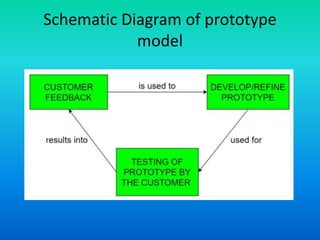
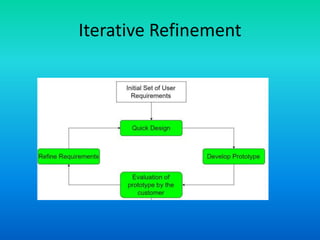
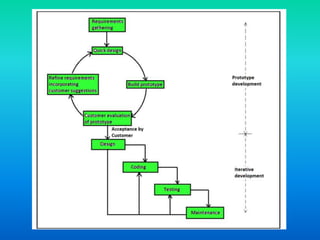
The document discusses the prototype model of software development. It defines prototyping as building a working replication of a product to obtain customer feedback. In the prototype model, an initial prototype is developed, tested, and refined based on customer feedback until an acceptable final prototype is achieved, which then forms the basis for the final product. The model is useful when requirements are unclear or changing, as it allows customers to provide early input and for new requirements to be incorporated through iterative refinement of prototypes.