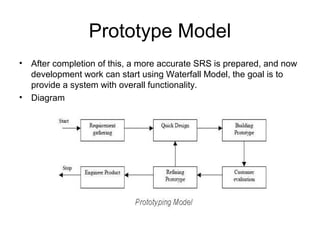
The document discusses the prototype model in software development, highlighting its necessity due to dependencies among project phases and the shortcomings of traditional models like Waterfall for complex or changing requirements. It explains that building a prototype allows for user feedback and iterative improvement before final development begins, leading to better outcomes. However, it also notes disadvantages such as slow progress, potential increased complexity, and the risks of client dissatisfaction.