Embed presentation
Downloaded 19 times


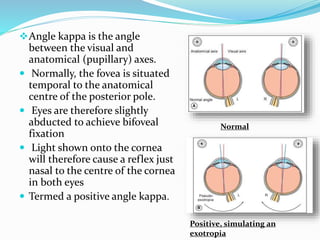
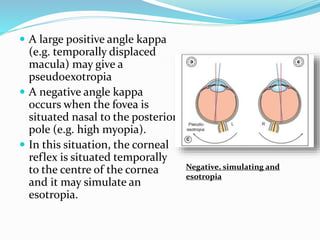


Pseudostrabismus is the perceived ocular deviation without actual squint, often mimicked by epicanthic folds or abnormal interpupillary distances. The angle kappa plays a crucial role, where a positive angle can simulate exotropia while a negative angle can mimic esotropia depending on the foveal positioning. Understanding these conditions is essential for accurate diagnosis and management.




