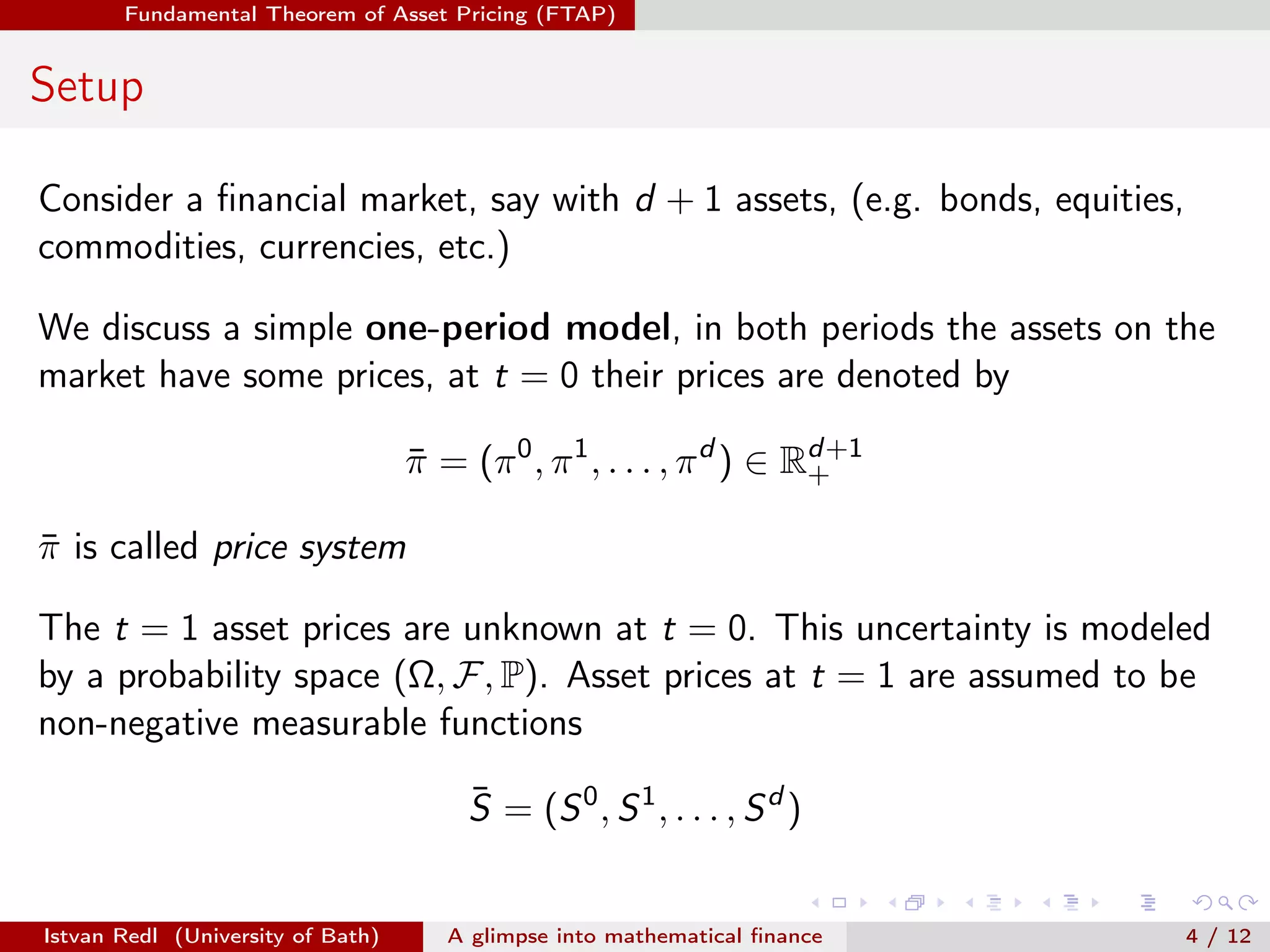
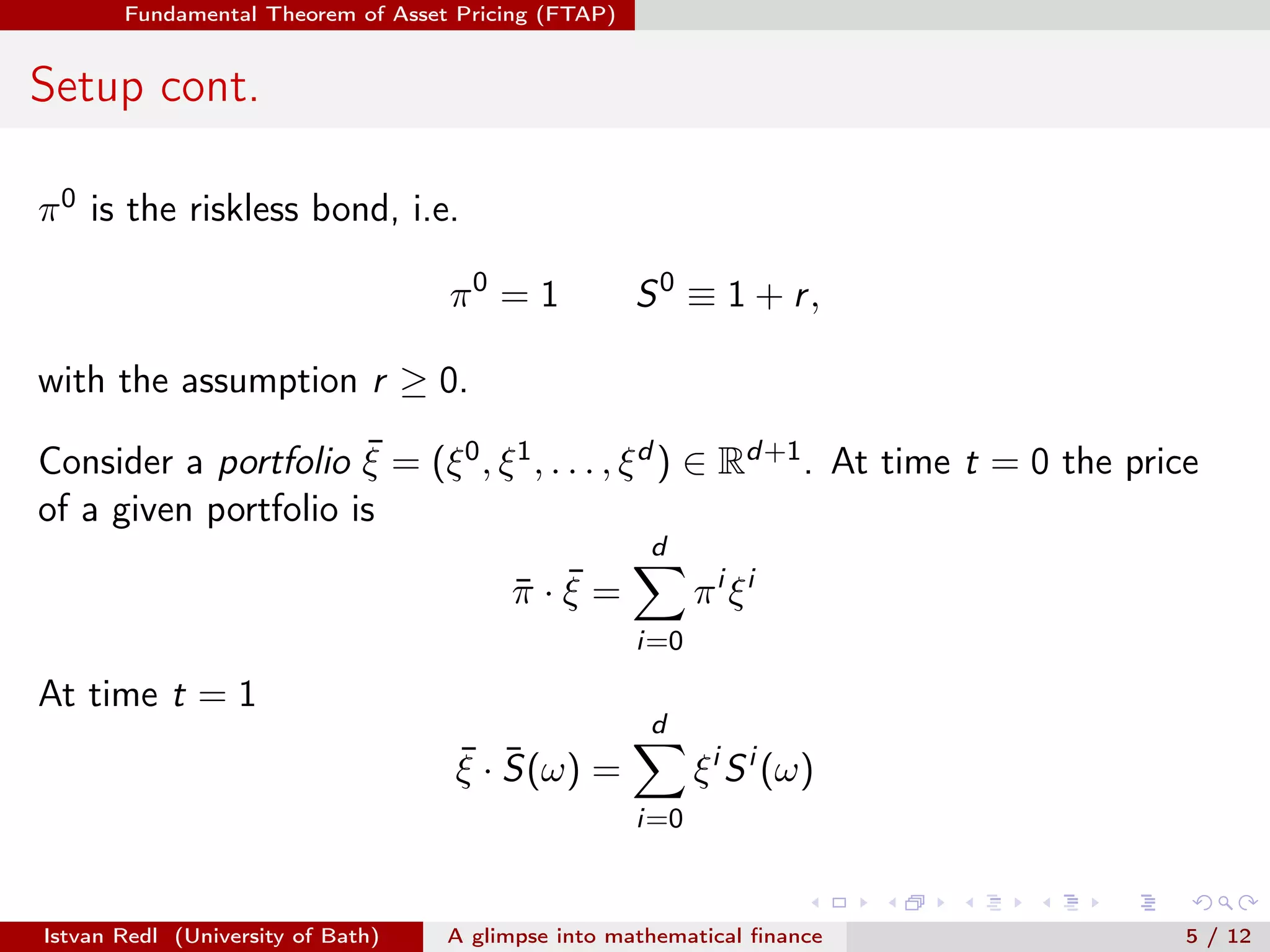
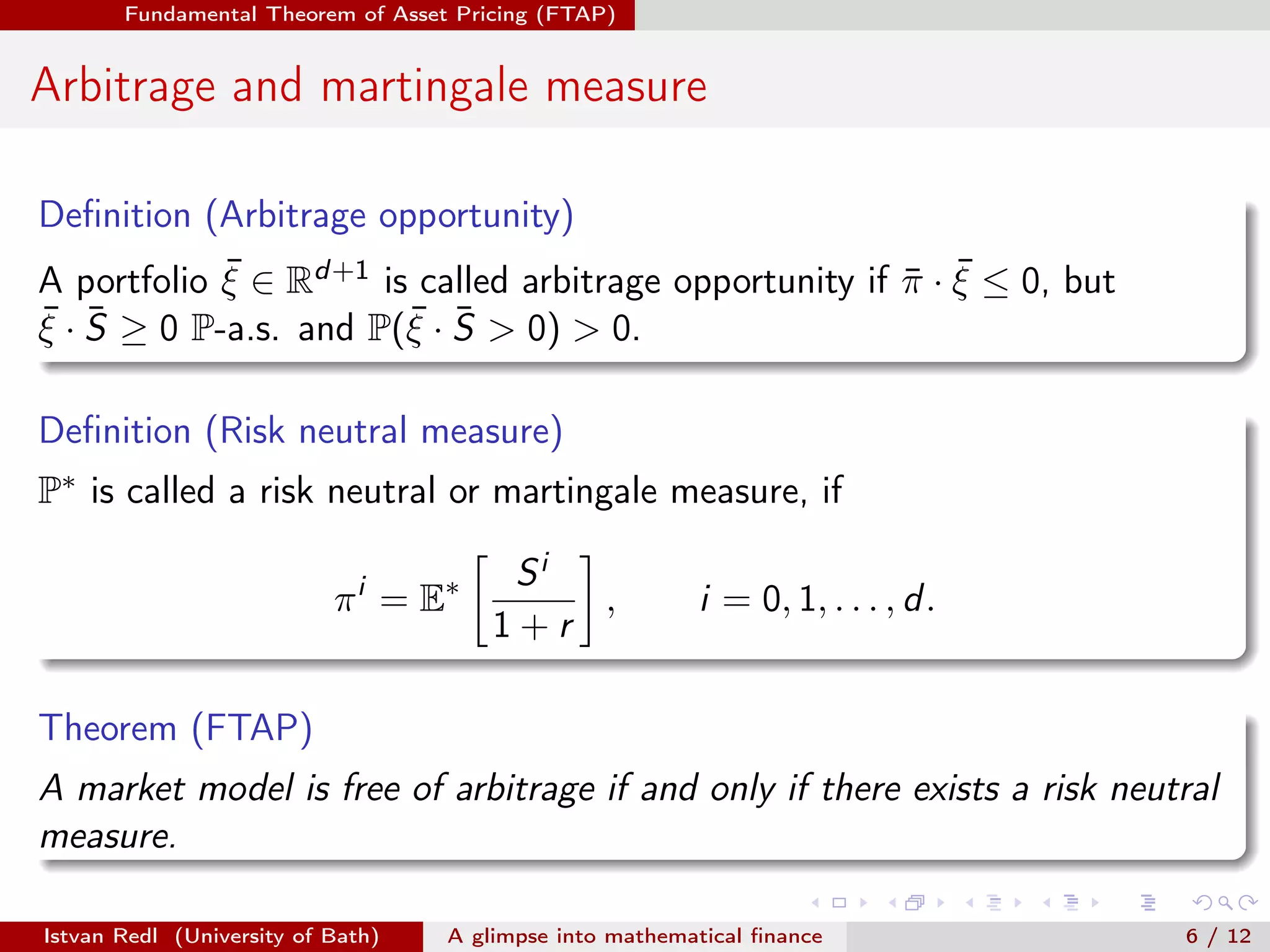
