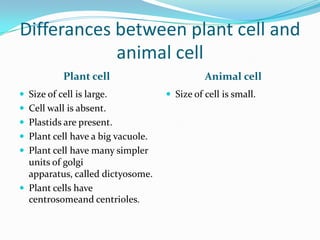
Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Robert Hooke first observed cells in 1665 while examining cork under a microscope. He saw the cork resembled a honeycomb consisting of boxes, which he called cells. There are two main types of cells - prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are smaller and lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells are larger with a nucleus and organelles. The cell theory proposed that all organisms are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function, and new cells are produced from existing cells. Key components of plant and animal cells include a nucleus, plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes, while plant cells