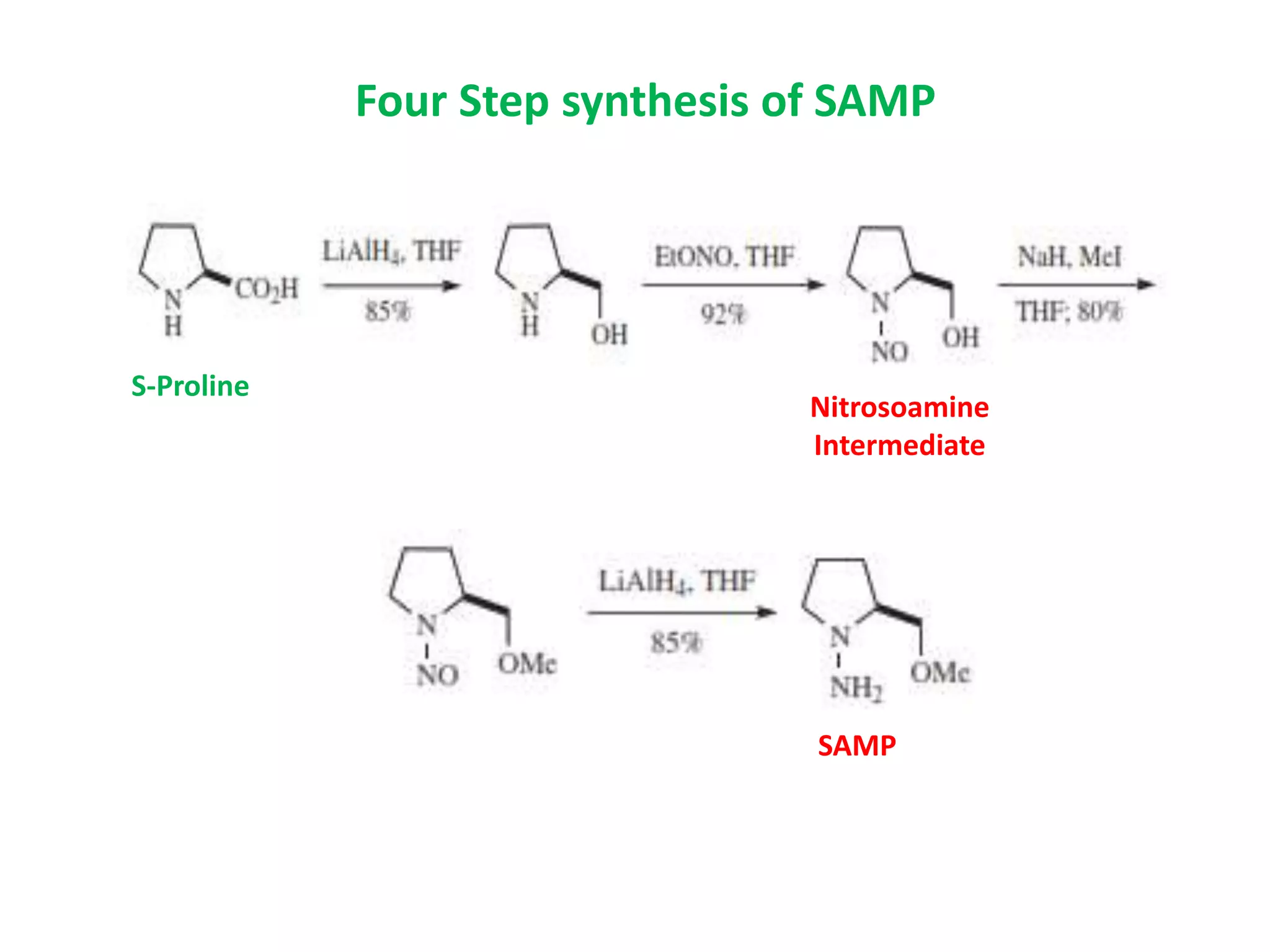
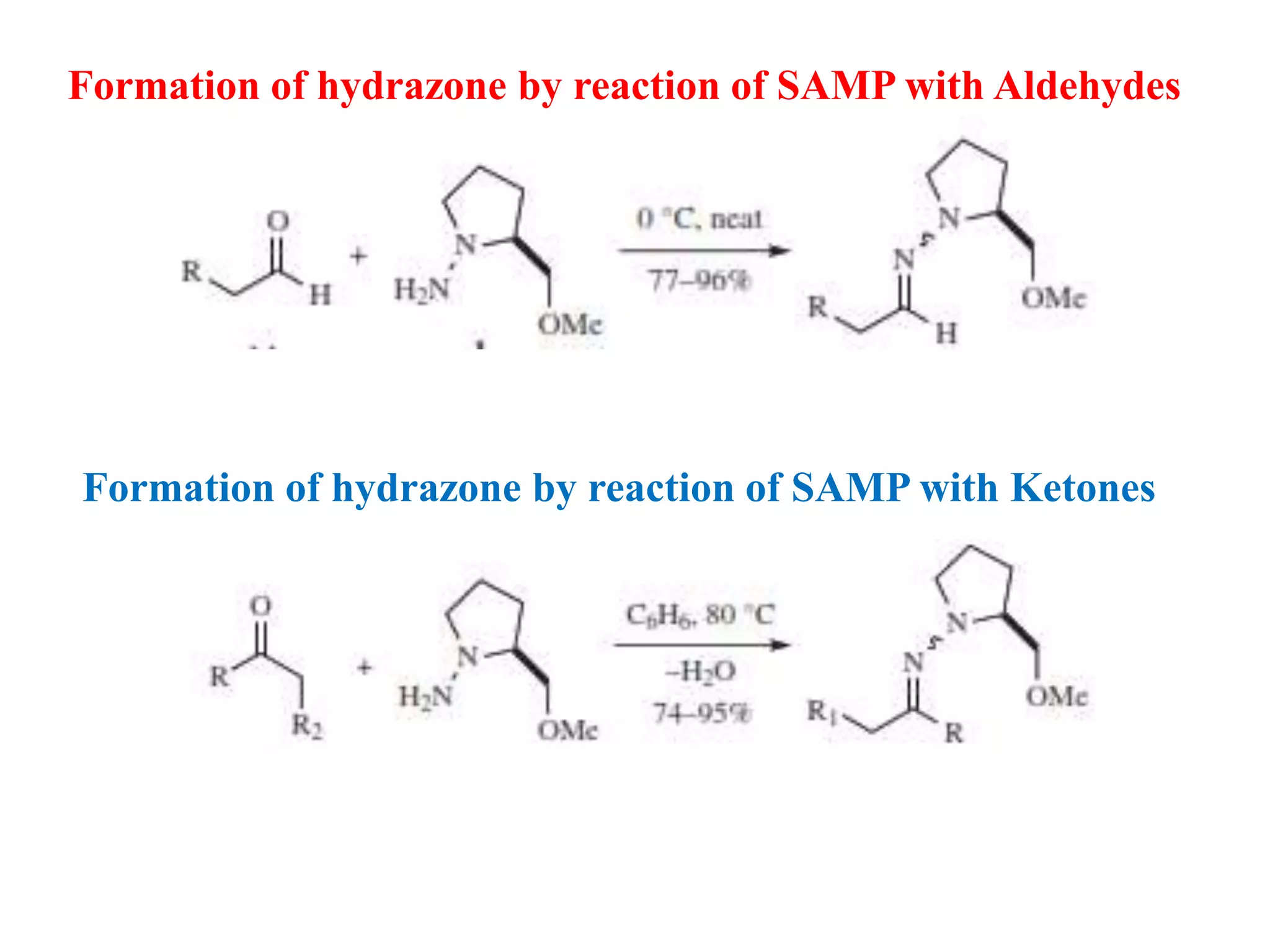
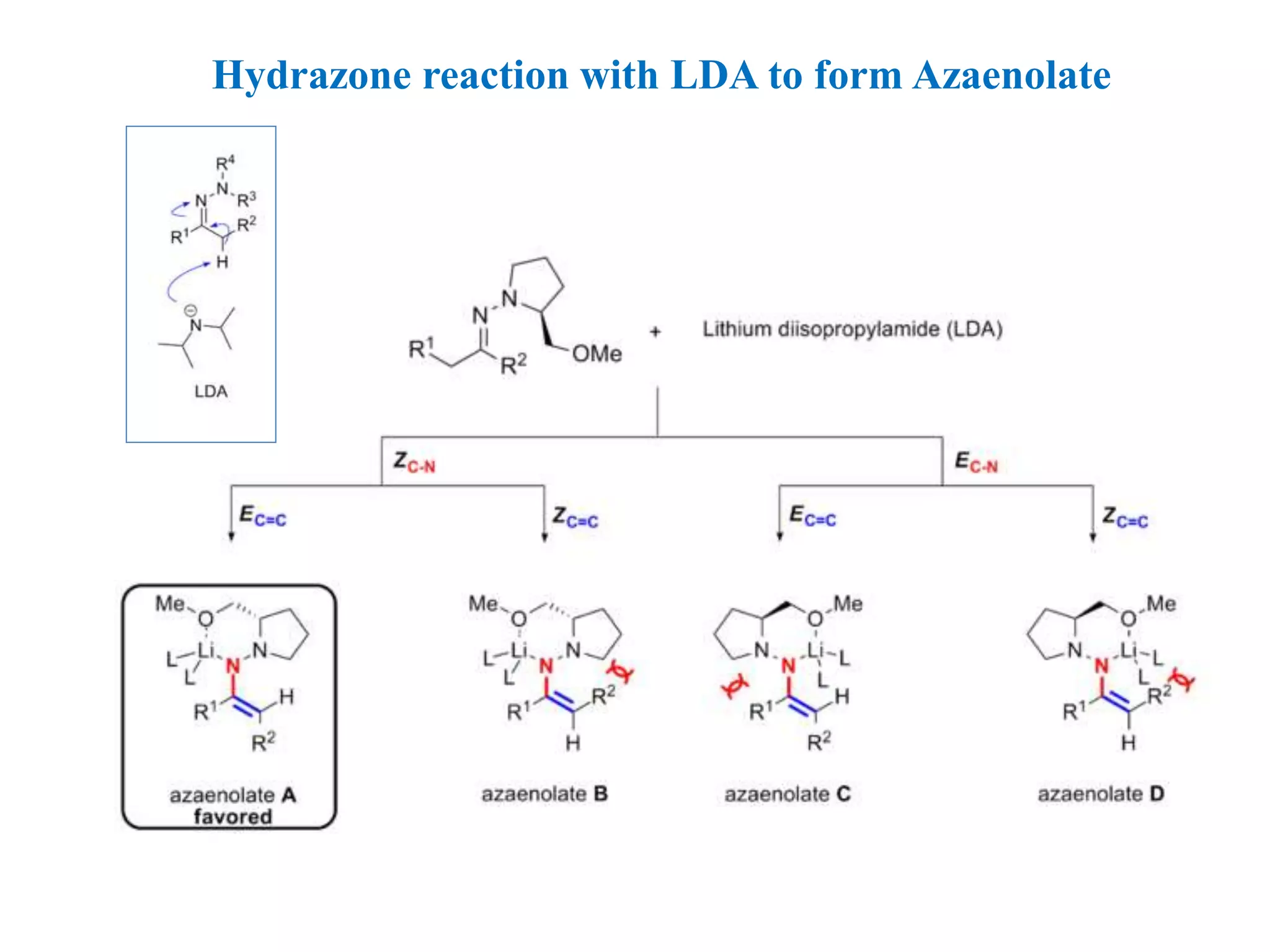
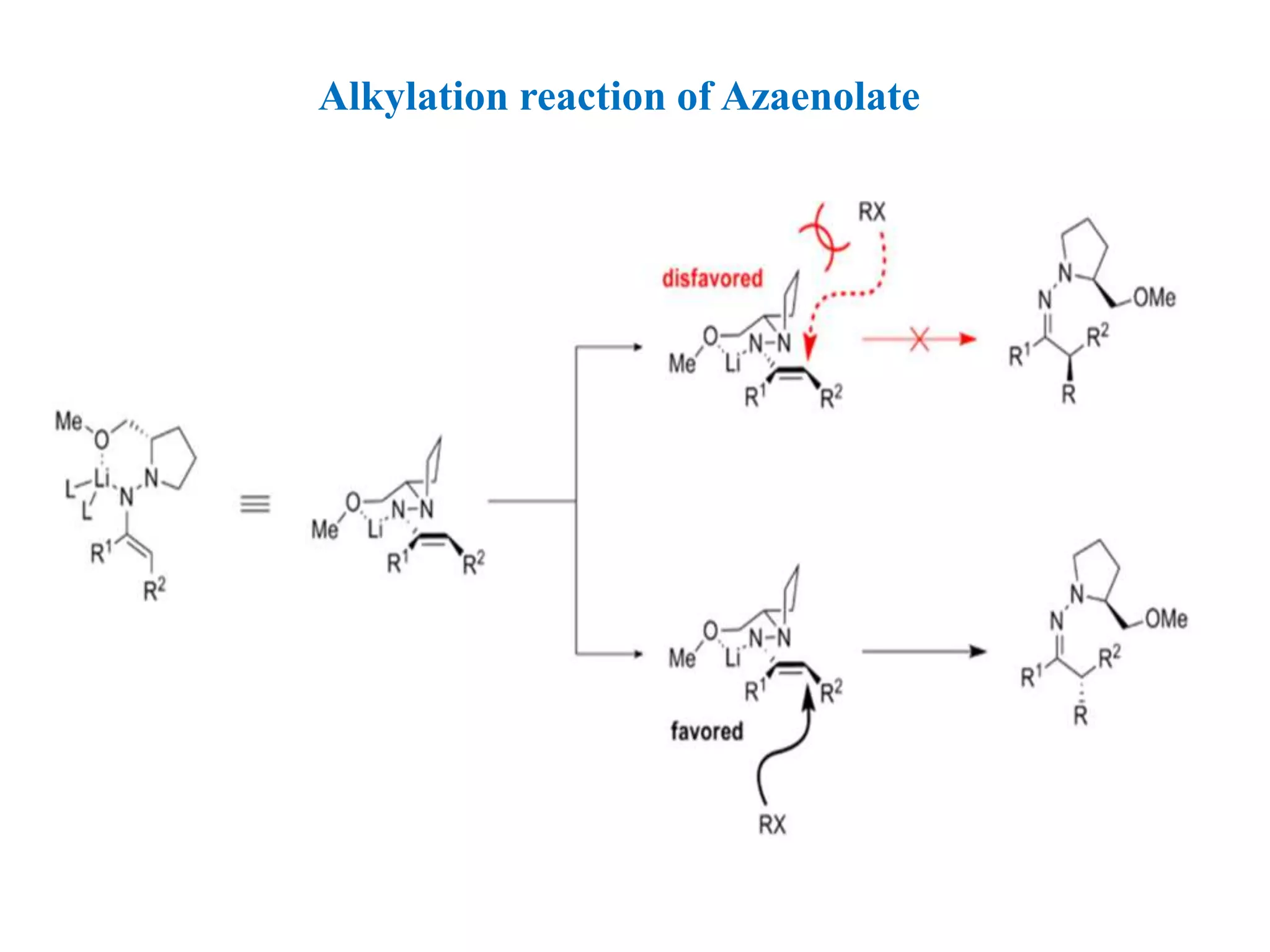
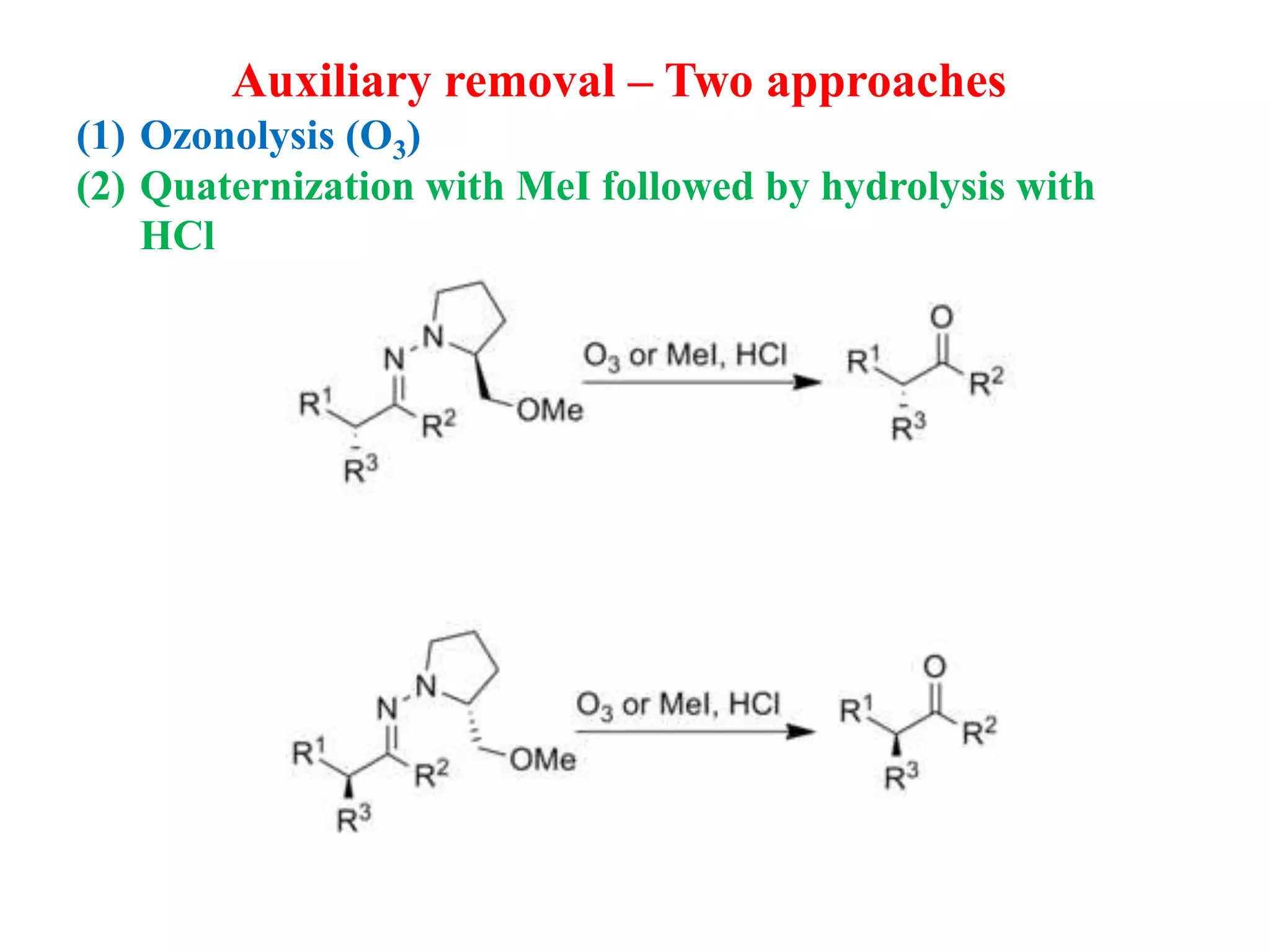
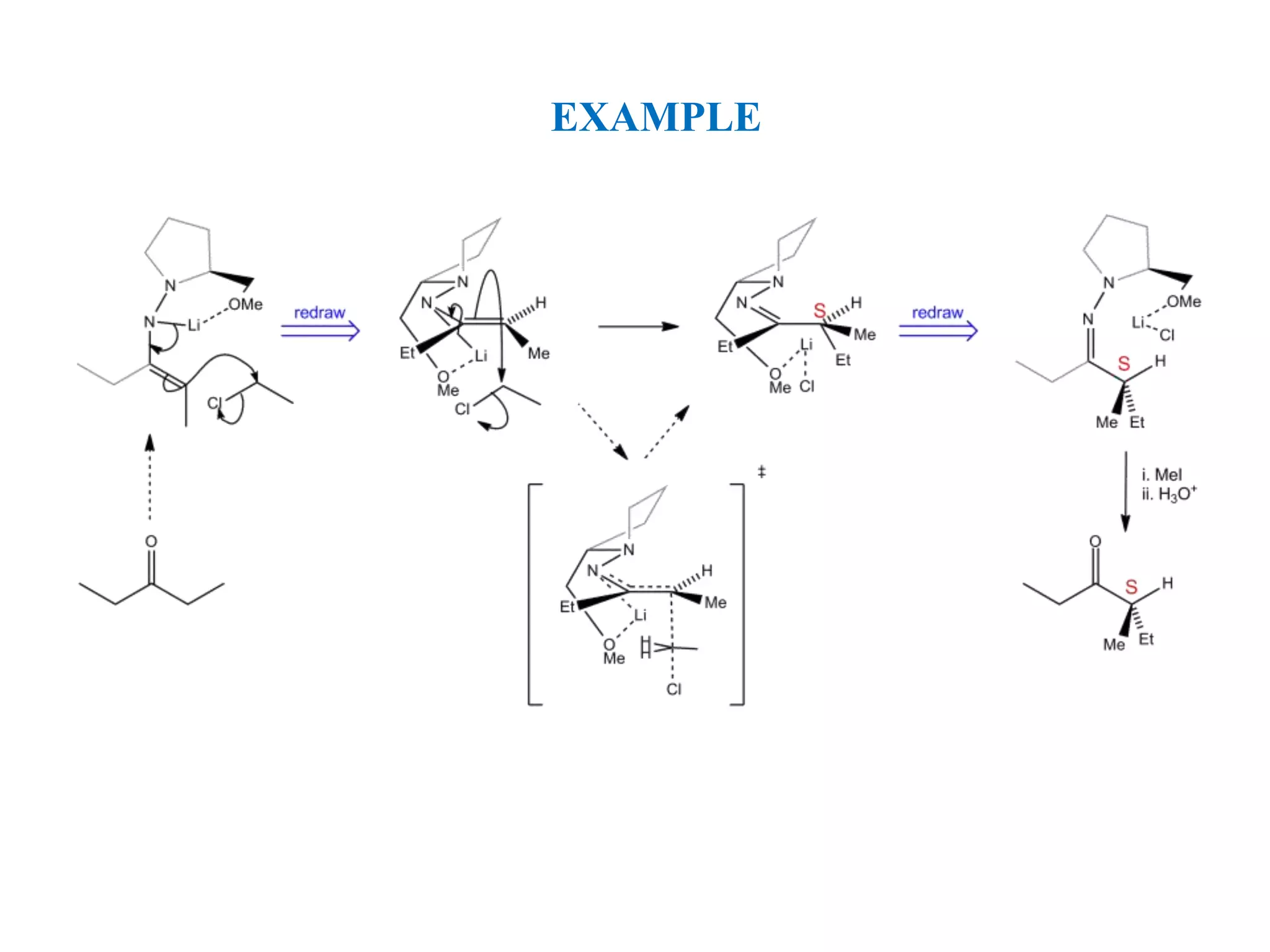
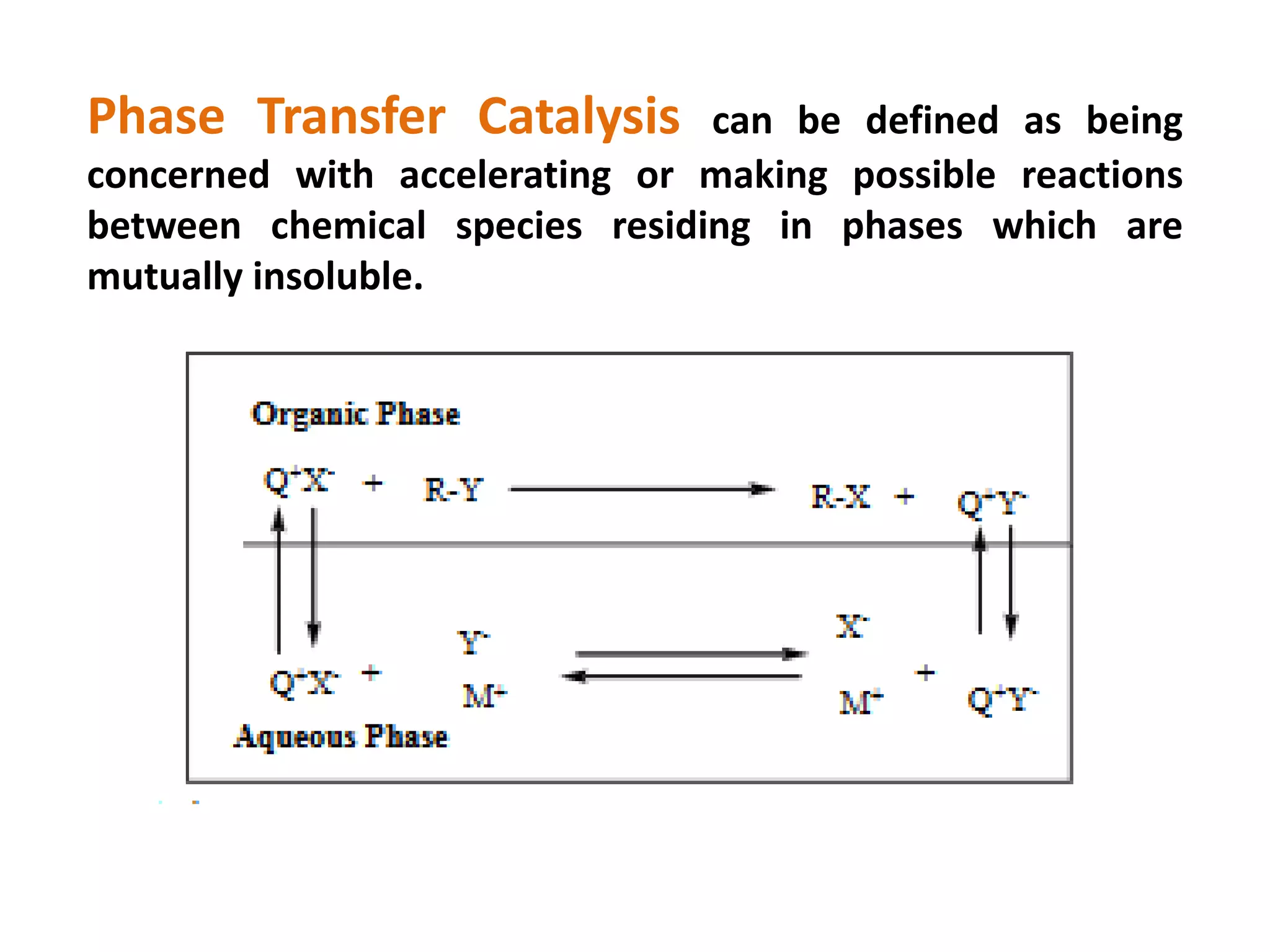
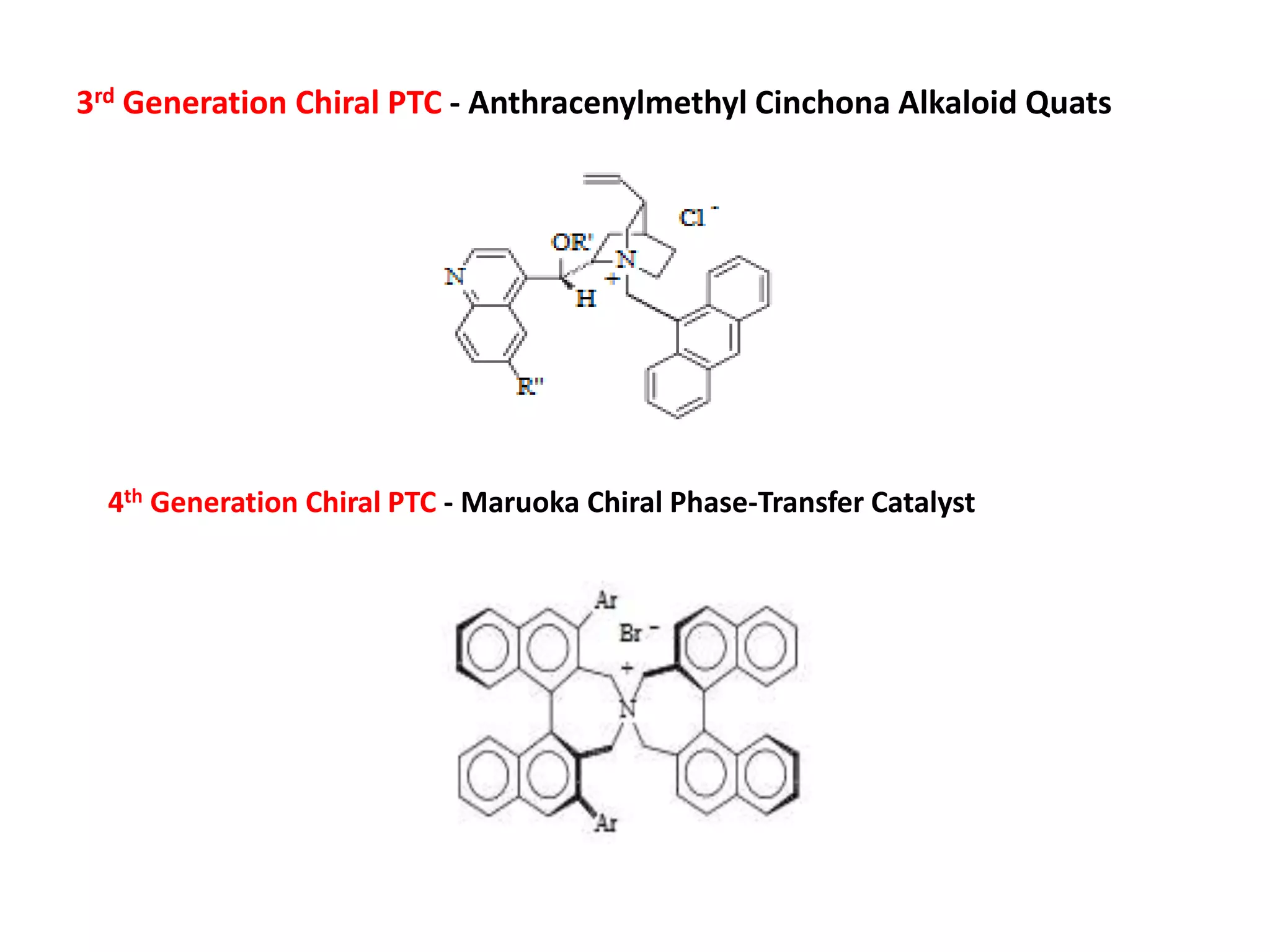
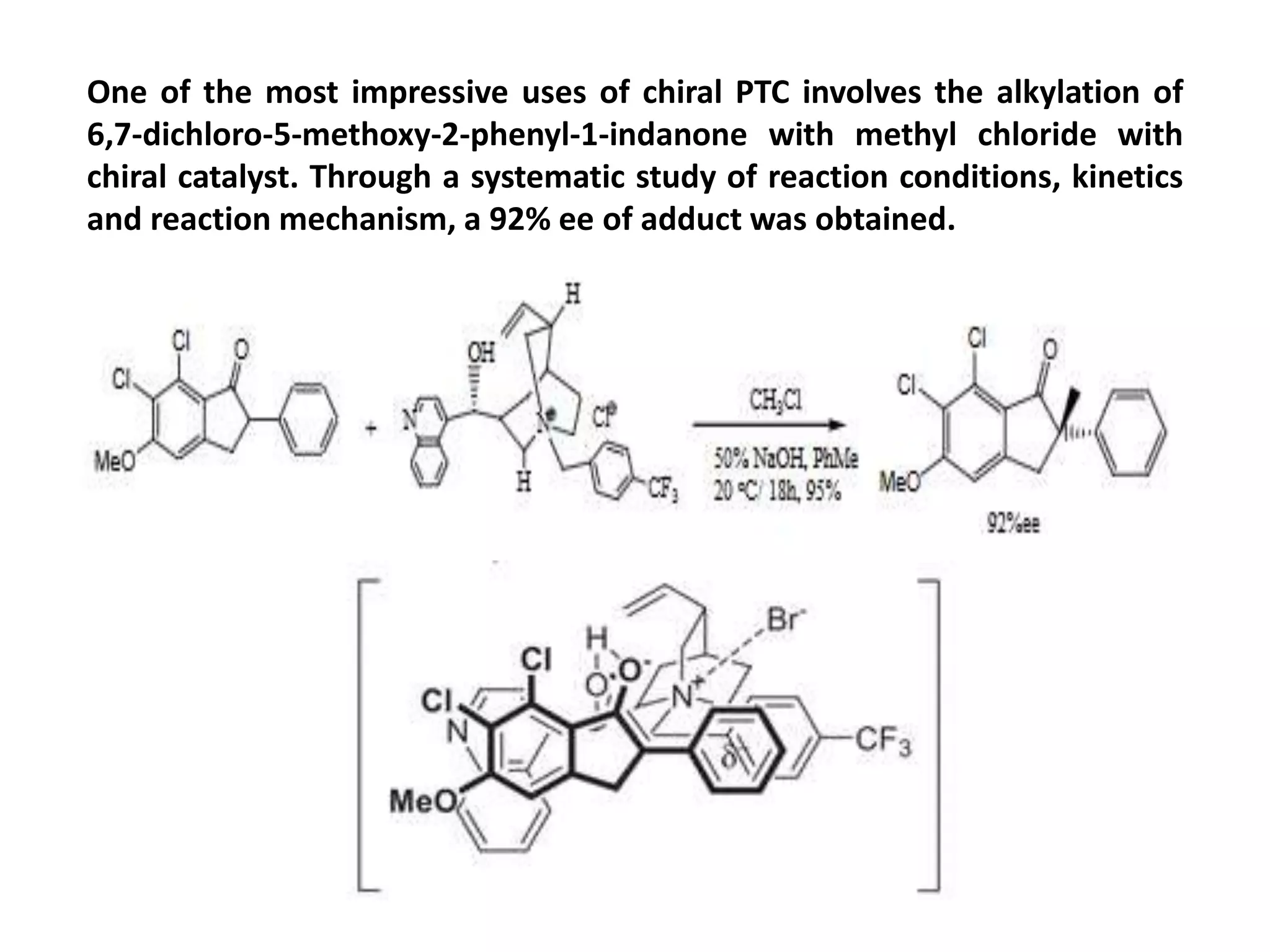
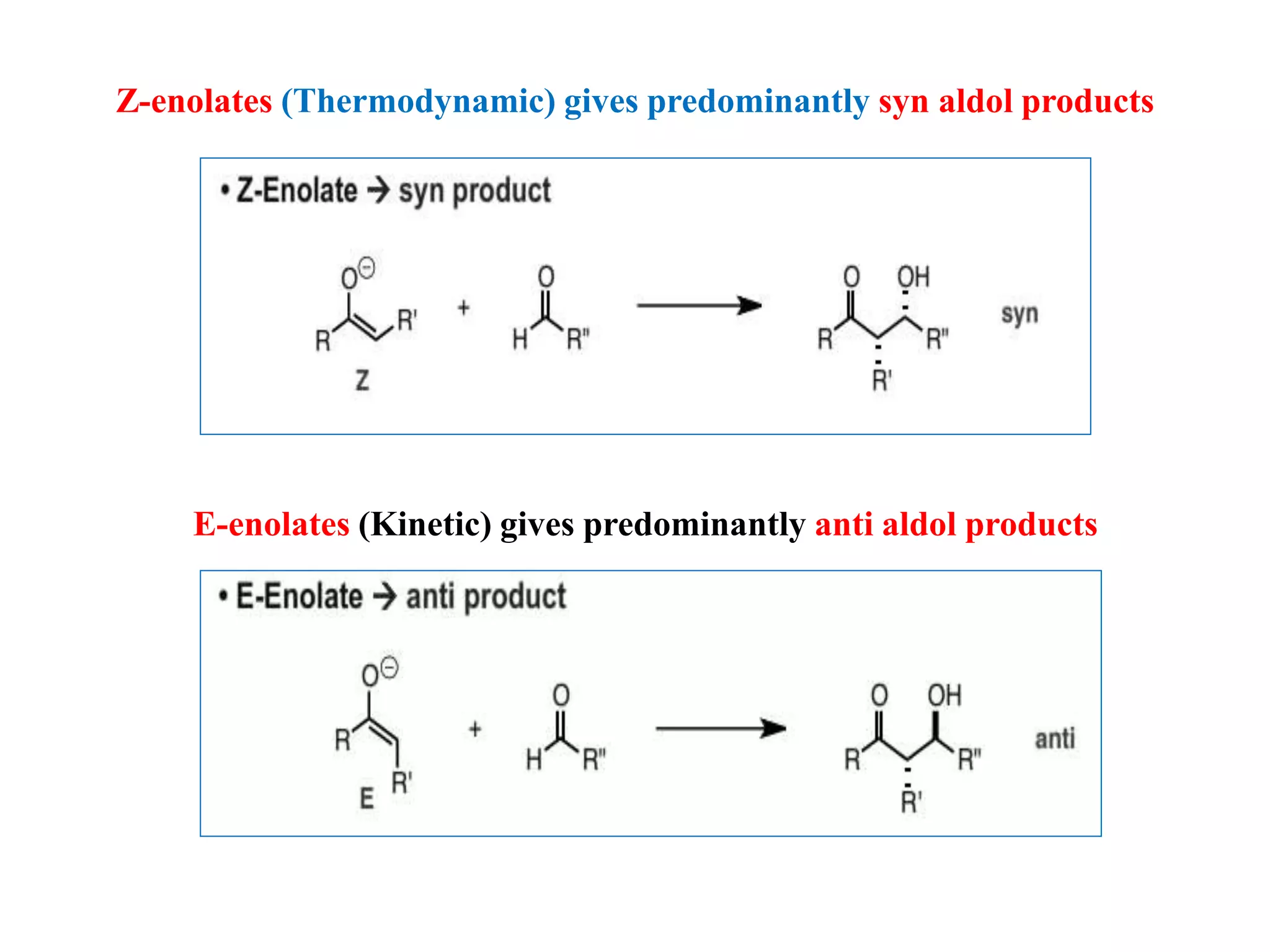
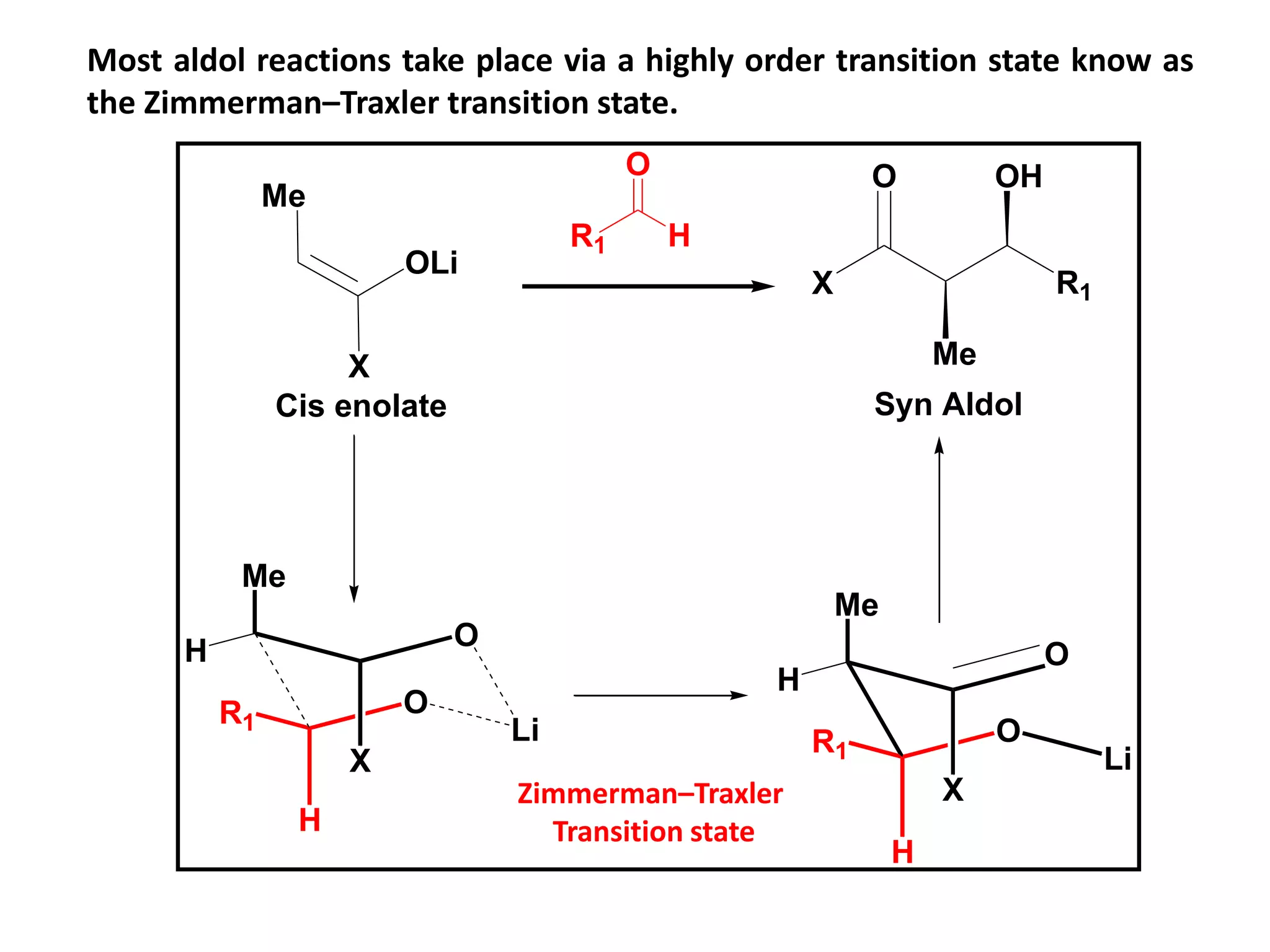
