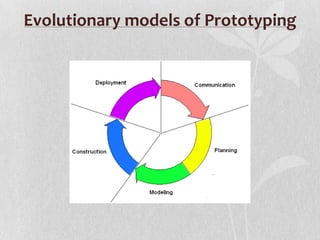
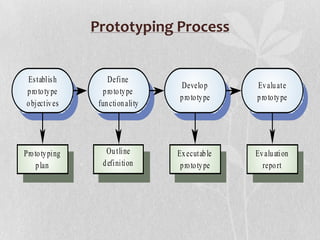
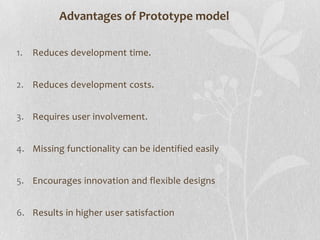
The document discusses prototype modeling. It defines a prototype as a working model built to test design aspects or concepts. There are different types of prototyping models and processes. Benefits of prototyping include exposing misunderstandings, identifying missing functionality, and encouraging innovation. Potential disadvantages are insufficient analysis if the focus is only on the prototype, user confusion between prototypes and finished systems, and excessive development time.