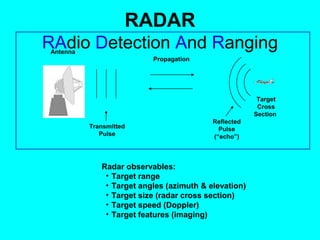
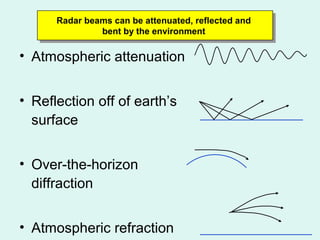
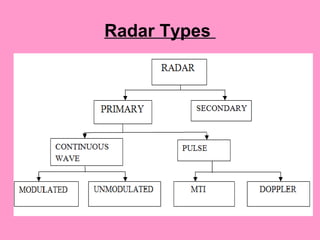
Radar uses radio waves to detect distant objects. It works by transmitting radio pulses and measuring their reflection off targets to determine range, angle, speed and other characteristics. There are two main types of radar: continuous wave radar which transmits a continuous radio signal, and pulsed radar which uses high power pulses. Radar has many applications including air traffic control, weather observation, speed enforcement, and military uses like air defense and missile guidance. It can operate in all weather conditions and is a vital detection system.













![BIBLIOGRAPHY
M. Kulkarni, “Microwave and Radar Engineering”, 3rd edition, Umesh Publication,
2003, pp. 493 – 536
Merri.I.skolnik, “Intoduction to Radar System”, 3rd edition, Tata McGraw Hill, 2003
“Types of Radar”, Engineers Garage,2012[online]. Available:
http://www.engineersgarage.com/articles/type-of-radars [accessed: September 2012]
References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radar
http://www.radartutorial.eu/01.basics/rb01.en.htm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminaronradarnew-140502090029-phpapp01/85/RADAR-17-320.jpg)