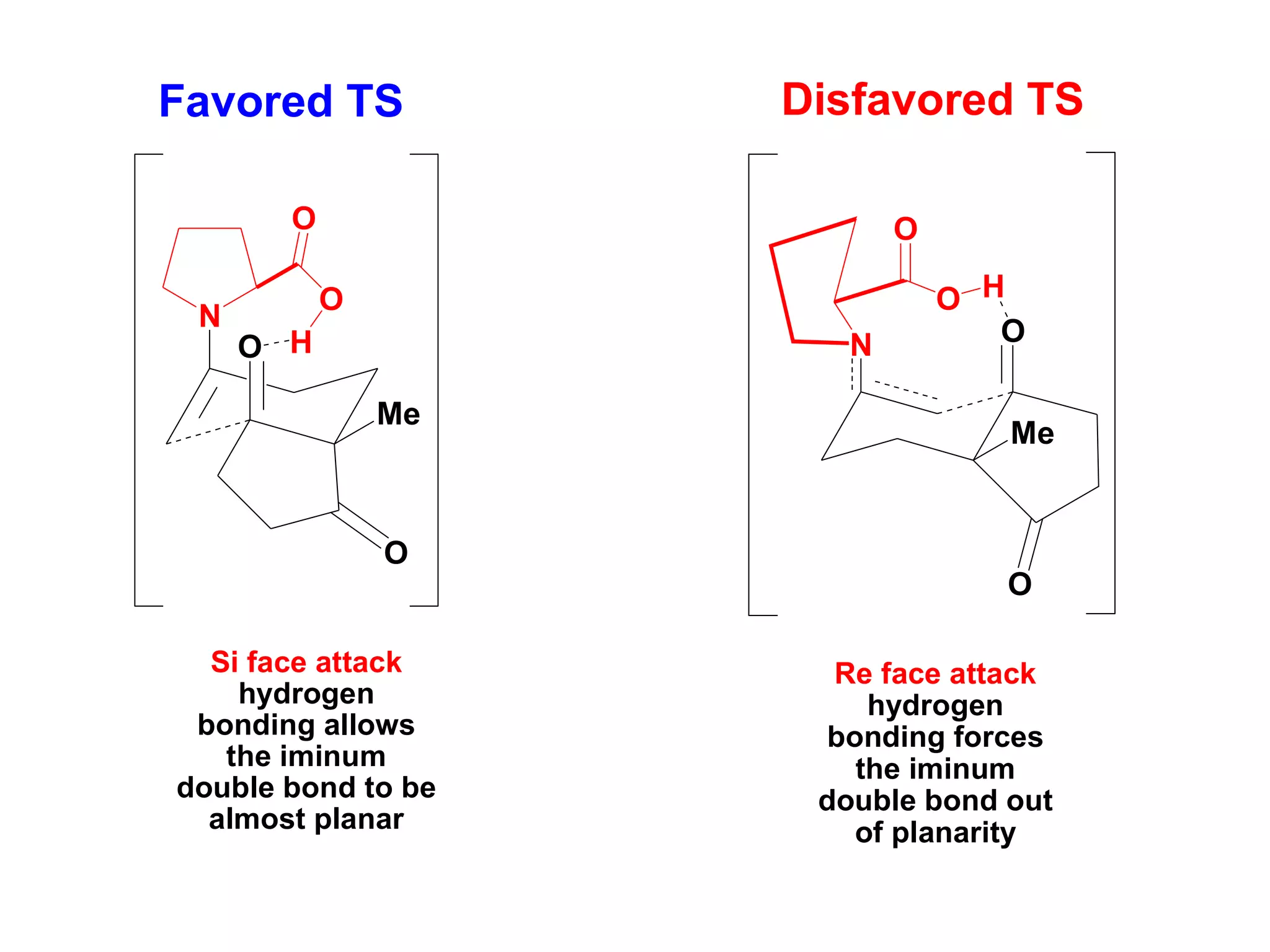
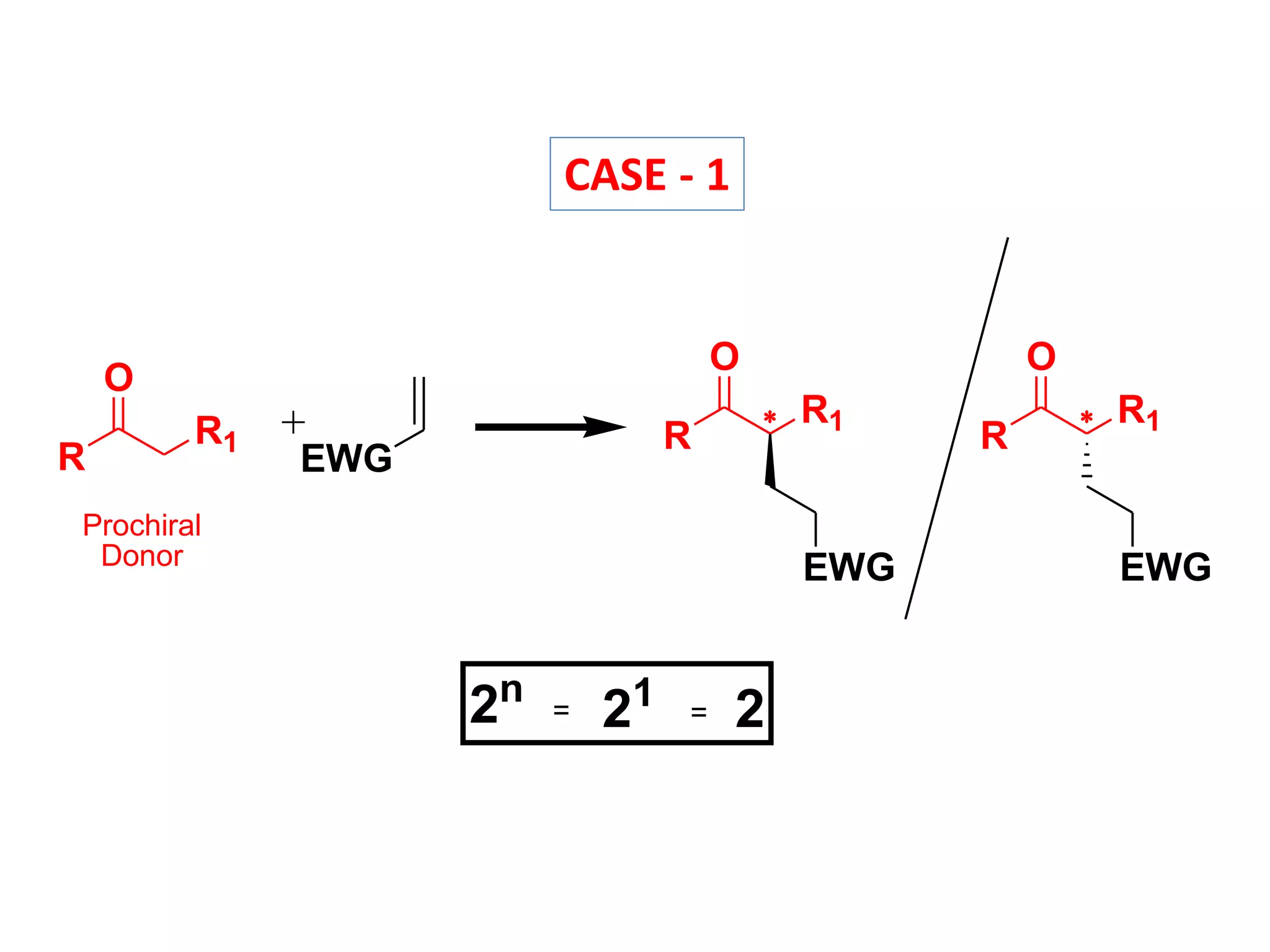
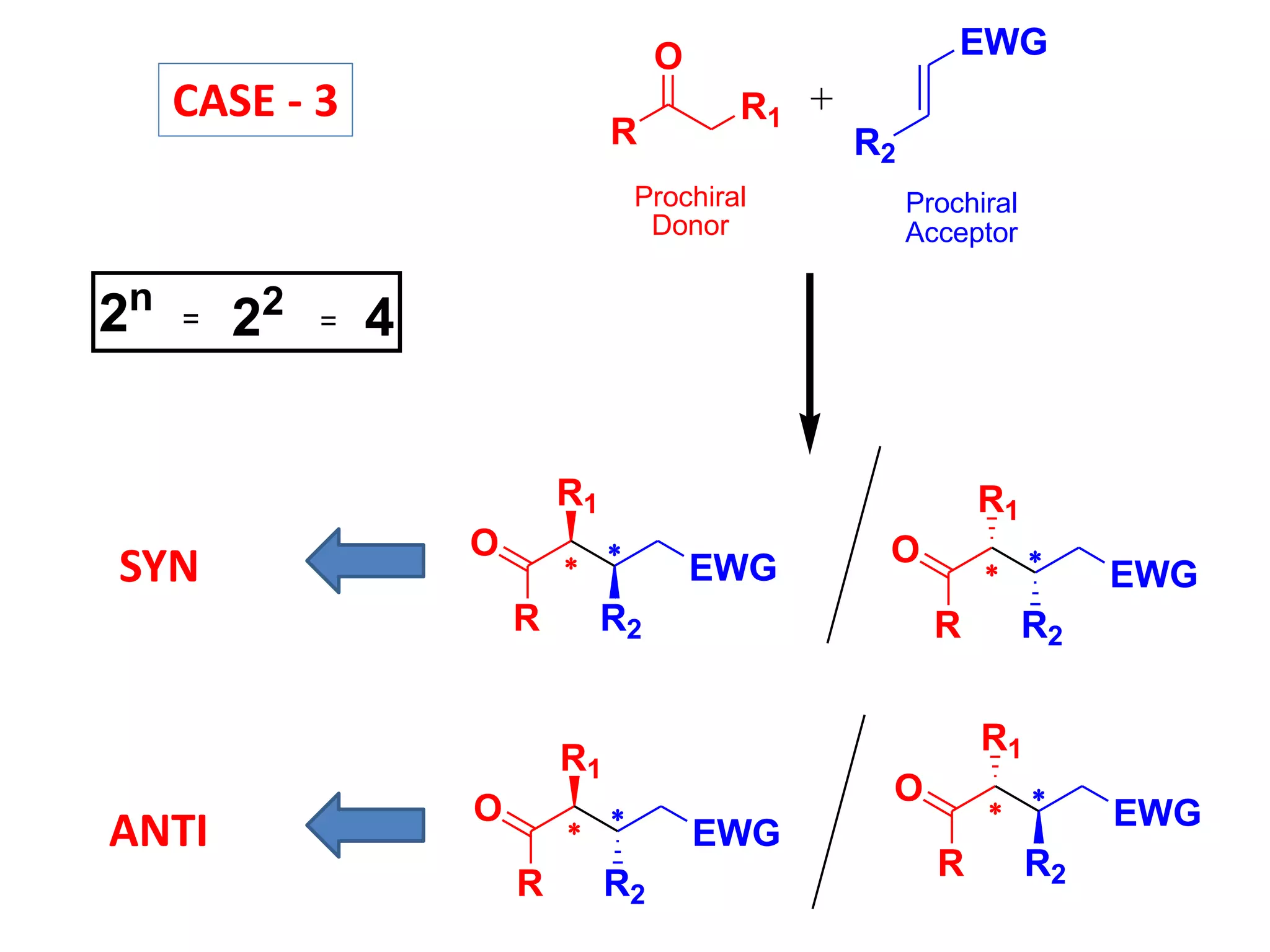
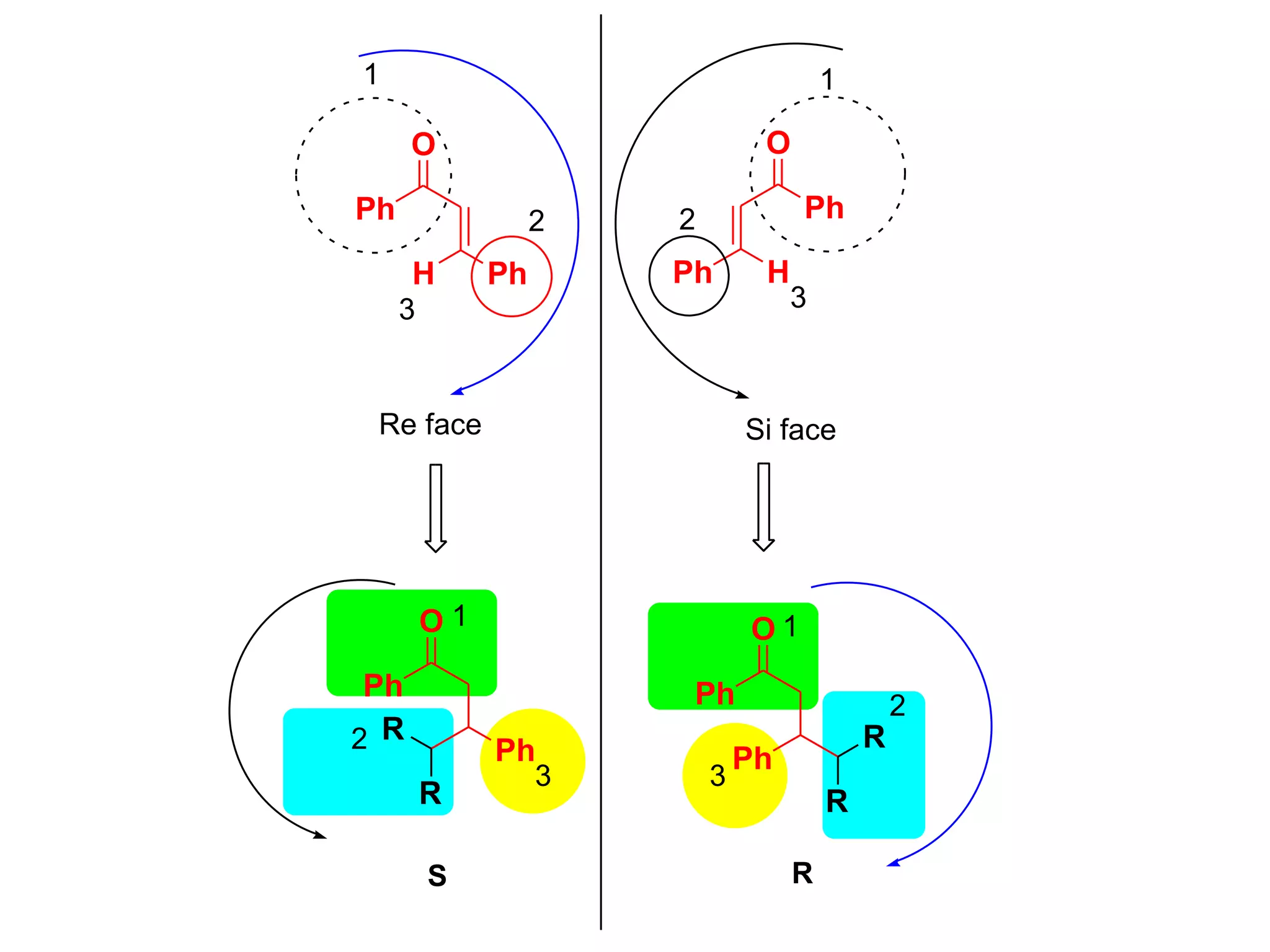
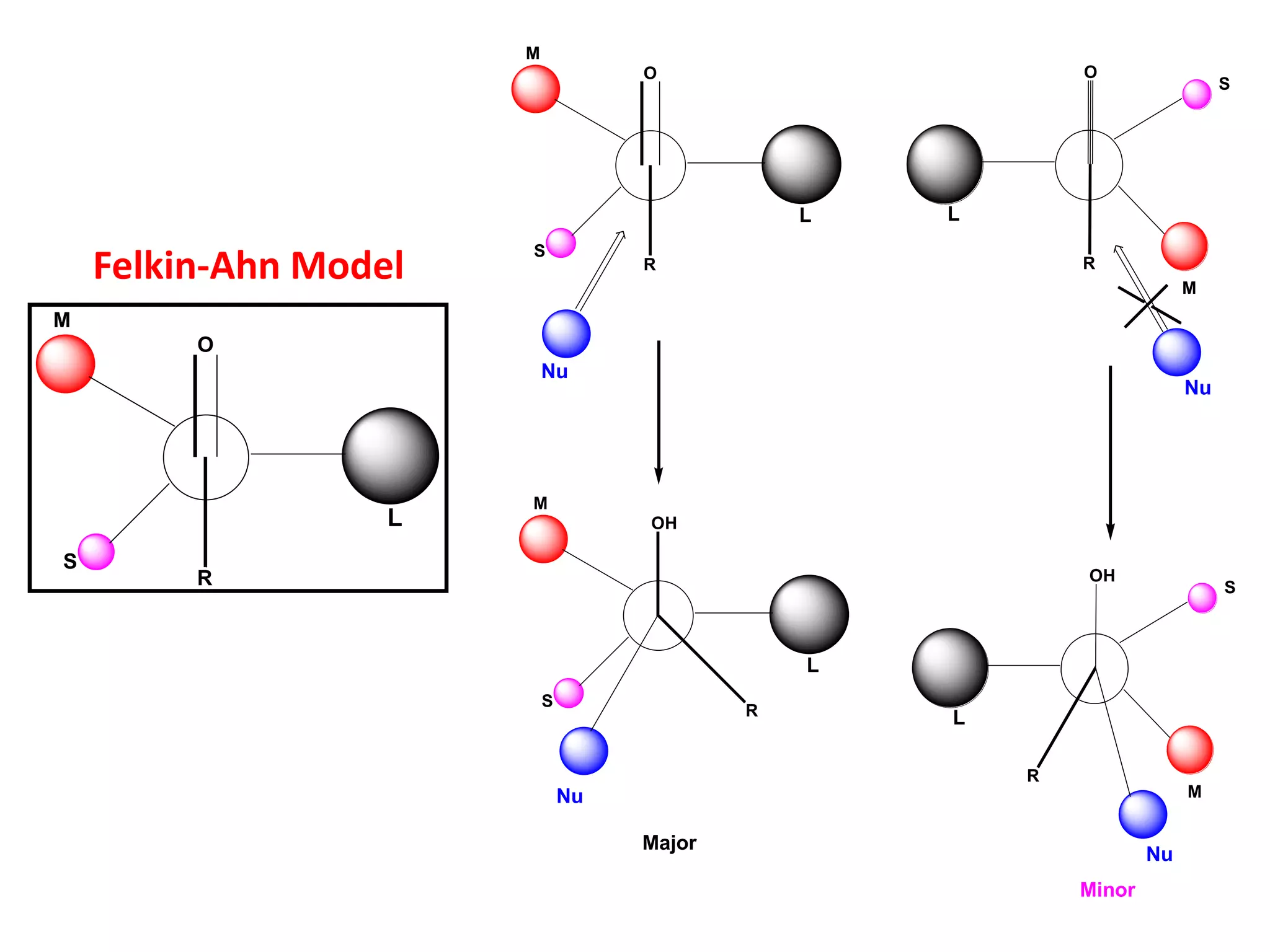
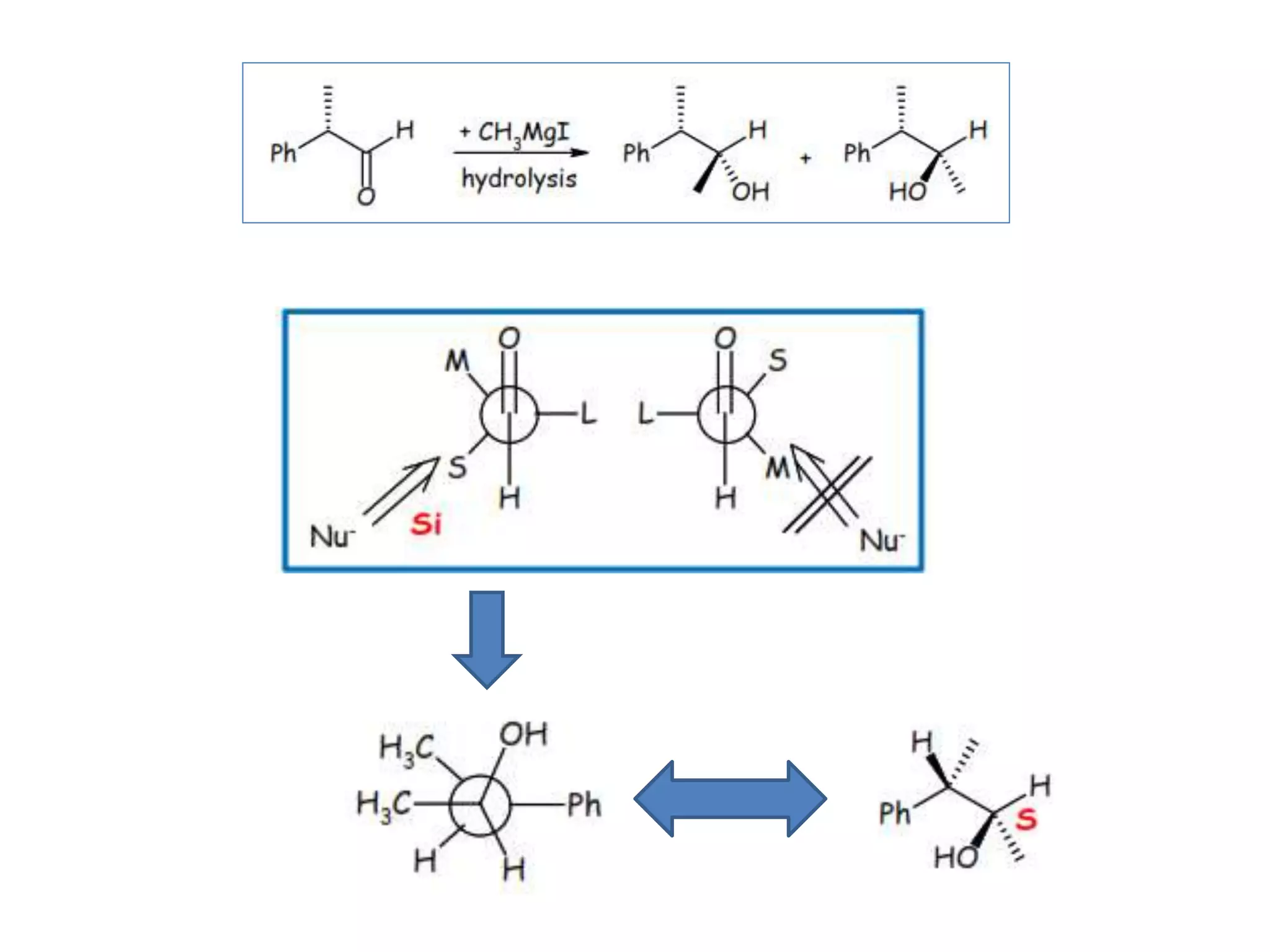
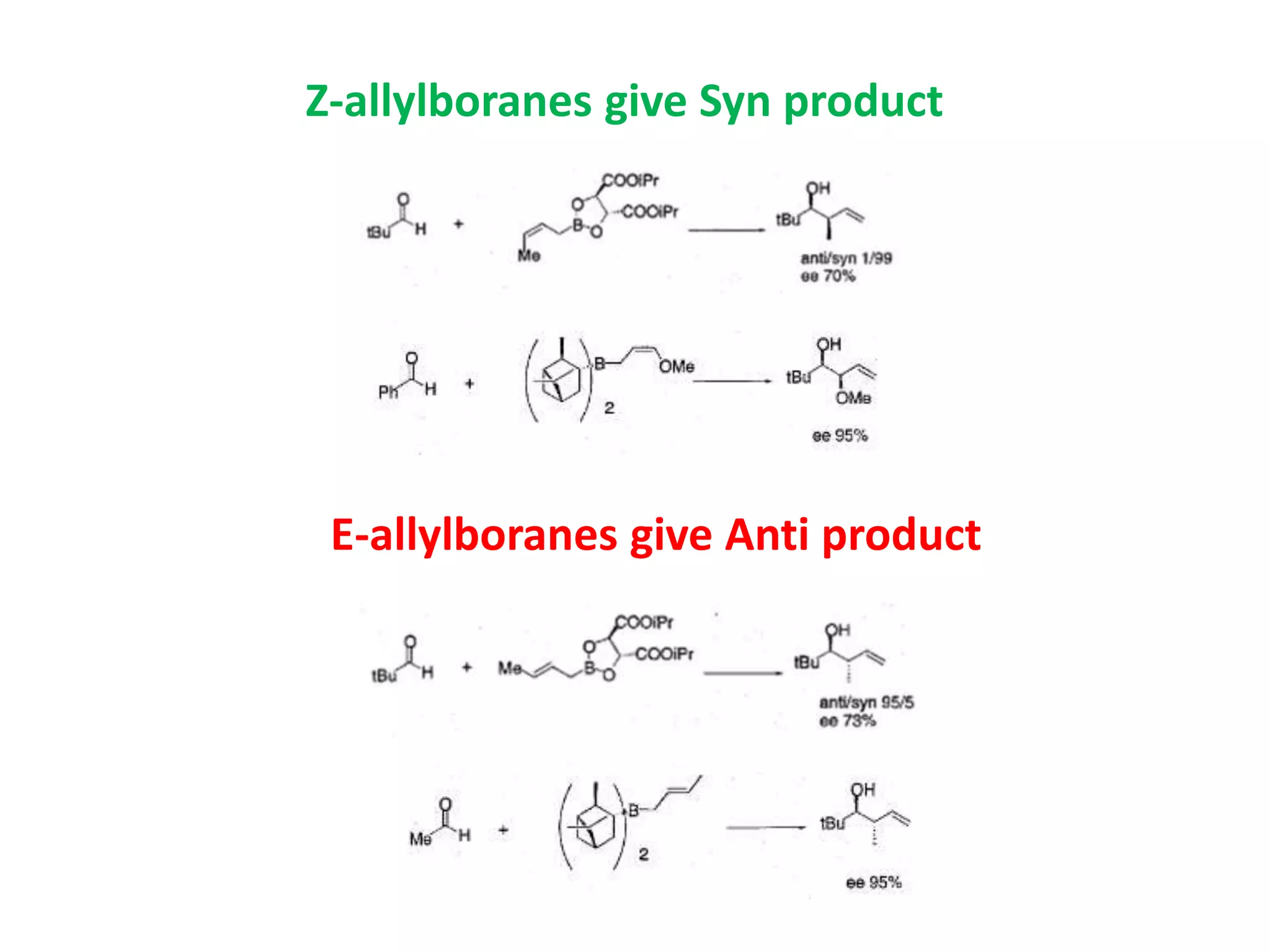
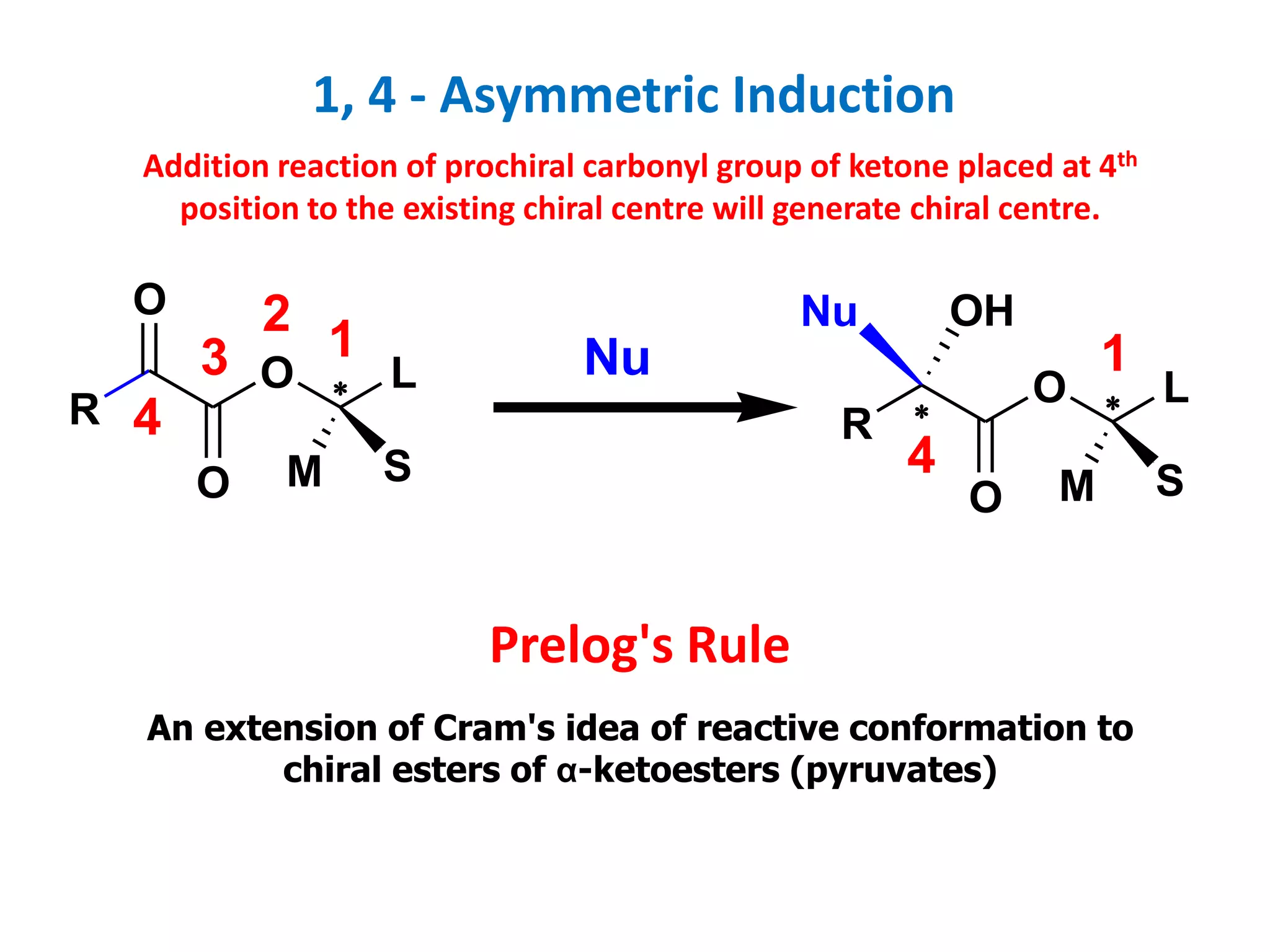
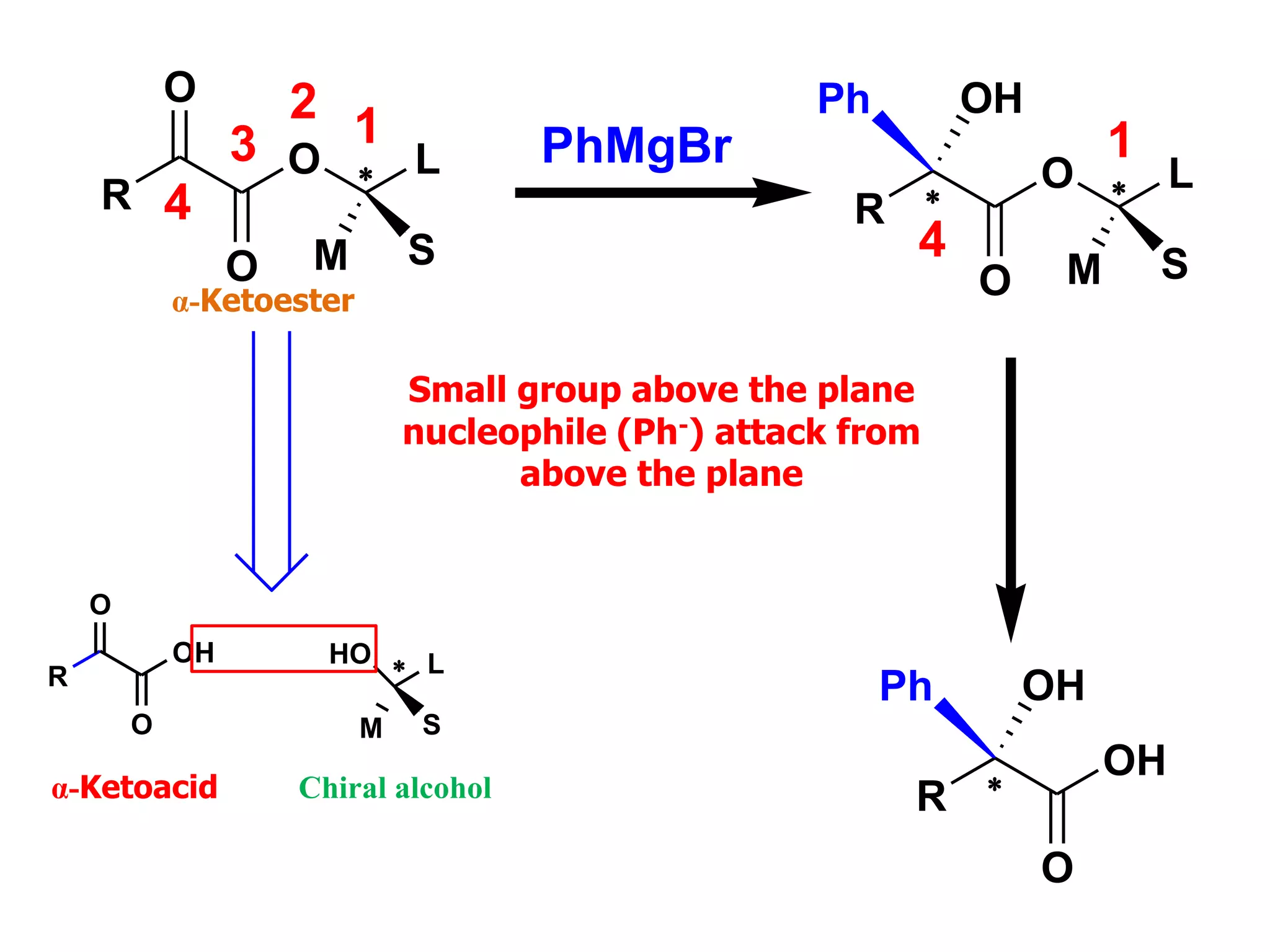
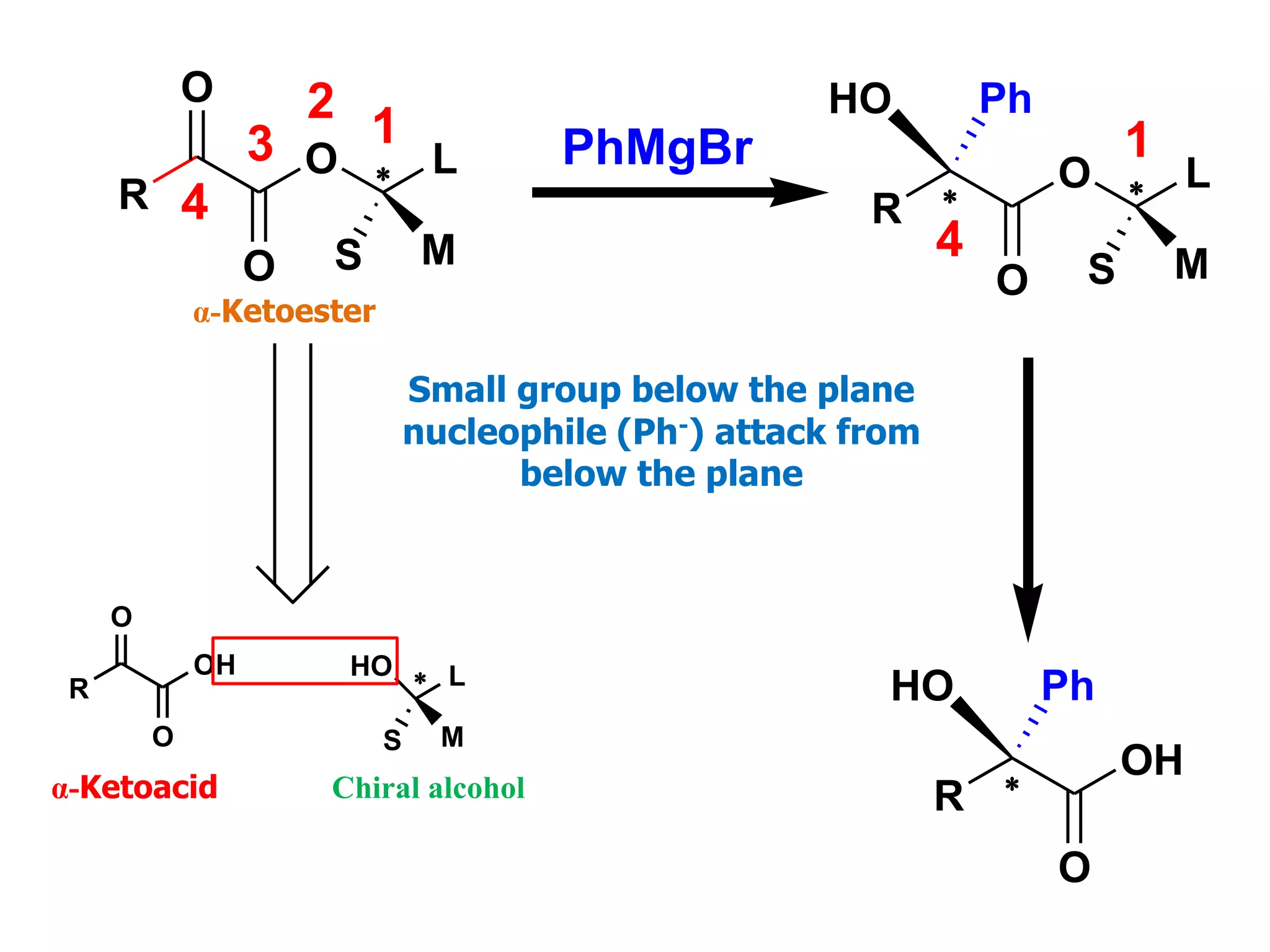
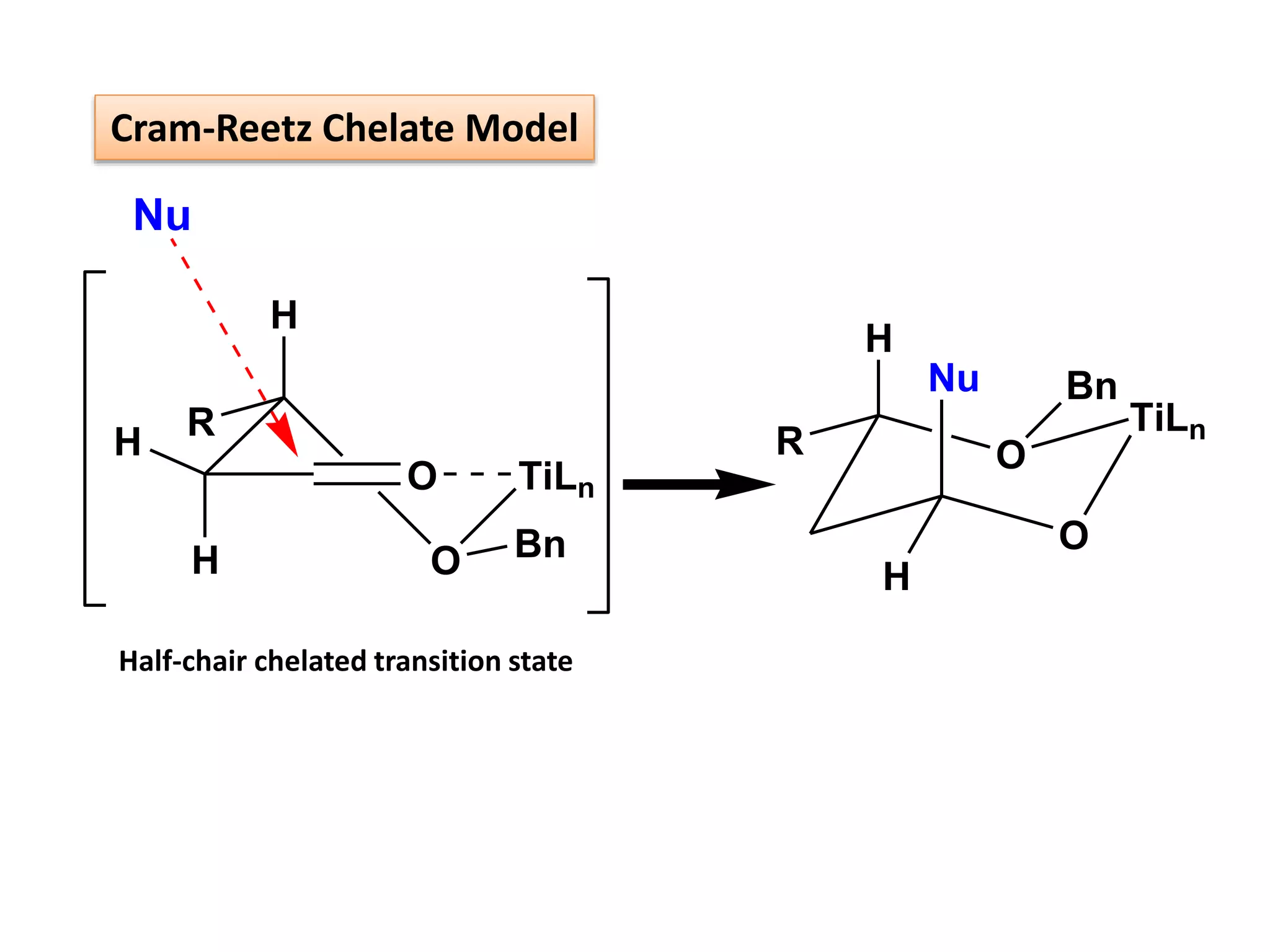
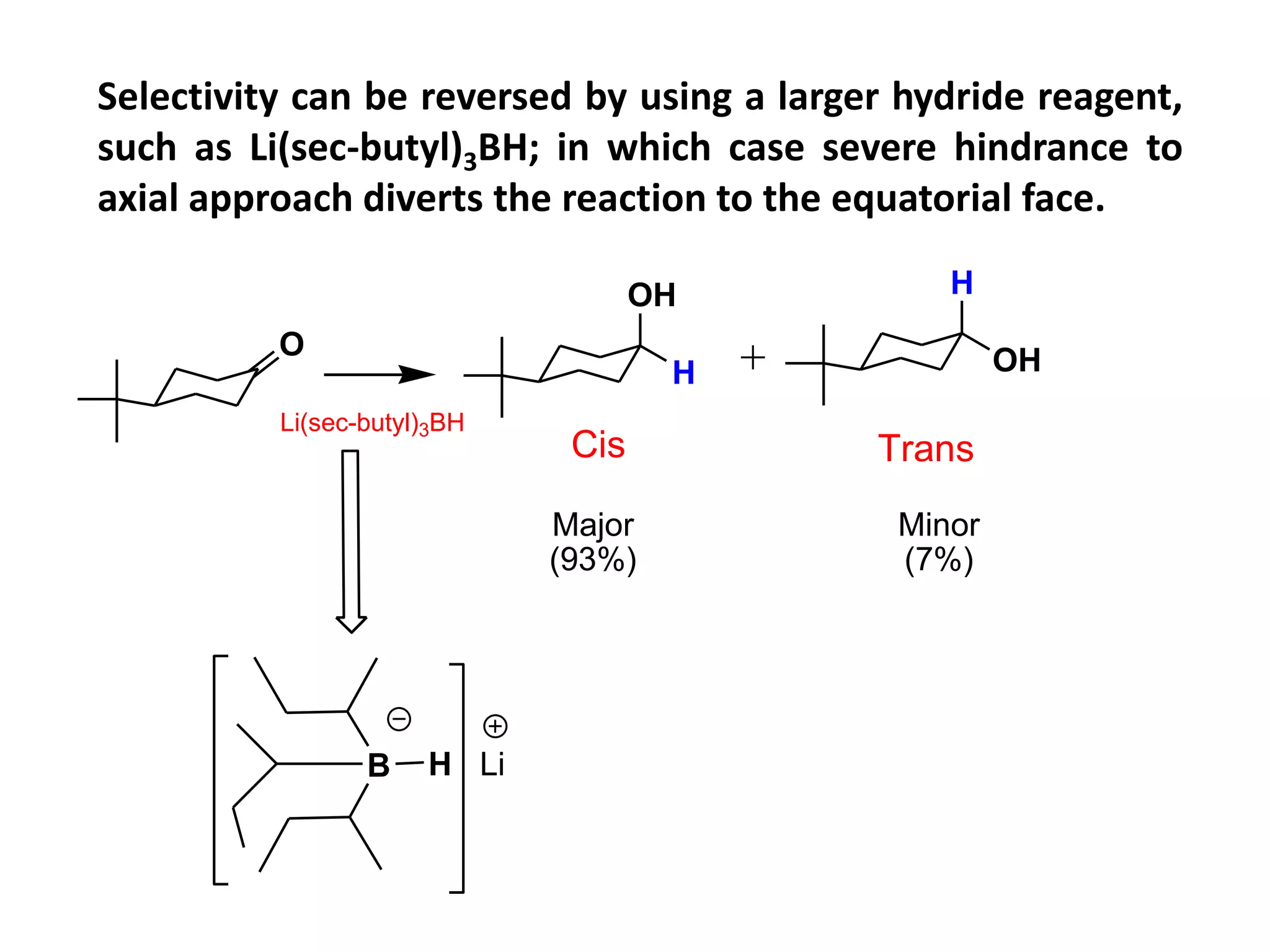
