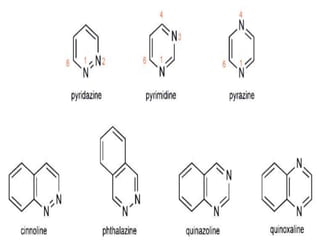
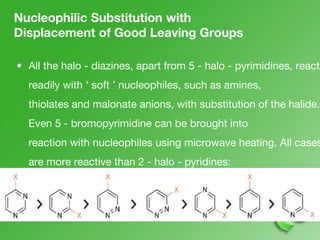
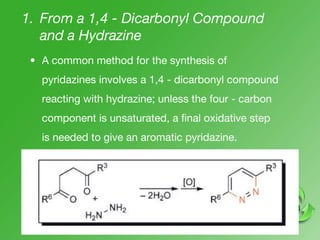
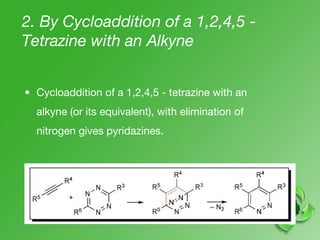
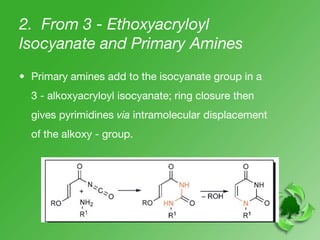
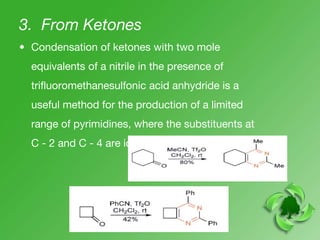
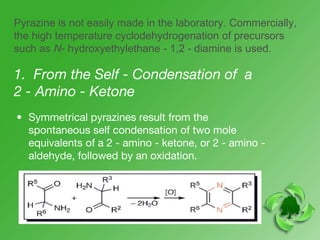
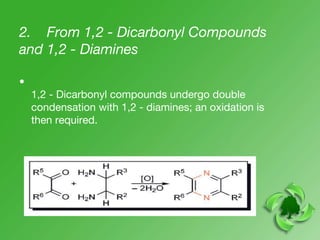
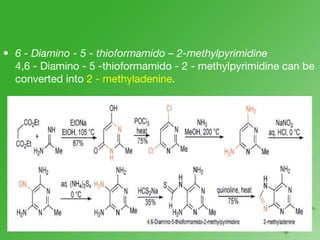
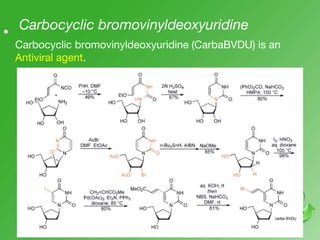
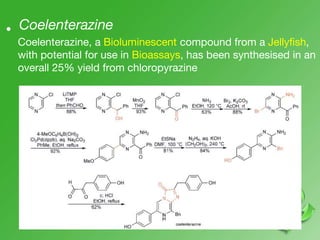
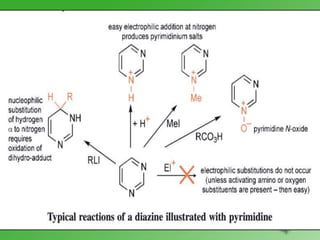
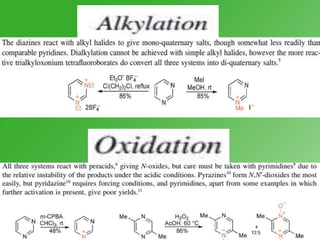
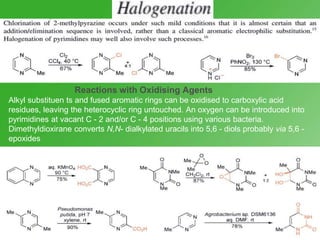
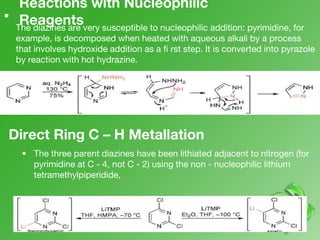
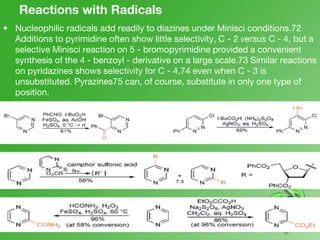
This document discusses heterocyclic compounds called diazines. It describes the three main types of diazines - pyridazine, pyrimidine, and pyrazine. It discusses their properties, including being stable, colorless compounds that are soluble in water. It then covers several common methods for synthesizing each type of diazine, such as using dicarbonyl compounds and hydrazines for pyridazines or dicarbonyls and diamines for pyrazines. The document concludes by covering some notable syntheses of specific diazines and their uses, as well as various reactions diazines undergo, such as reactions with oxidizing agents, nucleophilic reagents, and radicals.