Embed presentation
Download to read offline



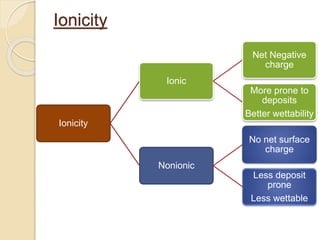




Soft contact lenses are made of hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), which was developed by Wichterle and Lim. HEMA contains a polar OH group that allows water to bind. Contact lenses can have water contents ranging from 38-80%, with lower water content lenses being more stable and easier to handle, and higher water content lenses having greater oxygen permeability but being less stable. Lenses can also be ionic or non-ionic, with ionic lenses being more deposit-prone but better wettable, and non-ionic lenses being less deposit-prone but less wettable. The FDA classifies soft contact lenses into four groups based on water content and ionicity. A lens's Dk, or






