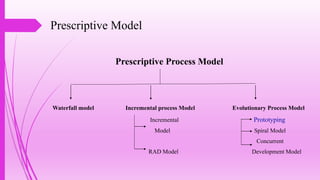
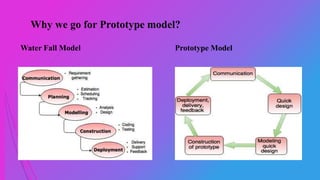
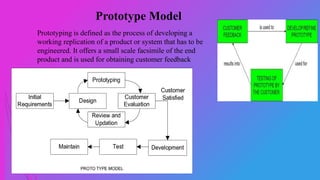
The document outlines the prototype model in software development, detailing team members, agenda, phases, advantages, and disadvantages. Prototyping offers a working model for customer feedback, involving quick design, construction, and refinement until user satisfaction is achieved. While it enhances understanding of customer needs and reduces risks, it also poses challenges such as high costs and potential delays.