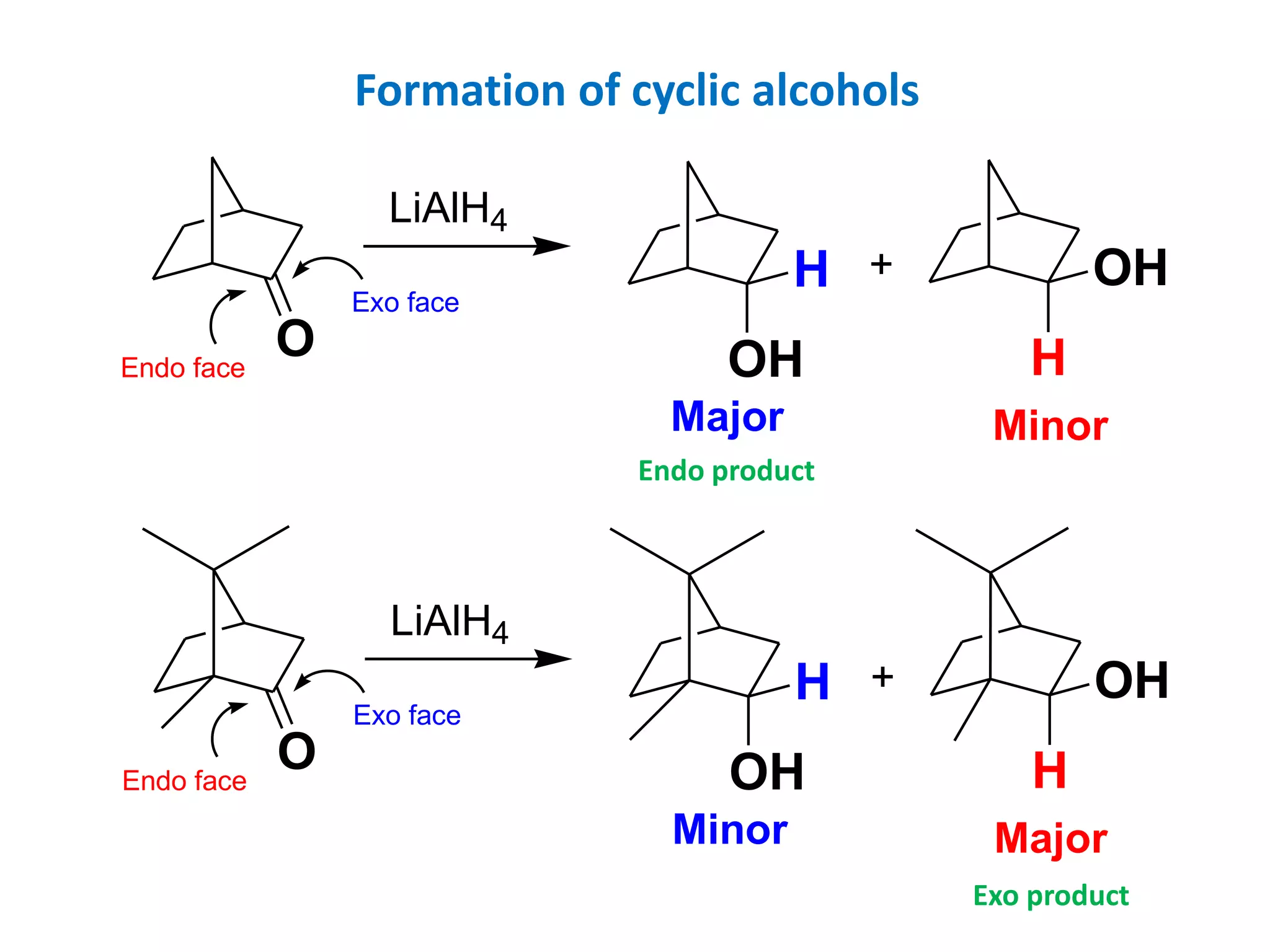
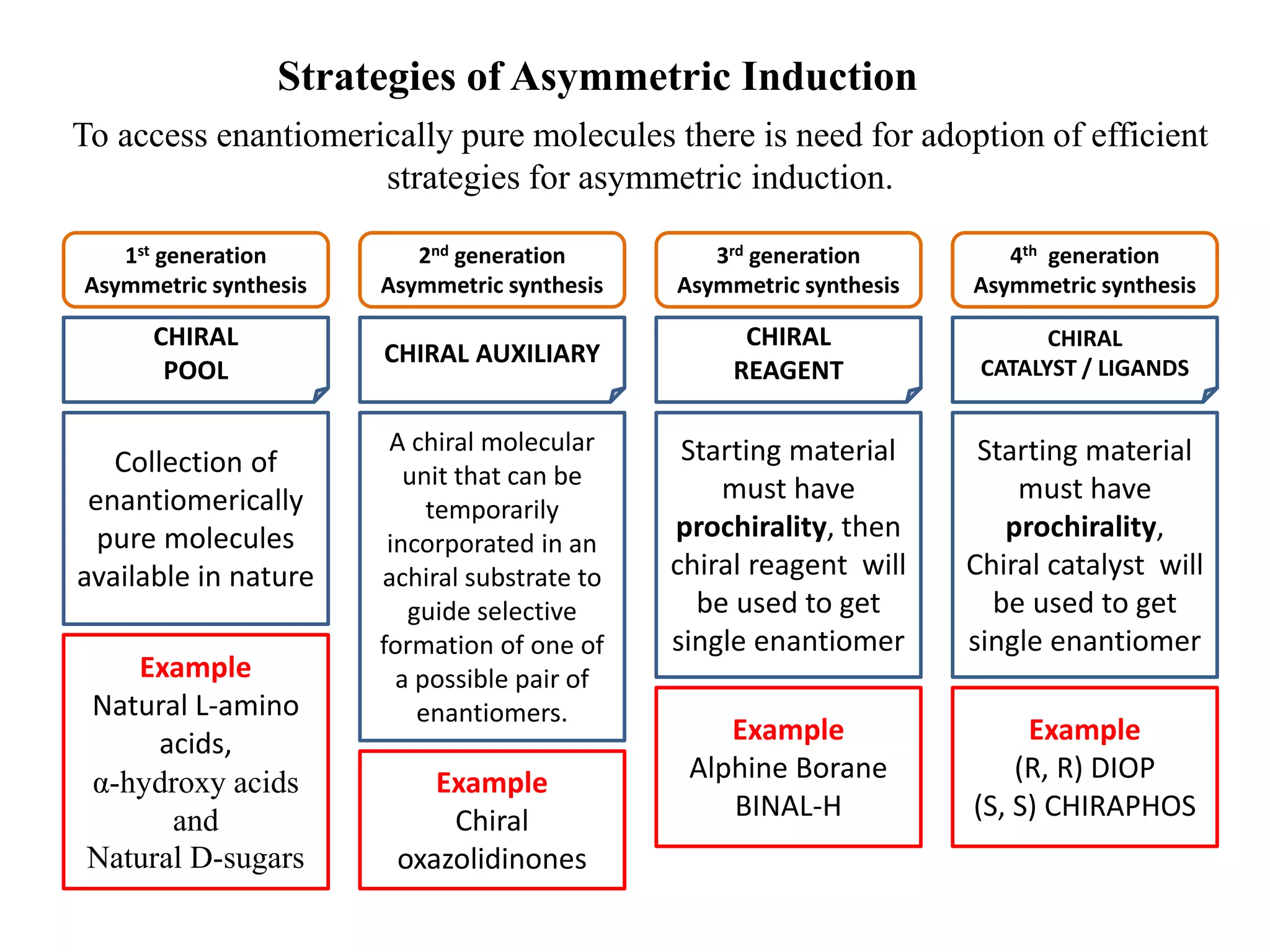
This document provides an overview of asymmetric synthesis and strategies for achieving asymmetric induction. It defines asymmetric synthesis as a reaction that yields predominantly one chiral stereoisomer. It discusses different strategies for asymmetric induction, including using a chiral auxiliary, chiral reagent/catalyst, or starting with a chiral pool