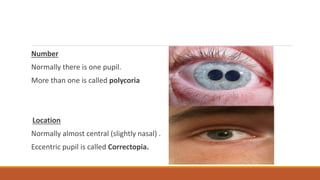
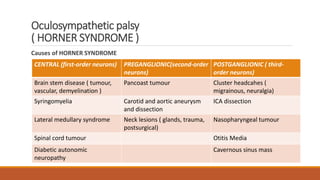
This document discusses the pupil in health and disease. It begins by describing the normal anatomy and function of the pupil, including its size, location, shape, and role in regulating light entry. It then covers various pupil reflexes and abnormalities such as anisocoria, mydriasis, miosis, light-near dissociation, Argyll Robertson pupils, and disorders of the third cranial nerve and sympathetic pathway. Causes, signs, and diagnostic tests for various pupil abnormalities are provided.