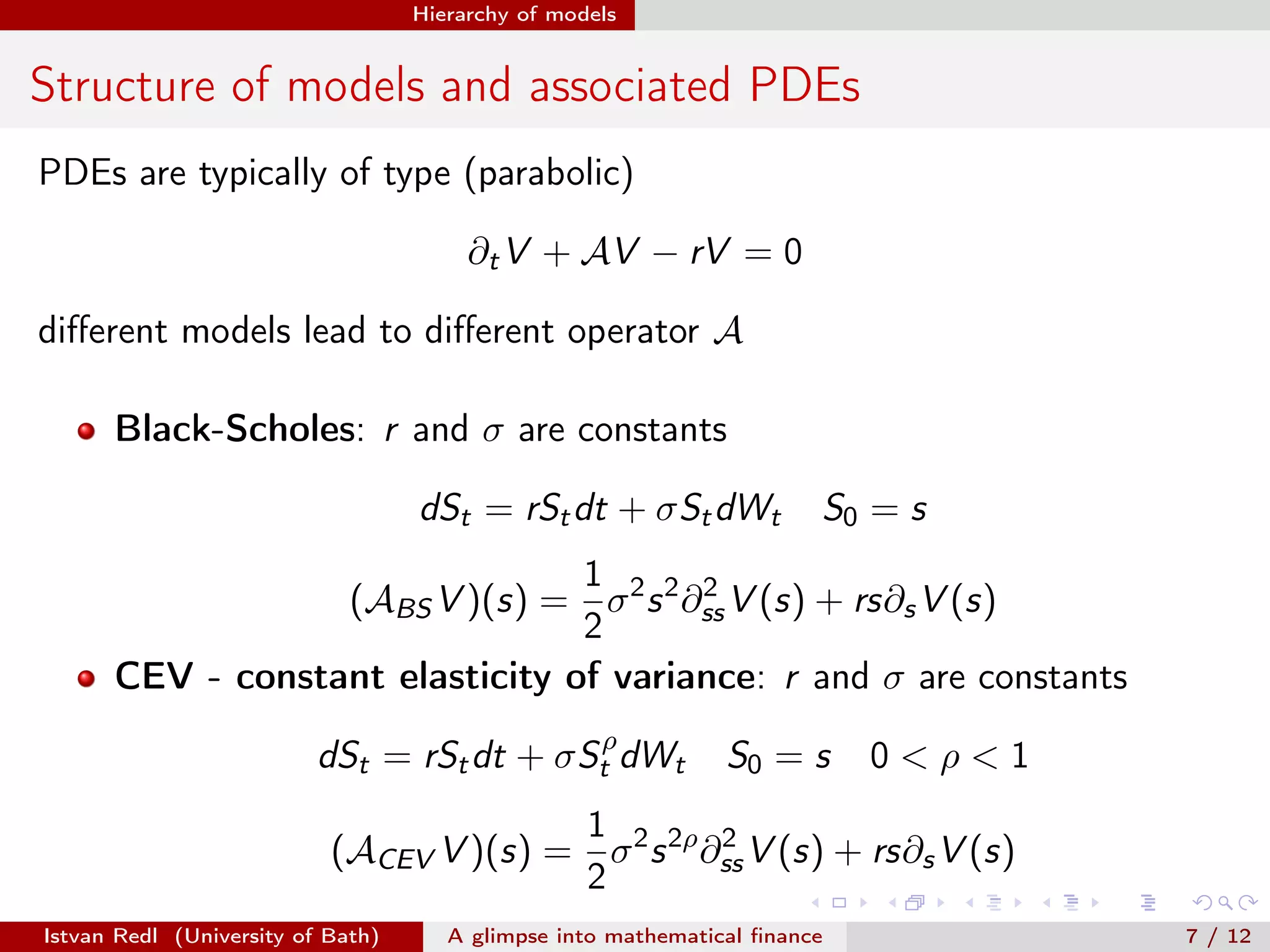
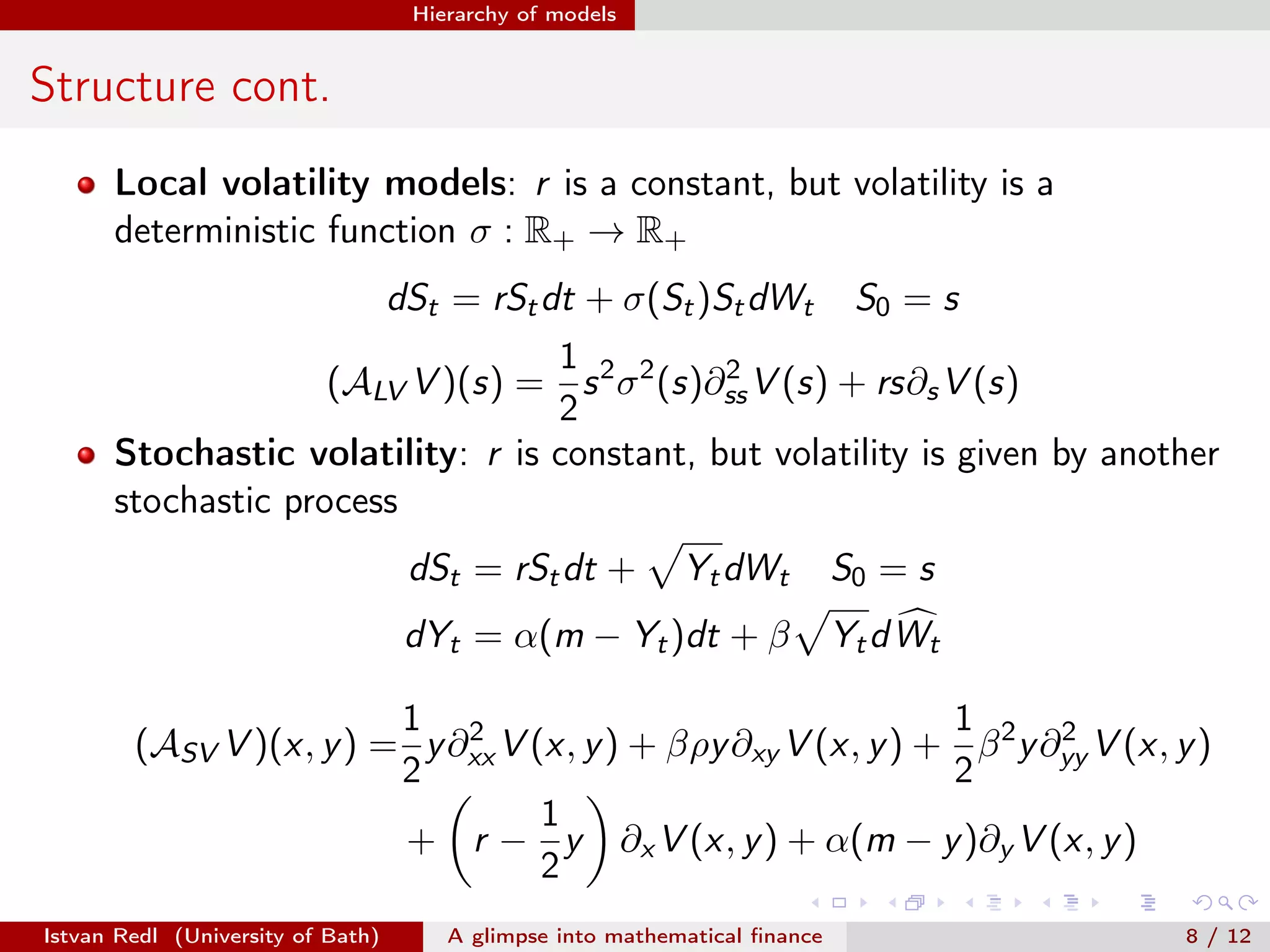