substrate. Specific examples are provided of chiral reagents like BINOL-H and Alpine borane that can be used to selectively reduce prochiral ketones. Chiral ligands like DIOP and CHIRAPHOS that are used with metal catalysts for asymmetric hydrogenation are also described.





![Enantiomeric Excess
For non-racemic or Scalemic mixtures of enantiomers, one enantiomer is more
abundant than the other. The composition of these mixtures is described by
the enantiomeric excess, which is the difference between the relative abundance of
the two enantiomers.
Enantiomeric excess (% ee) =
[R] - [S]
[R] + [S]
= % R - % S
Enantiomeric excess = Optical purity x 100 =
Observed rotationof mixture
Specific rotation of Pure enantiomer
x 100
% R + % S = 100
% ee
50% Major =
2
% ee
50% Minor =
2
+
-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymmetricsynthesis-201223143653/75/Asymmetric-Synthesis-7-2048.jpg)

![What is the e.e. of a solution containing 90% (+) and 10% (–)?
Enantiomeric excess (% ee) =
[R] - [S]
[R] + [S]
= % R - % S
% ee = 90% - 10%
% ee = 80%
% R = 90 %
% S = 10 %](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymmetricsynthesis-201223143653/75/Asymmetric-Synthesis-9-2048.jpg)
![What is the % ee of a solution with a specific rotation of –90o where the pure
solution rotates at –135o?
Enantiomeric excess = Optical purity x 100 =
Observed rotationof mixture
