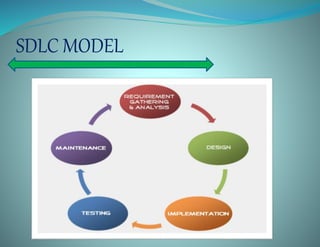
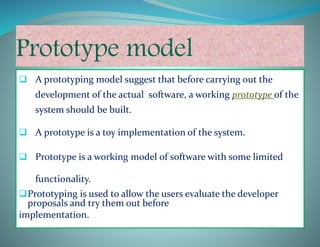
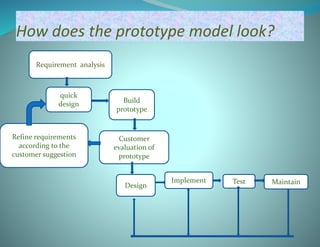
The document discusses the prototype model in software development. It defines a prototype model as building a working prototype of the system before full development to allow users to evaluate proposals. The key steps are requirements analysis, quick design, building the prototype, getting customer evaluation and feedback, and refining the prototype iteratively until the user is satisfied. Prototype models have advantages like early assessment, clarifying requirements, and ensuring user requirements are met. However, they can also be time-consuming and expensive if multiple prototypes are needed before finding the perfect fit.