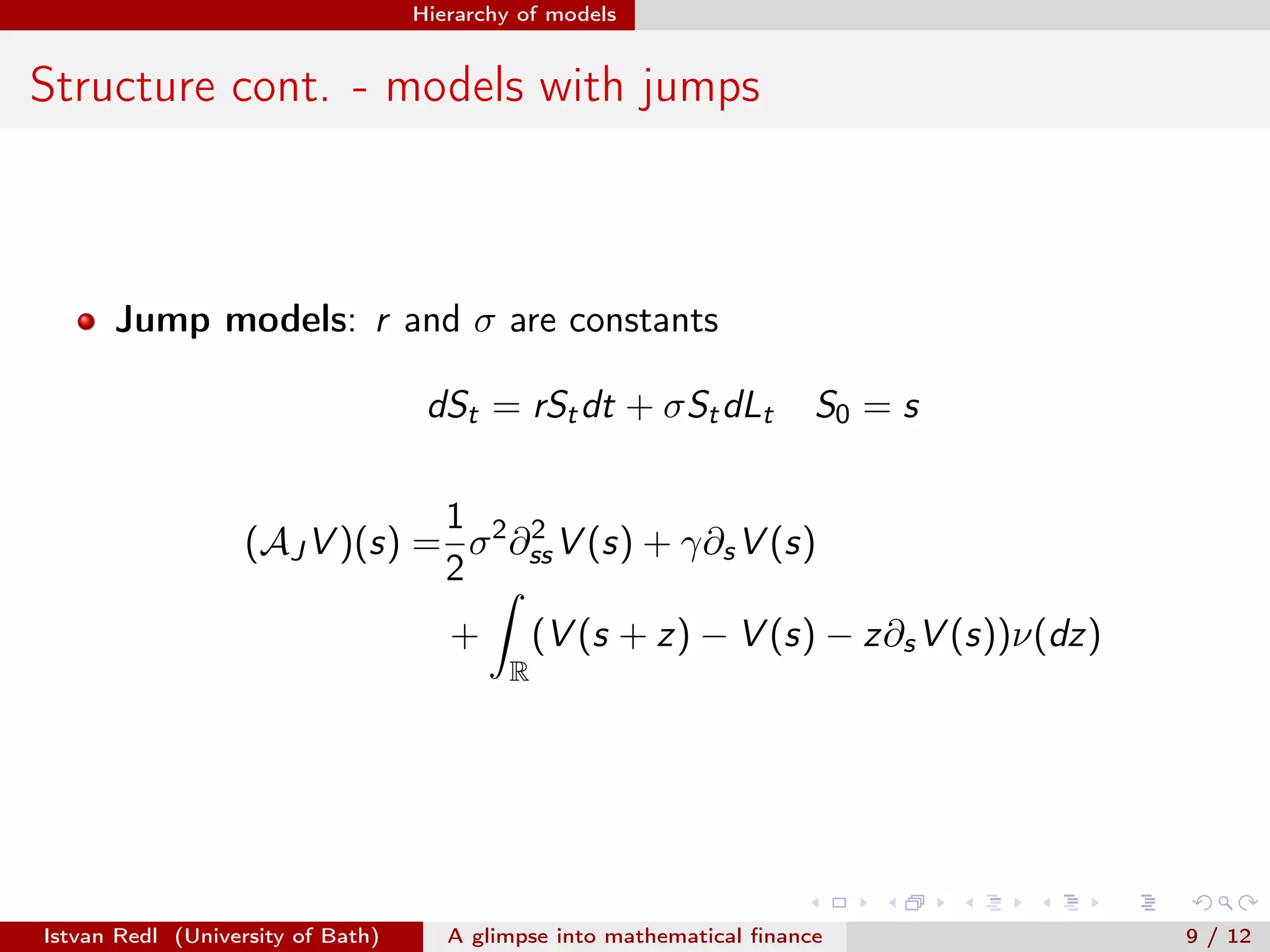
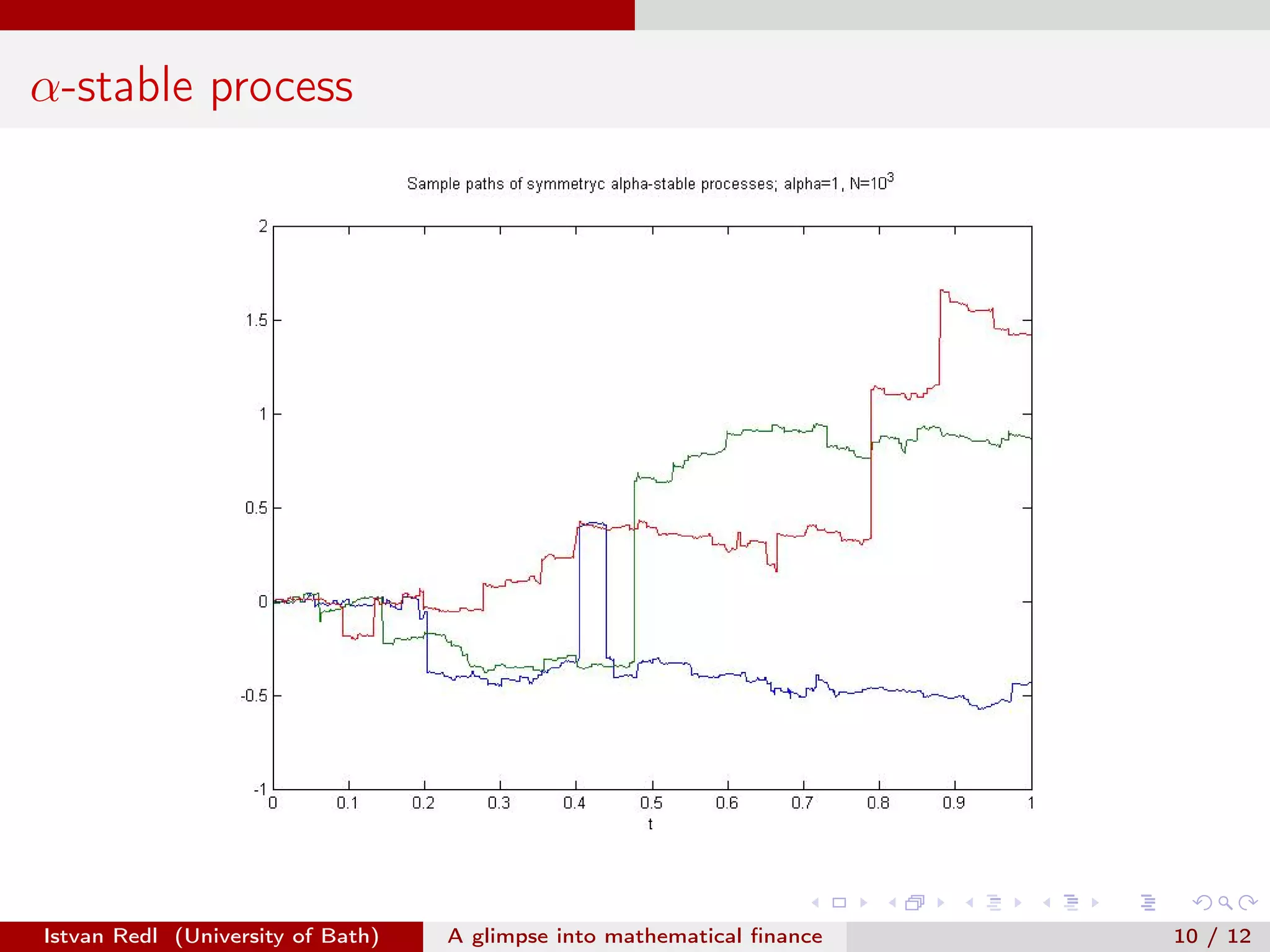
The document presents an overview of mathematical finance with a focus on option pricing models, highlighting its interdisciplinary nature and fundamental theorem of asset pricing (FTAP). It discusses the setup of financial markets, the concept of arbitrage opportunities, and introduces different modeling hierarchies including local and stochastic volatility models. The presentation concludes by inviting questions from the audience.