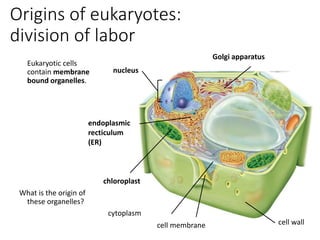
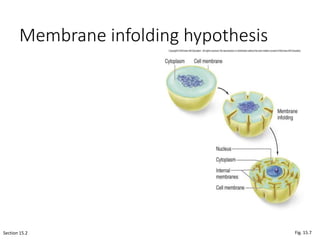
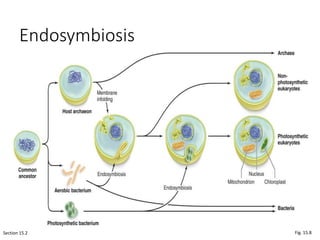
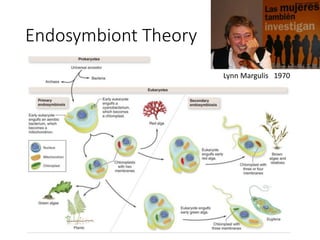
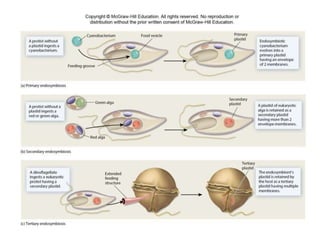
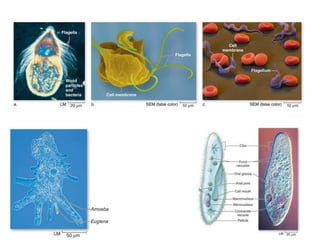
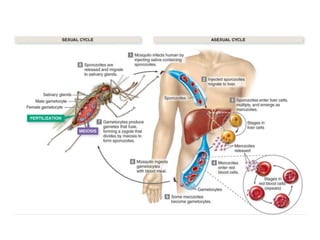
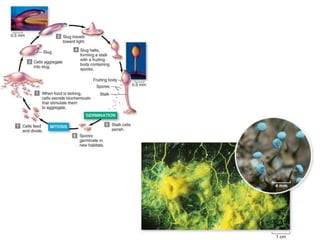
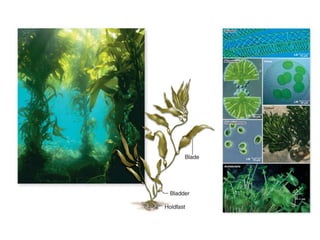
1. The document discusses protists, the most diverse eukaryotic kingdom. It describes how endosymbiosis led to the evolution of multicellular organisms from prokaryotic ancestors through the incorporation of membrane-bound organelles.
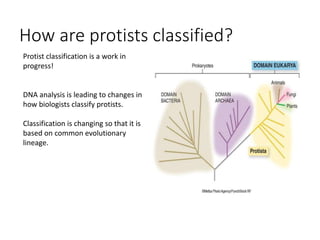
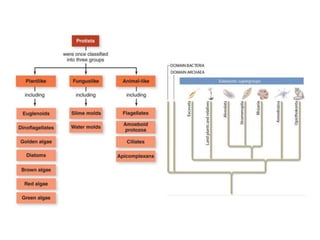
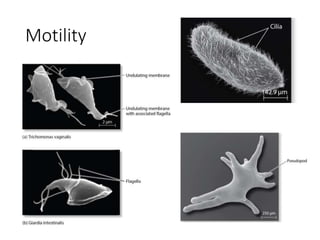
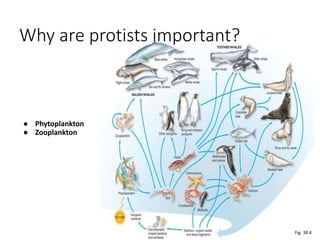
2. Protists are classified based on evolutionary lineages revealed by DNA analysis, though classification remains a work in progress. They exhibit a wide range of motility and fulfill important ecological roles as phytoplankton and zooplankton.
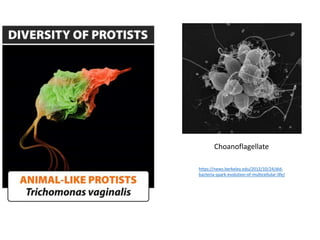
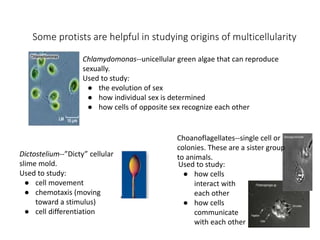
3. Examples like choanoflagellates, Chlamydomonas, and Dictyostelium are used to study the origins of multicellularity and cellular processes like sex determination, communication,