Pulmonary ventilation
- 2. z TOPICS OF DISCUSSION PULMONARY VENTILATION INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION EXCHANGE AND TRANSPORT OF OXYGEN AND CARBONDIOXIDE REPIRATORY CONTROL CENTERS IN BRAIN LUNG CAPACITIES AND LUNG VOLUMES
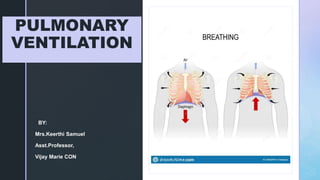
- 3. z INTRODUCTION RESPIRATION: The process of exchange of gases in the body . The following are the main steps: PULMONARY VENTILATION: or BREATHING is the inhalation and exhalation of the air and involves the exchange of air between the atmosphere and the alveoli of the lungs.
- 4. z RESPIRATION STEPS CONTD….. 1. EXTERNAL (PULMONARY ) RESPIRATION : exchange of gases between the alveoli and blood in the pulmonary capillaries across the respiratory membrane. In this process the capillary blood gains oxygen and loss carbon dioxide. 2. INTERNAL (TISSUE ) RESPIRATION: the exchange of gases between blood in systemic capillaries and tissue cells.in this step the blood looses oxygen and gains carbon dioxide. 3. CELLULAR RESPIRATION: within the cells the metabolic reaction that consume o2 and gives off co2 during the production of ATP are termed as CELLULAR RESPIRATION.
- 6. z PULMONARY VENTILATION In the pulmonary ventilation air flows between the atmosphere and the alveoli of the lungs because of the alternating pressure differences created by the contraction and relaxation of the respiratory muscles. Air moves into the lungs when the air pressure inside the lungs is less than the air pressure in the atmosphere. Air moves out of the lungs when the air pressure inside the lungs is greater than the air pressure in the atmosphere.
- 9. z INHALATION Just before respiration air pressure in the lungs and atmosphere is the same ( 760mmhg) For the air to flow into the lungs the pressure inside the lungs should be less than the atmospheric pressure. This happens when the size of the size of the lungs increases following the Boyles law. BREATHING IN IS CALLED INHALATION
- 11. z INHALATION-DIAPHRAGM The most important muscle of inhalation is the DIAPHRAGM- a dome shaped skeletal muscle that forms the floor of the thoracic cavity. It is innervated by fibers of the PHRENIC NERVES which emerge from the spinal cord at cervical levels 3,4 and 5 . Contraction of diaphragm causes it to flatten lowering its dome This increases the vertical diameter of the thoracic cavity.
- 12. z INHALATION Flattening of diaphragm increases the vertical diameter of the thoracic cavity. During quiet inhalation the diaphragm descends about 1cm reducing 1-3mmhg pressure thereby inhaling 500ml of air. In strenuous breathing the diaphragm descends 10cms which produces a pressure difference of 100mmhg and inhale 2-3lit of air.
- 13. z INHALATION Flattening of diaphragm increases the vertical diameter of the thoracic cavity. During quiet inhalation the diaphragm descends about 1cm reducing 1-3mmhg pressure thereby inhaling 500ml of air. In strenuous breathing the diaphragm descends 10cms which produces a pressure difference of 100mmhg and inhale 2-3lit of air.
- 14. z INHALATION Contraction of diaphragm is responsible for 75% of the air that enters the lungs during quiet breathing. Advanced pregnancy and obesity or confining abdominal clothing can prevent complete decent of the diaphragm.
- 15. z INHALATION- EXTERNALINTERCOSALS The next important muscles of inspiration. When these muscles contract they elevate the ribs. Elevation increases the anteroposterior diameter and lateral diameters of the chest cavity. Contraction of external intercostals is responsible for 25% of air that enters into the lungs during normal quiet breathing
- 16. z During quiet inhalations the pressure between the two membranes that is the INTRAPLEURAL PRESSURE is always sub atmospheric. Just before inhalation it is about 4mmhg less than the atmospheric pressure about 756mmhg at an atmospheric pressure of 760mm hg. As the diaphragm and external intercostal contract the overall size of the thoracic cavity increases along with the volume of the pleural cavity. This causes the intrapleural pressure to decrease to 756mmhg During the expansion of the thorax both the parietal and visceral pleura are adhered tightly due to the surface tension between them. The parietal pleura is pulled in all directions and along with it the visceral pleura and lungs are also pulled
- 17. z As the volume of the lung increases this way the alveolar pressure inside the lungs also drops from 760 to 758mmhg establishing a pressure difference. Since the air flows from an area of higher pressure to the lower pressure area INHALATION occurs. During forceful breathing the ACCESSORY MUSCLES of respiration (very little contribution) will help in inhalation The accessory muscles are – STERNOCLEIDOMASTOID- elevates the sternum SCALENE MUSCLES – elevates the first two ribs. PECTORALIS MINOR- elevates third to fifth ribs
- 18. z EXHALATION Breathing out is called EXHALATION, and is also due to pressure gradient. In this case the gradient is in opposite direction. The pressure in the lungs is greater than the pressure in the atmosphere. During quiet breathing exhalation is a passive process as no muscular contractions are involved. Exhalation results from ELASTIC RECOIL of the chest wall and lungs, which has natural tendency to spring back after they have been stretched. The two inwardly directed forces that contributes to elastic recoil are : The recoil of elastic fibers that were stretched during inhalation. The inward pull of the surface tension due to the film of the alveolar fluid.
- 19. z EXHALATION Inspiratory muscles relax; diaphragm relaxes, its dome shape superiorly due to its elasticity. Relaxation of external intercoastal causes depressed ribs. These movements decrease vertical, lateral and anteroposterior diameters of the thoracic cavity, which decreases the lung volume. The alveolar pressure increases to 762mmhg. And the air flows from the area of higher pressure in the alveoli to the area of lower pressure into the atmosphere.
- 20. z EXHALATION Exhalation becomes active only during forceful breathing Ex: playing wind instrument or exercise. During the these times muscles of exhalation the abdominals and internal intercostals contract which increases abdominal and thoracic pressure. This contraction moves the inferior ribs downwards and compresses the viscera forcing the diaphragm superiorly.
- 22. z FACTORS AFFEECTING PULMONARY VENTILATION 1. SURFACE TENSION: alveolar fluid quotes the luminal surface of the alveoli called surface tension. During breathing the surface tension must be overcome to expand the lungs during each inhalation. Surface tension is also responsible for lung elastic recoil. The SURFACTANT present in the alveolar fluid reduces the surface tension .deficiency of surfactant in babies is called Respiratory distress syndrome.
- 23. z FACTORS AFFEECTING PULMONARY VENTILATION 2. COMPLIANCE OF LUNGS: The effort needed to stretch the lungs is called compliance. High compliance- easy expansion of chest wall and lungs and the vice versa( analogy of an expansion of balloon) Compliance of lungs is related to two main factor: Surface tension Elasticity The lungs generally has high compliance but the conditions which decrease the compliance are: Scar lung tissues( TB) Edema of the lung tissue (pul.edema) Deficiency of surfactant Paralysis of muscles ( ICM)
- 24. z FACTORS AFFEECTING PULMONARY VENTILATION 3. AIRWAY RESISTANCE: The rate of the airflow depends on the pressure difference and resistance. The walls of the bronchioles offer some resistance to the normal airflow. Larger diameter airways has decreased resistance and vice versa. The airway diameter is regulated by degree of contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscle in the walls of airways which in turn is regulated by the signals from ANS.
