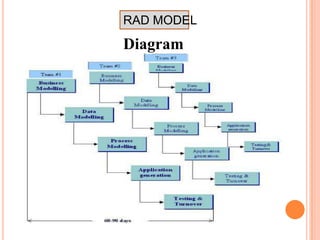
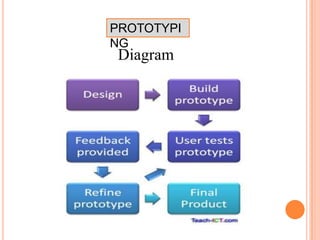
The document discusses the RAD model and prototyping. The RAD model is an incremental software development process where components are developed in parallel. It has four phases: requirements planning, user design, construction, and cutover. Prototyping involves creating initial versions of the system to get user feedback and evolve the design before full development. There are two types of prototypes: throwaway prototypes that are not part of the final system, and evolutionary prototypes that are iteratively improved based on user feedback.