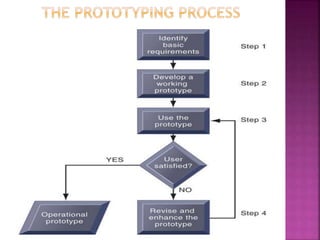
The document discusses prototyping, including defining it as quickly creating a working model to test design aspects and gather early user feedback. It outlines the prototyping process of identifying basic requirements, developing an initial prototype, reviewing it with users, and revising/enhancing it based on feedback in iterative cycles. The advantages of prototyping are reducing development time and costs while improving user involvement and satisfaction. Disadvantages include potential lack of requirements documentation and uncertain designs from frequent changes.