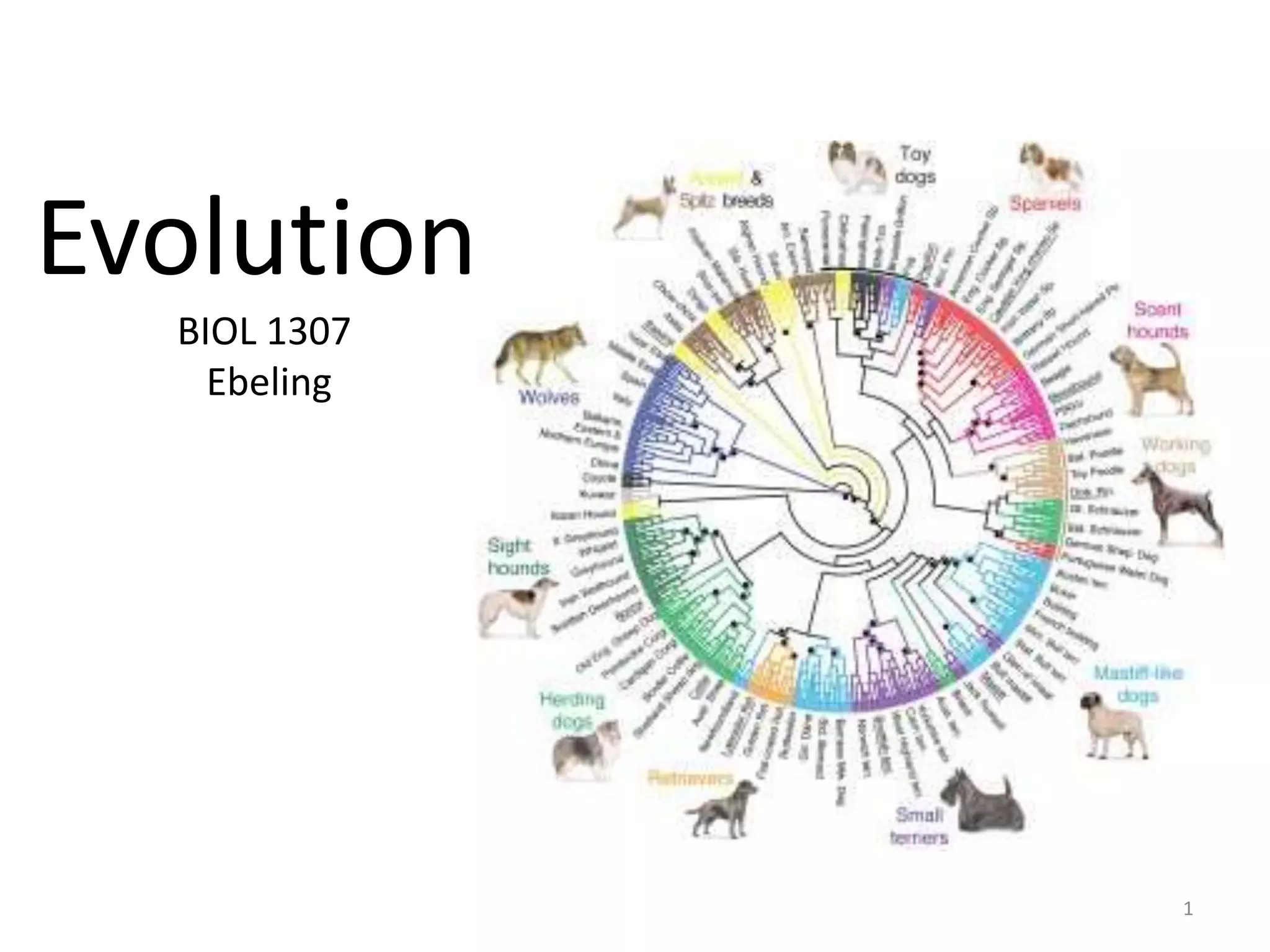
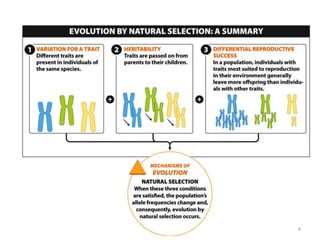
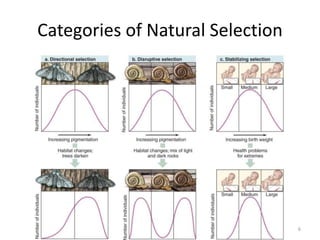
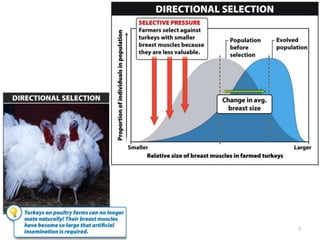
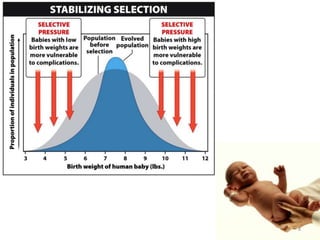
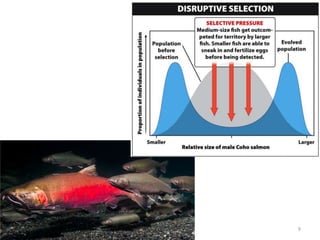
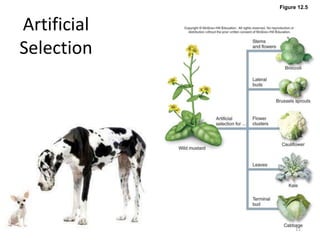
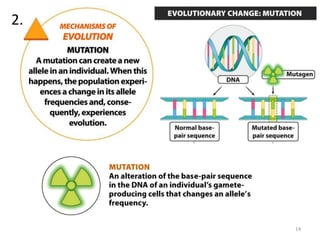
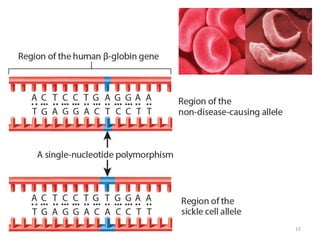
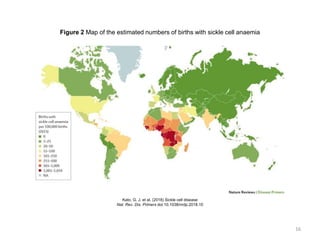
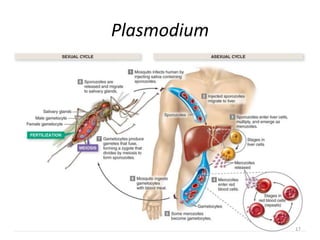
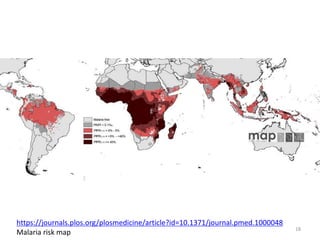
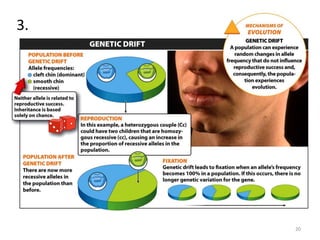
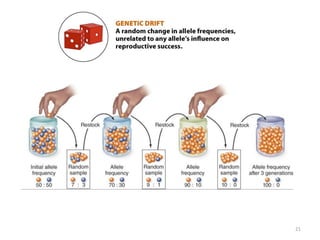
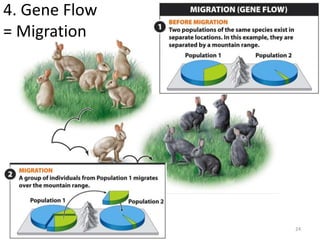
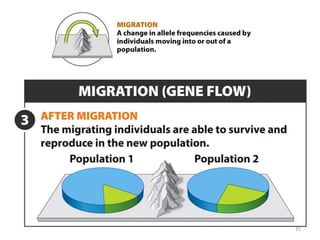
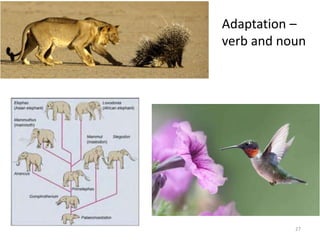
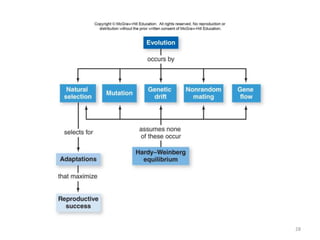
This document outlines learning objectives for a course on evolution. It covers key concepts like natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, and mechanisms of evolution. Specifically, it defines terms, compares types of selection pressure, and explains how evolutionary factors like mutation and population size can influence allele frequencies over time. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and examples of natural selection in specific populations are also discussed.