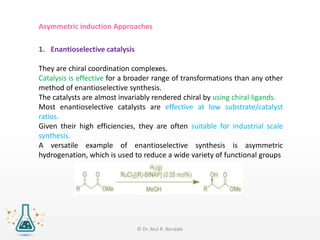
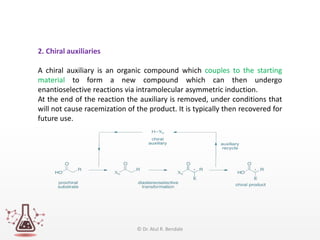
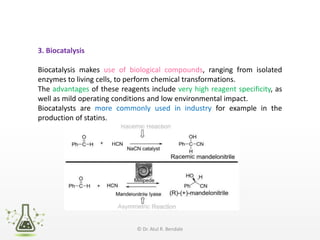
Asymmetric synthesis, or enantioselective synthesis, refers to chemical reactions that produce chiral products in unequal amounts, crucial in pharmaceuticals due to differing biological activities of enantiomers. This synthesis can be achieved through methods like partial and absolute asymmetric synthesis, utilizing chiral reagents or polarized light respectively. Biocatalysis and chiral auxiliaries are key strategies in achieving high levels of chirality, with each method exhibiting unique advantages and disadvantages.

![Asymmetric synthesis, also known as Enantioselective synthesis.
It is defined by IUPAC as: a chemical reaction (or reaction sequence) in
which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate
molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric (enantiomeric or
diastereoisomeric) products in unequal amounts.
More simply: The synthesis of an asymmetric compound carried with the
help of an optically active molecule or group is termed asymmetric
synthesis.
[Enantiomers are stereoisomers that have opposite configurations at every
chiral center.
Diastereomers are stereoisomers that differ at one or more chiral centers.]
© Dr. Atul R. Bendale](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/assymetricsynthesisatulshow-200424141333/85/Asymmetric-synthesis-2-320.jpg)