Specific rotation of Pure enantiomer
x 100
[α] pure = –135o
Data Given
[α] mixture = –90o
% ee =
–135o
X 100
– 90o
= 0.66 X 100
% ee = 66%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymmetricsynthesis-201223143653/75/Asymmetric-Synthesis-10-2048.jpg)
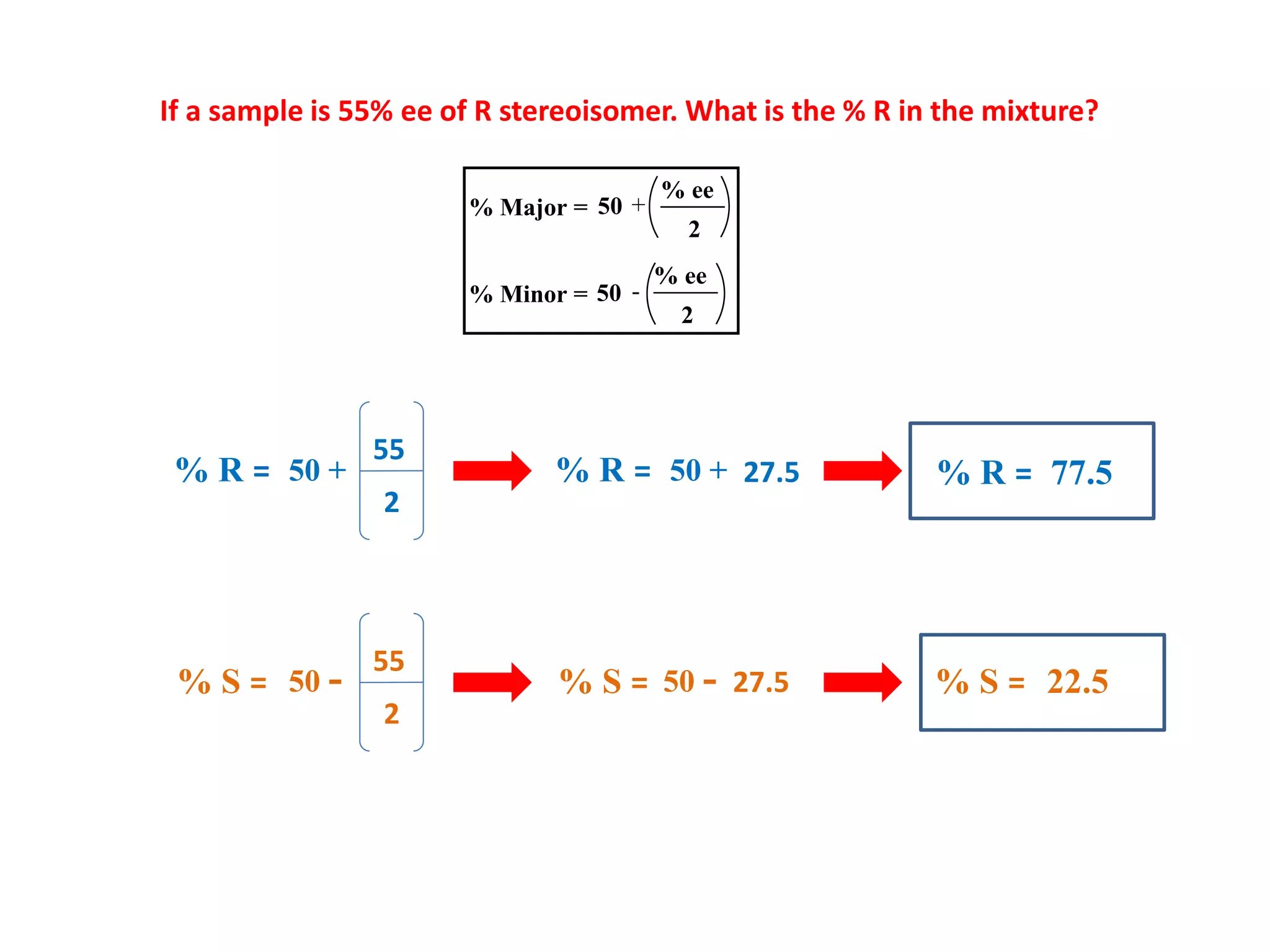
![A sample of a pure R-enantiomer has a specific rotation of -40o. A mixture of R/S
enantiomers has an observed optical rotation of +22o. What is the % ee of the
mixture?
