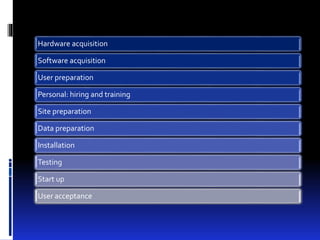
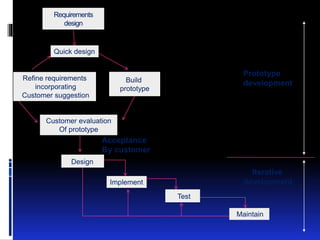
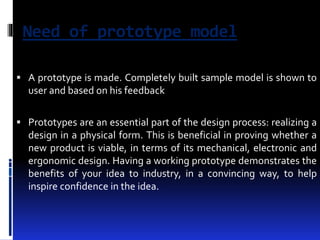
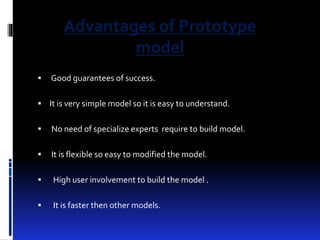
A prototype is an early sample or model created to test concepts or processes before final production. There are several types of prototyping models, including throwaway/rapid prototyping which uses minimal efforts to build prototypes that are discarded once requirements are understood, and evolutionary prototyping which builds functional prototypes to form the basis of future systems. The key steps in prototyping are requirements gathering, quick design, and building prototypes based on the design. Prototypes help expose issues, get early user feedback, and serve as a basis for specifications and testing before full system development.