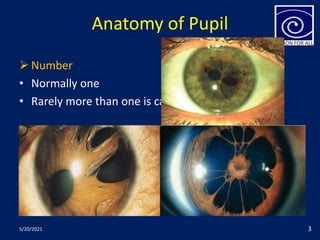
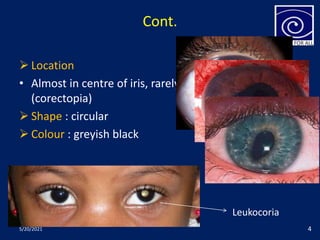
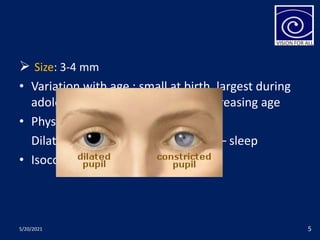
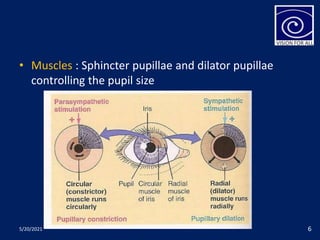
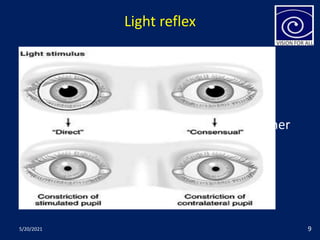
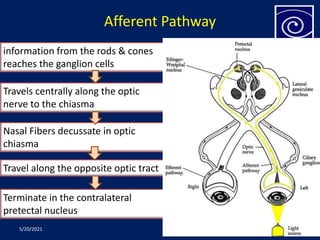
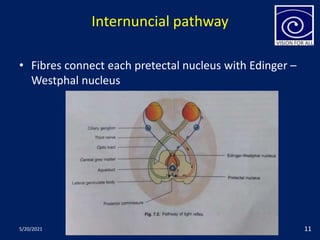
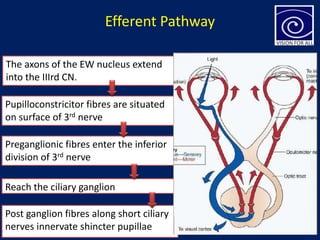
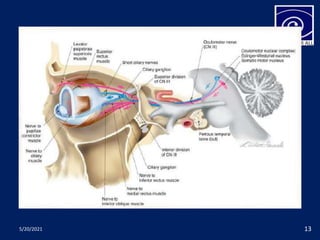
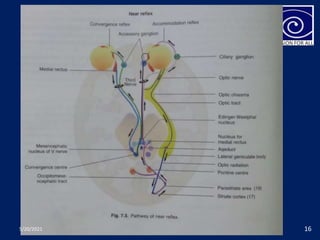
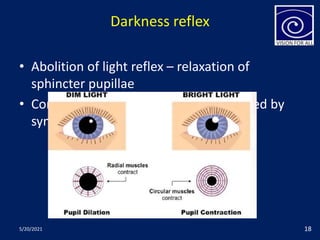
The pupil is a circular aperture located in the center of the iris that regulates the amount of light entering the eye. It has two muscles - the sphincter pupillae and dilator pupillae - that control its size. The pupillary reflex causes involuntary constriction or dilation of the pupil in response to light and near focus. There are several pupillary reflexes, including the light reflex which causes constriction when light hits the eye, and the near reflex which causes constriction during near vision due to convergence and accommodation of the eye. The pathways involve the retina, optic nerve, pretectal nucleus, and Edinger-Westphal nucleus.