[α] pure = –40o
Data Given
[α] mixture = +22o
% ee =
– 40o
X 100
– 22o
= 0.55 X 100
% ee = 55 %
Enantiomeric excess = Optical purity x 100 =
Observed rotationof mixture
Specific rotation of Pure enantiomer
x 100
R
The sample contains 55% more of the (R) enantiomer.
Thus, there is 55 % of (R) enantiomer + 45% of 1:1 mixture of (R = 22.5%) : (S=22.5%).
Therefore, 77.5 % (R) enantiomer and 22.5 % (S) enantiomer in the mixture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymmetricsynthesis-201223143653/75/Asymmetric-Synthesis-11-2048.jpg)






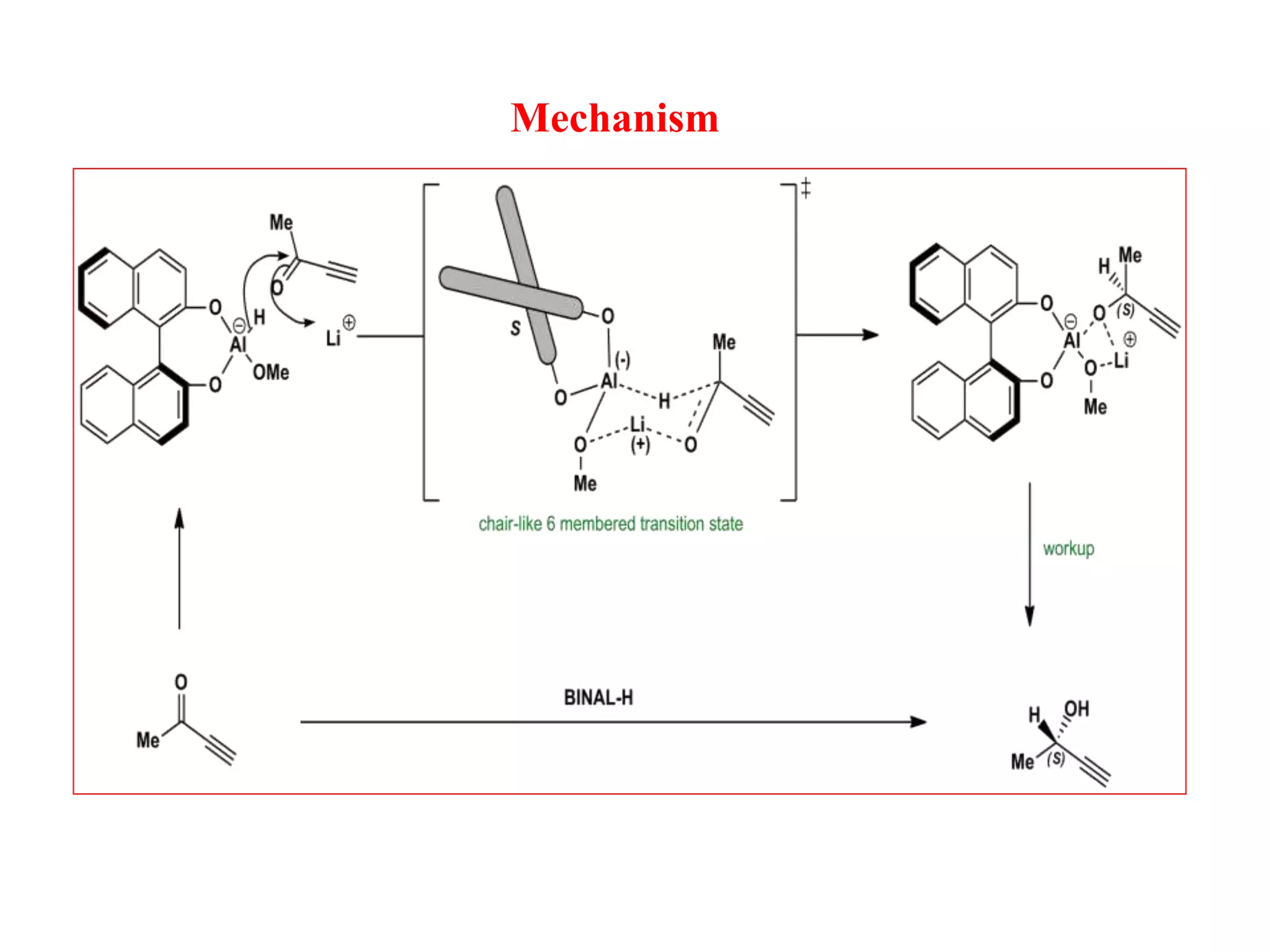

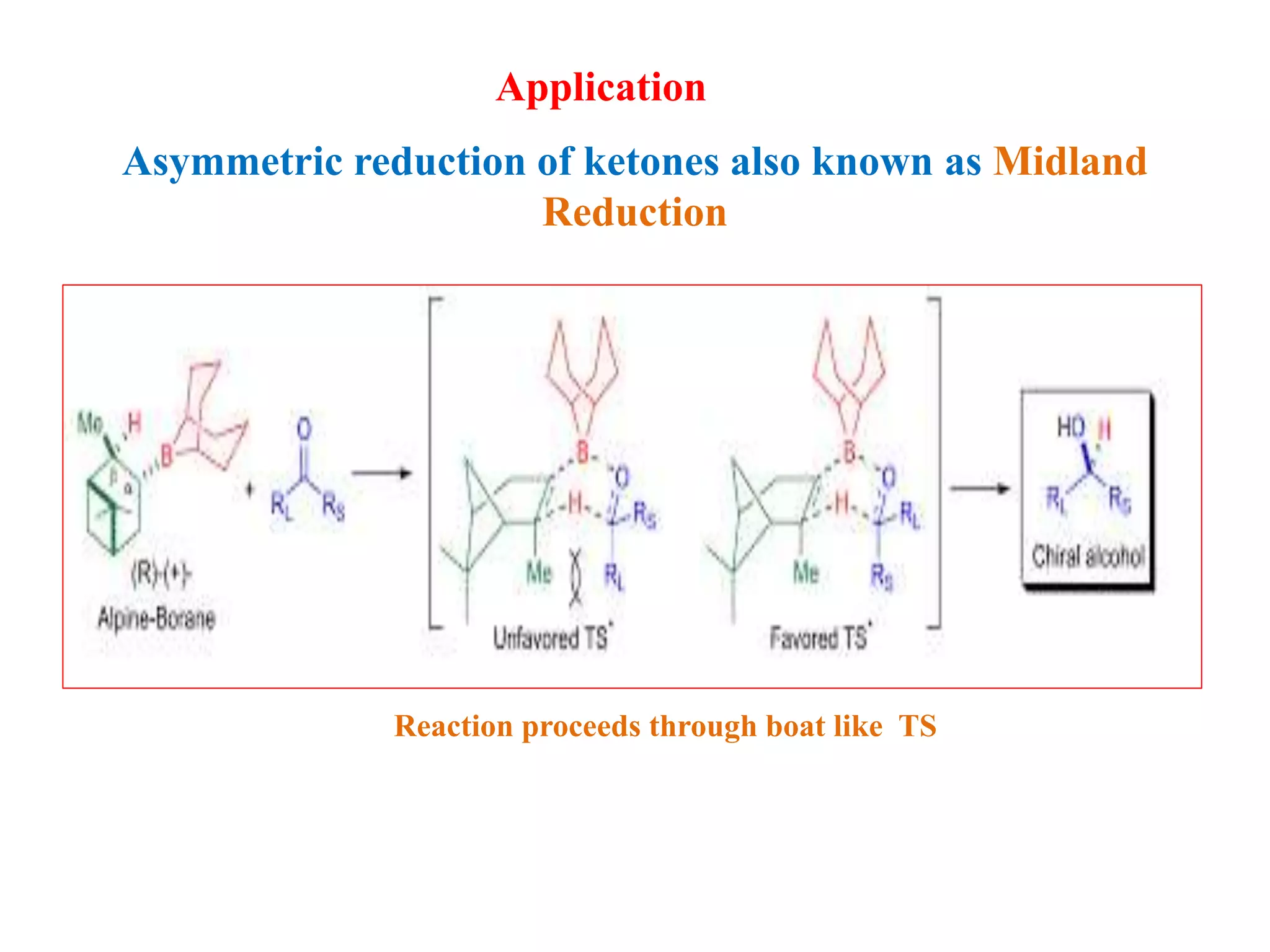
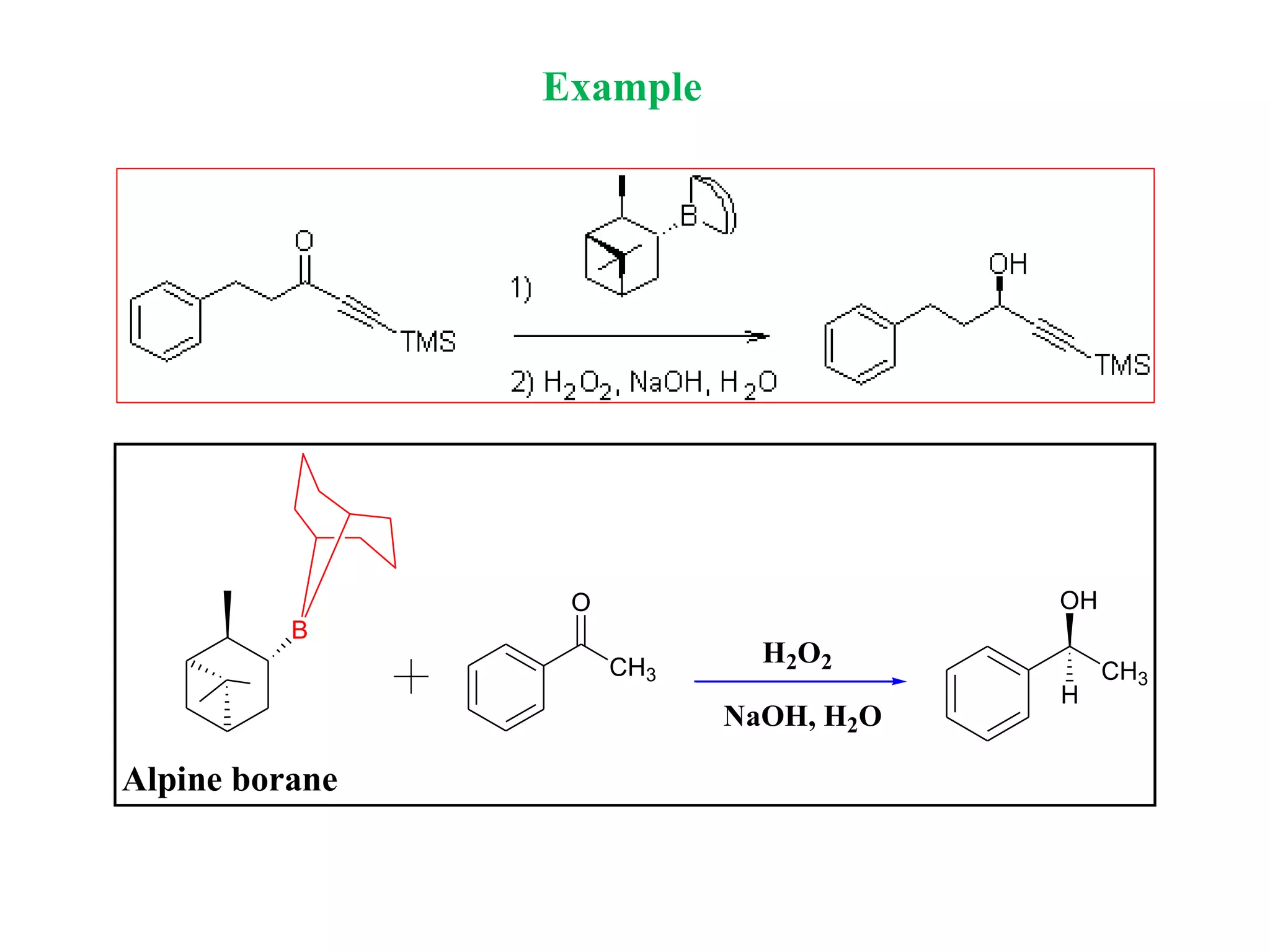
![Alpine borane is a chiral reagent
Preparation
THF
Reflux
H
B
9-bora-bicyclo[3.3.1]nonane(1R,5R)-2,6,6-
trimethylbicyclo[3.1.1]hept-2-
ene 9-BBN
-pinene
B
Alpine borane
Midland Reagent
H](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymmetricsynthesis-201223143653/75/Asymmetric-Synthesis-22-2048.jpg)
![(S)-2-PhenylButylMagnesium Chloride [(S)-PBMgCl]
Sterically hindered Grignard reagent transfer a β-H to
carbonyl group instead of undergoing nucleophilic addition
reaction.
MgCl
H
(S)-(2-phenylbutyl)magnesium chloride](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymmetricsynthesis-201223143653/75/Asymmetric-Synthesis-25-2048.jpg)

![(-) – Isobornyloxy aluminium dichloride [(-)-iBOAlCl2]
Used to reduce variety of carbonyl compounds with
enantioselection ranging from moderate to high (30-90%)
H
OAlCl2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asymmetricsynthesis-201223143653/75/Asymmetric-Synthesis-27-2048.jpg)